mirror of
https://github.com/acepanel/acepanel.github.io.git
synced 2026-02-04 03:07:16 +08:00
New Crowdin translations by GitHub Action (#75)
Co-authored-by: Crowdin Bot <support+bot@crowdin.com>
This commit is contained in:
committed by
 GitHub
GitHub
parent
54b68a69b8
commit
612a7cd5ec
@@ -16,8 +16,14 @@ export const config = defineConfig({
|
||||
items: sidebarQuickstart()
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "进阶指南",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
base: locale == 'zh_CN' ? '/advanced' : `/${locale}/advanced`,
|
||||
items: sidebarAdvanced()
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "常见问题",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
base: locale == 'zh_CN' ? '/faq' : `/${locale}/faq`,
|
||||
items: sidebarFAQ()
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "版本历史",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
@@ -79,28 +85,239 @@ function nav(): DefaultTheme.NavItem[] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
function sidebarQuickstart(): DefaultTheme.SidebarItem[] {
|
||||
return [{
|
||||
text: "安装面板",
|
||||
text: "动态与公告",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "AcePanel 3.0 正式发布",
|
||||
link: '/news/acepanel-3-release'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "介绍",
|
||||
link: '/introduction'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "安装",
|
||||
link: '/install'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "挂载分区",
|
||||
link: '/disk'
|
||||
text: "升级",
|
||||
link: '/upgrade'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "管理面板",
|
||||
link: '/panel'
|
||||
text: "第一个网站",
|
||||
link: '/first-website'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "管理容器",
|
||||
link: '/container'
|
||||
text: "第一个容器",
|
||||
link: '/first-container'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "第一个项目",
|
||||
link: '/first-project'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "命令行",
|
||||
link: '/cli'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "卸载",
|
||||
link: '/uninstall'
|
||||
}];
|
||||
}
|
||||
function sidebarAdvanced(): DefaultTheme.SidebarItem[] {
|
||||
return [{
|
||||
text: "应用",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/app'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "原生应用",
|
||||
link: '/app/native'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "运行环境",
|
||||
link: '/app/environment'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "容器模版",
|
||||
link: '/app/template'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "容器",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/container'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "容器",
|
||||
link: '/container/container'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "编排",
|
||||
link: '/container/compose'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "镜像",
|
||||
link: '/container/image'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "网络",
|
||||
link: '/container/network'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "卷",
|
||||
link: '/container/volume'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "网站",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/website'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "反向代理",
|
||||
link: '/website/proxy'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "PHP",
|
||||
link: '/website/php'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "纯静态",
|
||||
link: '/website/static'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "项目",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/project'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Go",
|
||||
link: '/project/go'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Java",
|
||||
link: '/project/java'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Node.js",
|
||||
link: '/project/nodejs'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "PHP",
|
||||
link: '/project/php'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Python",
|
||||
link: '/project/python'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "通用",
|
||||
link: '/project/general'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "数据库",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/database'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "数据库",
|
||||
link: '/database/database'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "用户",
|
||||
link: '/database/user'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "服务器",
|
||||
link: '/database/server'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "证书",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/cert'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "证书",
|
||||
link: '/cert/cert'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "账号",
|
||||
link: '/cert/account'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "DNS",
|
||||
link: '/cert/dns'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "监控",
|
||||
link: '/monitor'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "文件",
|
||||
link: '/file'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "备份",
|
||||
link: '/backup'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "终端",
|
||||
link: '/ssh'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "任务",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "计划任务",
|
||||
link: '/task/schedule'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "面板任务",
|
||||
link: '/task/panel'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "工具箱",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "概述",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "进程",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/process'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "系统",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/system'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "SSH",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/ssh'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "磁盘",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/disk'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "日志清理",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/log'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Web 钩子",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/webhook'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "跑分",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/benchmark'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "设置",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "基本设置",
|
||||
link: '/setting/basic'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "安全设置",
|
||||
link: '/setting/safe'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "用户设置",
|
||||
link: '/setting/user'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "面板 API",
|
||||
link: '/api'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "安全性建议",
|
||||
link: '/safe'
|
||||
text: "安全建议",
|
||||
link: '/security'
|
||||
}];
|
||||
}
|
||||
function sidebarFAQ(): DefaultTheme.SidebarItem[] {
|
||||
return [{
|
||||
text: "面板",
|
||||
link: '/panel'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "常见问题",
|
||||
link: '/faq'
|
||||
text: "应用",
|
||||
link: '/application'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "数据库",
|
||||
link: '/database'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "网站",
|
||||
link: '/website'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "项目",
|
||||
link: '/project'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "容器",
|
||||
link: '/container'
|
||||
}];
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -16,10 +16,16 @@ export const config = defineConfig({
|
||||
items: sidebarQuickstart()
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "進階指南",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
base: locale == 'zh_CN' ? '/advanced' : `/${locale}/advanced`,
|
||||
items: sidebarAdvanced()
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "版本歷史",
|
||||
text: "FAQ",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
base: locale == 'zh_CN' ? '/faq' : `/${locale}/faq`,
|
||||
items: sidebarFAQ()
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Versions",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [...versions.map((version: string) => {
|
||||
return {
|
||||
@@ -79,28 +85,239 @@ function nav(): DefaultTheme.NavItem[] {
|
||||
}
|
||||
function sidebarQuickstart(): DefaultTheme.SidebarItem[] {
|
||||
return [{
|
||||
text: "安裝面板",
|
||||
text: 'News & Announcements',
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "AcePanel 3.0 Official Release",
|
||||
link: '/news/acepanel-3-release'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: 'Introduction',
|
||||
link: '/introduction'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: 'Install',
|
||||
link: '/install'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "掛載分區",
|
||||
link: '/disk'
|
||||
text: 'Upgrade',
|
||||
link: '/upgrade'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "管理面板",
|
||||
link: '/panel'
|
||||
text: 'First Website',
|
||||
link: '/first-website'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "管理容器",
|
||||
link: '/container'
|
||||
text: 'First Container',
|
||||
link: '/first-container'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: 'First Project',
|
||||
link: '/first-project'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: 'Command Line',
|
||||
link: '/cli'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: 'Uninstall',
|
||||
link: '/uninstall'
|
||||
}];
|
||||
}
|
||||
function sidebarAdvanced(): DefaultTheme.SidebarItem[] {
|
||||
return [{
|
||||
text: "面板 API",
|
||||
text: "Apps",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/app'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Native Apps",
|
||||
link: '/app/native'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Runtimes",
|
||||
link: '/app/environment'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Container Templates",
|
||||
link: '/app/template'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Containers",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/container'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Containers",
|
||||
link: '/container/container'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Compose",
|
||||
link: '/container/compose'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Images",
|
||||
link: '/container/image'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Networks",
|
||||
link: '/container/network'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Volumes",
|
||||
link: '/container/volume'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Websites",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/website'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Reverse Proxy",
|
||||
link: '/website/proxy'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "PHP",
|
||||
link: '/website/php'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Static",
|
||||
link: '/website/static'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Projects",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/project'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Go",
|
||||
link: '/project/go'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Java",
|
||||
link: '/project/java'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Node.js",
|
||||
link: '/project/nodejs'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "PHP",
|
||||
link: '/project/php'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Python",
|
||||
link: '/project/python'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "General",
|
||||
link: '/project/general'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Databases",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/database'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Databases",
|
||||
link: '/database/database'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Users",
|
||||
link: '/database/user'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Servers",
|
||||
link: '/database/server'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Certificates",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/cert'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Certificates",
|
||||
link: '/cert/cert'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Accounts",
|
||||
link: '/cert/account'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "DNS",
|
||||
link: '/cert/dns'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Monitor",
|
||||
link: '/monitor'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Files",
|
||||
link: '/file'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Backup",
|
||||
link: '/backup'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Terminal",
|
||||
link: '/ssh'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Tasks",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Scheduled Tasks",
|
||||
link: '/task/schedule'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Panel Tasks",
|
||||
link: '/task/panel'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Toolbox",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Overview",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Processes",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/process'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "System",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/system'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "SSH",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/ssh'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Disk",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/disk'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Log Cleanup",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/log'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Webhooks",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/webhook'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Benchmark",
|
||||
link: '/toolbox/benchmark'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Settings",
|
||||
collapsed: true,
|
||||
items: [{
|
||||
text: "Basic Settings",
|
||||
link: '/setting/basic'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Security Settings",
|
||||
link: '/setting/safe'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "User Management",
|
||||
link: '/setting/user'
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: 'Panel API',
|
||||
link: '/api'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "安全性建議",
|
||||
link: '/safe'
|
||||
text: 'Security Recommendations',
|
||||
link: '/security'
|
||||
}];
|
||||
}
|
||||
function sidebarFAQ(): DefaultTheme.SidebarItem[] {
|
||||
return [{
|
||||
text: "Panel",
|
||||
link: '/panel'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "常見問題",
|
||||
link: '/faq'
|
||||
text: "Application",
|
||||
link: '/application'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Database",
|
||||
link: '/database'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Website",
|
||||
link: '/website'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Project",
|
||||
link: '/project'
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
text: "Container",
|
||||
link: '/container'
|
||||
}];
|
||||
}
|
||||
72
zh_CN/about.md
Normal file
72
zh_CN/about.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar: false
|
||||
prev: false
|
||||
next: false
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<script setup>
|
||||
import { VPTeamMembers } from 'vitepress/theme'
|
||||
|
||||
const members = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
avatar: 'https://weavatar.com/avatar/18e77debb1bc0000c0b50757b8f1bebb2c3e4df3d494124f776c15dbc1ebe8a5',
|
||||
name: '耗子',
|
||||
desc: '创始人 & CEO',
|
||||
links: [
|
||||
{ icon: 'github', link: 'https://github.com/devhaozi' },
|
||||
{ icon: 'bilibili', link: 'https://space.bilibili.com/8067' }
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
avatar: 'https://weavatar.com/avatar/f6b23deadaa481f0b3ea75ad94f246881ed2326117efebad6f2799ea165779b9',
|
||||
name: '靓仔',
|
||||
desc: '技术负责人',
|
||||
links: [
|
||||
{ icon: 'github', link: 'https://github.com/205125' }
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
|
||||
# 关于
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 是一款专业的服务器运维管理面板,致力于为用户提供简单、高效、安全的服务器管理解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
| 愿景 | 使命 | 价值观 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------- | -------------- |
|
||||
| 成为领先的服务器管理解决方案提供商 | 让服务器管理变得简单而高效 | 用户至上、创新驱动、专业专注 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 团队介绍
|
||||
|
||||
<VPTeamMembers size="small" :members="members" />
|
||||
|
||||
## 发展历程
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2026 - 3.0 时代
|
||||
在 2026 年,我们推出了备受期待的 3.0 版本,推出了全新的用户界面和更多高级功能
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2025 - 稳步发展
|
||||
在 2025 年,我们专注于优化用户体验和增强系统稳定性,发布了 2.4 系列版本
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2024 - 全新起航
|
||||
面板得到了众多赞助商的支持,2024 年下半年发布了全新的 2.3 版本
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2023 - 技术积累
|
||||
使用 Go 对面板进行重写,发布 2.0 2.1 系列版本,积累了大量开发经验
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2022 - 项目立项
|
||||
2022 年中项目立项,年末发布 1.0 版本
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 联系我们
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 联系方式 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 企业微信 | [点击联系](https://work.weixin.qq.com/kfid/kfc20ea8e38b5a4e73a) |
|
||||
| QQ | [826896000](https://wpa.qq.com/msgrd?v=3&uin=826896000&site=qq&menu=yes) |
|
||||
| 电子邮件 | [haozi@loli.email](mailto:haozi@loli.email) |
|
||||
| 公司地址 | 天津市武清区黄庄街道泉里路1号智库大厦206室 |
|
||||
661
zh_CN/advanced/api.md
Normal file
661
zh_CN/advanced/api.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,661 @@
|
||||
# API 参考文档
|
||||
|
||||
## 概述
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 提供了一套安全的 RESTful 接口,用于与面板进行交互。 所有 API 请求都需要进行 HMAC-SHA256 签名认证以确保通信的安全性和完整性。 所有 API 请求都需要进行 HMAC-SHA256 签名认证以确保通信的安全性和完整性。
|
||||
|
||||
## 基础信息
|
||||
|
||||
- **基础 URL**: `http(s)://your-panel-domain/{entry}/api/`
|
||||
- **内容类型**: 所有请求和响应均使用 `application/json`
|
||||
- **字符编码**: UTF-8
|
||||
|
||||
## 认证机制
|
||||
|
||||
API 使用 HMAC-SHA256 签名算法进行认证。每个请求必须包含以下 HTTP 头: 每个请求必须包含以下 HTTP 头:
|
||||
|
||||
| 头部名称 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `Content-Type` | 设置为 `application/json` |
|
||||
| `X-Timestamp` | 当前 UNIX 时间戳(秒) |
|
||||
| `Authorization` | 身份验证信息,格式为 `HMAC-SHA256 Credential={id}, Signature={signature}` |
|
||||
|
||||
## 签名算法
|
||||
|
||||
签名过程包含四个主要步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 构造规范化请求
|
||||
|
||||
规范化请求字符串由以下部分组成,各部分之间使用换行符(\n)分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP方法
|
||||
规范化路径
|
||||
规范化查询字符串
|
||||
请求体的SHA256哈希值
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:规范化路径应始终使用 `/api/` 开头的路径部分,忽略入口前缀。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 构造待签名字符串
|
||||
|
||||
待签名字符串包含以下部分,各部分使用换行符(\n)分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256"
|
||||
时间戳
|
||||
规范化请求的SHA256哈希值
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 计算签名
|
||||
|
||||
使用您的令牌(token)对待签名字符串进行 HMAC-SHA256 计算,然后将结果转换为十六进制字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 构造授权头
|
||||
|
||||
将计算得到的签名添加到 `Authorization` 头:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 Credential={id}, Signature={signature}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"crypto/hmac"
|
||||
"crypto/sha256"
|
||||
"encoding/hex"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
// 创建一个获取用户信息的请求
|
||||
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", "http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info", nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Error creating request:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 设置内容类型
|
||||
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
|
||||
|
||||
// 签名请求 - 传入您的用户ID和API令牌
|
||||
if err = SignReq(req, uint(16), "YourSecretToken"); err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Error signing request:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 发送请求
|
||||
client := &http.Client{}
|
||||
resp, err := client.Do(req)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Error sending request:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer resp.Body.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
// 处理响应
|
||||
body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Error reading response:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println("Response Status:", resp.Status)
|
||||
fmt.Println("Response Body:", string(body))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SignReq 对HTTP请求进行签名
|
||||
func SignReq(req *http.Request, id uint, token string) error {
|
||||
// 步骤一:构造规范化请求
|
||||
var body []byte
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
|
||||
if req.Body != nil {
|
||||
// 读取并保存请求体
|
||||
body, err = io.ReadAll(req.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 恢复请求体以便后续使用
|
||||
req.Body = io.NopCloser(bytes.NewReader(body))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 规范化路径
|
||||
canonicalPath := req.URL.Path
|
||||
if !strings.HasPrefix(canonicalPath, "/api") {
|
||||
index := strings.Index(canonicalPath, "/api")
|
||||
if index != -1 {
|
||||
canonicalPath = canonicalPath[index:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
canonicalRequest := fmt.Sprintf("%s\n%s\n%s\n%s",
|
||||
req.Method,
|
||||
canonicalPath,
|
||||
req.URL.Query().Encode(),
|
||||
SHA256(string(body)))
|
||||
|
||||
// 步骤二:设置时间戳和构造待签名字符串
|
||||
timestamp := time.Now().Unix()
|
||||
req.Header.Set("X-Timestamp", fmt.Sprintf("%d", timestamp))
|
||||
|
||||
stringToSign := fmt.Sprintf("%s\n%d\n%s",
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256",
|
||||
timestamp,
|
||||
SHA256(canonicalRequest))
|
||||
|
||||
// 步骤三:计算签名
|
||||
signature := HMACSHA256(stringToSign, token)
|
||||
|
||||
// 步骤四:设置Authorization头
|
||||
authHeader := fmt.Sprintf("HMAC-SHA256 Credential=%d, Signature=%s", id, signature)
|
||||
req.Header.Set("Authorization", authHeader)
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func SHA256(str string) string {
|
||||
sum := sha256.Sum256([]byte(str))
|
||||
dst := make([]byte, hex.EncodedLen(len(sum)))
|
||||
hex.Encode(dst, sum[:])
|
||||
return string(dst)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func HMACSHA256(data string, secret string) string {
|
||||
h := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(secret))
|
||||
h.Write([]byte(data))
|
||||
return hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## PHP 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* AcePanel API 请求示例 (PHP)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
function signRequest($method, $url, $body, $id, $token) {
|
||||
// 解析URL并获取路径
|
||||
$parsedUrl = parse_url($url);
|
||||
$path = $parsedUrl['path'];
|
||||
$query = isset($parsedUrl['query']) ? $parsedUrl['query'] : '';
|
||||
|
||||
// 规范化路径
|
||||
$canonicalPath = $path;
|
||||
if (strpos($path, '/api') !== 0) {
|
||||
$apiPos = strpos($path, '/api');
|
||||
if ($apiPos !== false) {
|
||||
$canonicalPath = substr($path, $apiPos);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算请求体的SHA256哈希值
|
||||
$bodySha256 = hash('sha256', $body ?: '');
|
||||
|
||||
// 构造规范化请求
|
||||
$canonicalRequest = implode("\n", [
|
||||
$method,
|
||||
$canonicalPath,
|
||||
$query,
|
||||
$bodySha256
|
||||
]);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取当前时间戳
|
||||
$timestamp = time();
|
||||
|
||||
// 构造待签名字符串
|
||||
$stringToSign = implode("\n", [
|
||||
'HMAC-SHA256',
|
||||
$timestamp,
|
||||
hash('sha256', $canonicalRequest)
|
||||
]);
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算签名
|
||||
$signature = hash_hmac('sha256', $stringToSign, $token);
|
||||
|
||||
// 返回签名和时间戳
|
||||
return [
|
||||
'timestamp' => $timestamp,
|
||||
'signature' => $signature,
|
||||
'id' => $id
|
||||
];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 示例请求
|
||||
$apiUrl = 'http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info';
|
||||
$method = 'GET';
|
||||
$body = ''; // 对于GET请求,通常没有请求体
|
||||
$id = 16;
|
||||
$token = 'YourSecretToken';
|
||||
|
||||
// 生成签名信息
|
||||
$signingData = signRequest($method, $apiUrl, $body, $id, $token);
|
||||
|
||||
// 准备HTTP请求头
|
||||
$headers = [
|
||||
'Content-Type: application/json',
|
||||
'X-Timestamp: ' . $signingData['timestamp'],
|
||||
'Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 Credential=' . $signingData['id'] . ', Signature=' . $signingData['signature']
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
// 使用cURL发送请求
|
||||
$ch = curl_init($apiUrl);
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers);
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST, $method);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!empty($body)) {
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $body);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 执行请求并获取响应
|
||||
$response = curl_exec($ch);
|
||||
$statusCode = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE);
|
||||
curl_close($ch);
|
||||
|
||||
// 输出结果
|
||||
echo "响应状态码: " . $statusCode . PHP_EOL;
|
||||
echo "响应内容: " . $response . PHP_EOL;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
import hmac
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from urllib.parse import urlparse, parse_qs
|
||||
|
||||
def sha256_hash(text):
|
||||
"""计算字符串的SHA256哈希值"""
|
||||
return hashlib.sha256(text.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
|
||||
|
||||
def hmac_sha256(key, message):
|
||||
"""使用HMAC-SHA256算法计算签名"""
|
||||
return hmac.new(key.encode('utf-8'), message.encode('utf-8'), hashlib.sha256).hexdigest()
|
||||
|
||||
def sign_request(method, url, body, user_id, token):
|
||||
"""为API请求生成签名"""
|
||||
# 解析URL
|
||||
parsed_url = urlparse(url)
|
||||
path = parsed_url.path
|
||||
query = parsed_url.query
|
||||
|
||||
# 规范化路径
|
||||
canonical_path = path
|
||||
if not path.startswith('/api'):
|
||||
api_pos = path.find('/api')
|
||||
if api_pos != -1:
|
||||
canonical_path = path[api_pos:]
|
||||
|
||||
# 构造规范化请求
|
||||
body_str = body if body else ""
|
||||
canonical_request = "\n".join([
|
||||
method,
|
||||
canonical_path,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
sha256_hash(body_str)
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
# 获取当前时间戳
|
||||
timestamp = int(time.time())
|
||||
|
||||
# 构造待签名字符串
|
||||
string_to_sign = "\n".join([
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256",
|
||||
str(timestamp),
|
||||
sha256_hash(canonical_request)
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
# 计算签名
|
||||
signature = hmac_sha256(token, string_to_sign)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"timestamp": timestamp,
|
||||
"signature": signature,
|
||||
"id": user_id
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 示例请求
|
||||
api_url = "http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info"
|
||||
method = "GET"
|
||||
body = "" # GET请求通常没有请求体
|
||||
user_id = 16
|
||||
token = "YourSecretToken"
|
||||
|
||||
# 生成签名信息
|
||||
signing_data = sign_request(method, api_url, body, user_id, token)
|
||||
|
||||
# 准备HTTP请求头
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Content-Type": "application/json",
|
||||
"X-Timestamp": str(signing_data["timestamp"]),
|
||||
"Authorization": f"HMAC-SHA256 Credential={signing_data['id']}, Signature={signing_data['signature']}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 发送请求
|
||||
response = requests.request(
|
||||
method=method,
|
||||
url=api_url,
|
||||
headers=headers,
|
||||
data=body
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 输出结果
|
||||
print(f"响应状态码: {response.status_code}")
|
||||
print(f"响应内容: {response.text}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Java 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.net.URI;
|
||||
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
|
||||
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
|
||||
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
|
||||
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
|
||||
import java.security.MessageDigest;
|
||||
import java.time.Instant;
|
||||
import javax.crypto.Mac;
|
||||
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
|
||||
import java.util.Base64;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* AcePanel API 请求示例 (Java)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class AcePanelApiExample {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
// 示例请求
|
||||
String apiUrl = "http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info";
|
||||
String method = "GET";
|
||||
String body = ""; // 对于GET请求,通常没有请求体
|
||||
int id = 16;
|
||||
String token = "YourSecretToken";
|
||||
|
||||
// 生成签名信息
|
||||
SigningData signingData = signRequest(method, apiUrl, body, id, token);
|
||||
|
||||
// 准备HTTP请求
|
||||
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
|
||||
HttpRequest.Builder requestBuilder = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
|
||||
.uri(URI.create(apiUrl))
|
||||
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
|
||||
.header("X-Timestamp", String.valueOf(signingData.timestamp))
|
||||
.header("Authorization", "HMAC-SHA256 Credential=" + signingData.id +
|
||||
", Signature=" + signingData.signature);
|
||||
|
||||
// 设置请求方法和请求体
|
||||
if (method.equals("GET")) {
|
||||
requestBuilder.GET();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
requestBuilder.method(method, HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(body));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
HttpRequest request = requestBuilder.build();
|
||||
|
||||
// 发送请求
|
||||
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
|
||||
|
||||
// 输出结果
|
||||
System.out.println("响应状态码: " + response.statusCode());
|
||||
System.out.println("响应内容: " + response.body());
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (Exception e) {
|
||||
e.printStackTrace();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static class SigningData {
|
||||
long timestamp;
|
||||
String signature;
|
||||
int id;
|
||||
|
||||
SigningData(long timestamp, String signature, int id) {
|
||||
this.timestamp = timestamp;
|
||||
this.signature = signature;
|
||||
this.id = id;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public static SigningData signRequest(String method, String url, String body, int id, String token) throws Exception {
|
||||
// 解析URL
|
||||
URI uri = new URI(url);
|
||||
String path = uri.getPath();
|
||||
String query = uri.getQuery() != null ? uri.getQuery() : "";
|
||||
|
||||
// 规范化路径
|
||||
String canonicalPath = path;
|
||||
if (!path.startsWith("/api")) {
|
||||
int apiPos = path.indexOf("/api");
|
||||
if (apiPos != -1) {
|
||||
canonicalPath = path.substring(apiPos);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算请求体的SHA256哈希值
|
||||
String bodySha256 = sha256Hash(body != null ? body : "");
|
||||
|
||||
// 构造规范化请求
|
||||
String canonicalRequest = String.join("\n",
|
||||
method,
|
||||
canonicalPath,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
bodySha256);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取当前时间戳
|
||||
long timestamp = Instant.now().getEpochSecond();
|
||||
|
||||
// 构造待签名字符串
|
||||
String stringToSign = String.join("\n",
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256",
|
||||
String.valueOf(timestamp),
|
||||
sha256Hash(canonicalRequest));
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算签名
|
||||
String signature = hmacSha256(token, stringToSign);
|
||||
|
||||
// 返回签名和时间戳
|
||||
return new SigningData(timestamp, signature, id);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static String sha256Hash(String text) throws Exception {
|
||||
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
|
||||
byte[] hash = digest.digest(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
|
||||
return bytesToHex(hash);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static String hmacSha256(String key, String message) throws Exception {
|
||||
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
|
||||
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "HmacSHA256");
|
||||
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
|
||||
byte[] hash = mac.doFinal(message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
|
||||
return bytesToHex(hash);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
|
||||
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
|
||||
for (byte b : bytes) {
|
||||
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
|
||||
if (hex.length() == 1) {
|
||||
hexString.append('0');
|
||||
}
|
||||
hexString.append(hex);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return hexString.toString();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Node.js 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const crypto = require('crypto');
|
||||
const axios = require('axios');
|
||||
const url = require('url');
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 计算字符串的SHA256哈希值
|
||||
* @param {string} text 待哈希的字符串
|
||||
* @returns {string} 哈希结果(十六进制)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function sha256Hash(text) {
|
||||
return crypto.createHash('sha256').update(text || '').digest('hex');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 使用HMAC-SHA256算法计算签名
|
||||
* @param {string} key 密钥
|
||||
* @param {string} message 待签名的消息
|
||||
* @returns {string} 签名结果(十六进制)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function hmacSha256(key, message) {
|
||||
return crypto.createHmac('sha256', key).update(message).digest('hex');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 为API请求生成签名
|
||||
* @param {string} method HTTP方法
|
||||
* @param {string} apiUrl API地址
|
||||
* @param {string} body 请求体
|
||||
* @param {number} id 用户ID
|
||||
* @param {string} token 密钥
|
||||
* @returns {object} 包含签名、时间戳和ID的对象
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function signRequest(method, apiUrl, body, id, token) {
|
||||
// 解析URL
|
||||
const parsedUrl = new url.URL(apiUrl);
|
||||
const path = parsedUrl.pathname;
|
||||
const query = parsedUrl.search.slice(1); // 移除开头的'?'
|
||||
|
||||
// 规范化路径
|
||||
let canonicalPath = path;
|
||||
if (!path.startsWith('/api')) {
|
||||
const apiPos = path.indexOf('/api');
|
||||
if (apiPos !== -1) {
|
||||
canonicalPath = path.slice(apiPos);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 构造规范化请求
|
||||
const canonicalRequest = [
|
||||
method,
|
||||
canonicalPath,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
sha256Hash(body || '')
|
||||
].join('\n');
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取当前时间戳
|
||||
const timestamp = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
|
||||
|
||||
// 构造待签名字符串
|
||||
const stringToSign = [
|
||||
'HMAC-SHA256',
|
||||
timestamp,
|
||||
sha256Hash(canonicalRequest)
|
||||
].join('\n');
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算签名
|
||||
const signature = hmacSha256(token, stringToSign);
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
timestamp,
|
||||
signature,
|
||||
id
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 发送API请求
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function sendApiRequest() {
|
||||
// 示例请求参数
|
||||
const apiUrl = 'http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info';
|
||||
const method = 'GET';
|
||||
const body = ''; // GET请求通常没有请求体
|
||||
const id = 16;
|
||||
const token = 'YourSecretToken';
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
// 生成签名信息
|
||||
const signingData = signRequest(method, apiUrl, body, id, token);
|
||||
|
||||
// 准备HTTP请求头
|
||||
const headers = {
|
||||
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
|
||||
'X-Timestamp': signingData.timestamp,
|
||||
'Authorization': `HMAC-SHA256 Credential=${signingData.id}, Signature=${signingData.signature}`
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// 发送请求
|
||||
const response = await axios({
|
||||
method,
|
||||
url: apiUrl,
|
||||
headers,
|
||||
data: body || undefined
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 输出结果
|
||||
console.log(`响应状态码: ${response.status}`);
|
||||
console.log(`响应内容: ${JSON.stringify(response.data)}`);
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('请求出错:', error.message);
|
||||
if (error.response) {
|
||||
console.error(`响应状态码: ${error.response.status}`);
|
||||
console.error(`响应内容: ${JSON.stringify(error.response.data)}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 执行请求
|
||||
sendApiRequest();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见响应码
|
||||
|
||||
| HTTP 状态码 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------- | ------- |
|
||||
| 200 | 请求成功 |
|
||||
| 401 | 身份验证失败 |
|
||||
| 403 | 权限不足 |
|
||||
| 404 | 资源不存在 |
|
||||
| 422 | 请求参数错误 |
|
||||
| 500 | 服务器内部错误 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 安全建议
|
||||
|
||||
1. **保护您的 API 令牌**:不要在客户端代码中硬编码或公开您的 API 令牌
|
||||
2. **定期轮换令牌**:定期更改您的 API 令牌以提高安全性
|
||||
3. **配置 IP 白名单**:在生产环境中使用 IP 白名单限制访问
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题解答
|
||||
|
||||
### 签名验证失败
|
||||
|
||||
如果遇到签名验证失败,请检查:
|
||||
|
||||
- 确保使用了正确的 API 令牌和 ID
|
||||
- 检查客户端与服务器的时间是否准确,时间戳偏差大于 300 秒会导致验证失败
|
||||
- 确保请求体在计算签名前后没有被修改
|
||||
- 确保 URL 路径处理正确,注意规范化路径时需要移除入口前缀
|
||||
|
||||
### 请求超时
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查网络连接
|
||||
- 确认服务器状态
|
||||
- 考虑增加客户端的超时设置
|
||||
40
zh_CN/advanced/app.md
Normal file
40
zh_CN/advanced/app.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
# 应用
|
||||
|
||||
应用模块是 AcePanel 的核心功能之一,用于管理服务器上的各类软件。 通过应用模块,你可以方便地安装、配置和管理 Web 服务器、数据库、运行环境等常用软件。
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能分类
|
||||
|
||||
应用模块分为三个部分:
|
||||
|
||||
- **原生应用**:直接安装在系统上的软件,如 Nginx、MySQL、Redis 等
|
||||
- **运行环境**:各类编程语言的运行时环境,如 PHP、Node.js、Python、Go、Java 等
|
||||
- **容器模板**:基于 Docker 的一键部署模板,可快速部署各类应用
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 原生应用 vs 容器模板
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | 原生应用 | 容器模板 |
|
||||
| ---- | ---------- | ---------- |
|
||||
| 性能 | 更高 | 略有损耗 |
|
||||
| 隔离性 | 共享系统环境 | 完全隔离 |
|
||||
| 部署难度 | 需要配置 | 一键部署 |
|
||||
| 资源占用 | 较低 | 较高 |
|
||||
| 适用场景 | 生产环境、高性能需求 | 快速测试、多版本共存 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 应用分类
|
||||
|
||||
原生应用按功能预设了多个分类,包括但不限于:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Web 服务器**:Nginx、OpenResty、Apache
|
||||
- **数据库**:MySQL、MariaDB、PostgreSQL、Percona
|
||||
- **容器**:Docker、Podman
|
||||
- **中间件**:Redis、Memcached
|
||||
- **存储**:MinIO、S3fs
|
||||
- **工具**:phpMyAdmin、Pure-FTPd、Supervisor、Rsync、Frp
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [原生应用](./app/native) - 了解如何安装和管理原生应用
|
||||
- [运行环境](./app/environment) - 了解如何安装编程语言运行环境
|
||||
- [容器模板](./app/template) - 了解如何使用容器模板快速部署应用
|
||||
98
zh_CN/advanced/app/environment.md
Normal file
98
zh_CN/advanced/app/environment.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
# 运行环境
|
||||
|
||||
运行环境用于安装各类编程语言的运行时,为网站和项目提供执行环境。
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持的语言
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 支持以下编程语言的运行环境:
|
||||
|
||||
| 语言 | 可用版本 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------- | ---------------------- |
|
||||
| Go | 1.20 - 1.25 | 适合构建高性能后端服务 |
|
||||
| Java | JDK 8, 11, 17, 21, 25 | 使用 Amazon Corretto 发行版 |
|
||||
| Node.js | 20, 22, 24 | 适合前端构建和 Node 应用 |
|
||||
| PHP | 7.4 - 8.5 | 适合 Web 开发 |
|
||||
| Python | 3.10 - 3.14 | 适合脚本和 Web 应用 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 运行环境列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **应用** 页面,点击 **运行环境** 标签查看可用的运行环境:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击顶部的语言分类可以筛选特定语言的版本:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 安装运行环境
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **应用** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **运行环境** 标签
|
||||
3. 选择需要的语言分类(或查看全部)
|
||||
4. 点击对应版本的 **安装** 按钮
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 版本选择建议
|
||||
|
||||
- 生产环境建议使用 LTS(长期支持)版本
|
||||
- 标注「已停止维护」的版本不建议用于新项目
|
||||
- 可以同时安装多个版本,在项目中指定使用
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 管理运行环境
|
||||
|
||||
已安装的运行环境会显示 **管理** 按钮。 点击进入管理页面:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 运行状态
|
||||
|
||||
显示运行环境的当前状态,提供启动、停止、重启、重载等操作。
|
||||
|
||||
### 模块管理(PHP)
|
||||
|
||||
PHP 运行环境提供模块管理功能,可以安装或卸载各种 PHP 模块:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
常用模块包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- **OPcache**:PHP 字节码缓存,提升性能
|
||||
- **Redis**:连接 Redis 数据库
|
||||
- **ImageMagick**:图像处理
|
||||
- **Swoole/Swow**:高性能异步框架
|
||||
- **ionCube**:PHP 代码加密解密
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
可以编辑 PHP 的主配置文件(php.ini)和 FPM 配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置为 CLI 默认版本
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **设置为 CLI 默认版本** 按钮,可以将当前版本设置为命令行默认使用的 PHP 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
## 多版本共存
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 支持同一语言的多个版本共存。 例如,你可以同时安装 PHP 7.4 和 PHP 8.3,不同的网站可以使用不同的 PHP 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
安装路径规则:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Go**:`/opt/ace/server/go/版本号`
|
||||
- **Java**:`/opt/ace/server/java/版本号`
|
||||
- **Node.js**:`/opt/ace/server/nodejs/版本号`
|
||||
- **PHP**:`/opt/ace/server/php/版本号`
|
||||
- **Python**:`/opt/ace/server/python/版本号`
|
||||
|
||||
## 在项目中使用
|
||||
|
||||
创建项目时,可以在项目设置中选择使用的运行环境版本。 详见 [项目管理](../project) 文档。
|
||||
|
||||
## 更新运行环境
|
||||
|
||||
当有新版本可用时,列表中会显示最新版本号。 你可以:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 卸载旧版本,安装新版本
|
||||
2. 保留旧版本,同时安装新版本(推荐)
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
更新运行环境版本可能导致依赖该版本的项目出现兼容性问题, 请在测试环境验证后再更新生产环境。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
83
zh_CN/advanced/app/native.md
Normal file
83
zh_CN/advanced/app/native.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
# 原生应用
|
||||
|
||||
原生应用是直接安装在系统上的软件,相比容器化部署具有更好的性能和更低的资源占用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 应用列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **应用** 页面,默认显示原生应用列表。 你可以通过顶部的分类标签筛选不同类型的应用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表中显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **应用名称**:软件名称
|
||||
- **描述**:软件的简要说明
|
||||
- **已安装版本**:当前安装的版本号(未安装则为空)
|
||||
- **在主页显示**:是否在面板首页的快捷应用中显示
|
||||
- **操作**:安装、管理或卸载
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装应用
|
||||
|
||||
点击应用右侧的 **安装** 按钮,会弹出安装对话框:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 选择渠道
|
||||
|
||||
部分应用提供多个版本渠道, 点击下拉框选择需要的版本系列:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 选择版本
|
||||
|
||||
选择渠道后,系统会自动填入该渠道的最新版本号:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击 **安装** 按钮开始安装。 安装过程中可以在 **任务** 页面查看详细日志。
|
||||
|
||||
## 管理应用
|
||||
|
||||
已安装的应用会显示 **管理** 按钮, 点击进入应用管理页面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 运行状态
|
||||
|
||||
管理页面首先显示应用的运行状态:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
提供以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
- **启动**:启动已停止的服务
|
||||
- **停止**:停止正在运行的服务
|
||||
- **重启**:重启服务(会中断连接)
|
||||
- **重载**:重新加载配置(不中断连接,推荐)
|
||||
|
||||
### 修改配置
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **修改配置** 标签,可以直接编辑应用的配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
修改配置文件前请确保了解每个参数的含义, 错误的配置可能导致服务无法启动。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 日志查看
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **运行日志** 或 **错误日志** 标签,可以查看应用的日志,便于排查问题。
|
||||
|
||||
## 卸载应用
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **卸载** 按钮可以卸载应用。 卸载前请确保:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 没有网站或项目依赖该应用
|
||||
2. 已备份重要的配置文件和数据
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
卸载数据库类应用(如 MySQL、PostgreSQL)会删除所有数据库数据, 请务必提前备份!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 主页快捷方式
|
||||
|
||||
开启 **在主页显示** 开关后,该应用会出现在面板首页的快捷应用区域,方便快速访问管理页面。
|
||||
99
zh_CN/advanced/app/template.md
Normal file
99
zh_CN/advanced/app/template.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# 容器模板
|
||||
|
||||
容器模板提供了基于 Docker 的一键部署方案,可以快速部署各类常用应用,无需手动配置。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
使用容器模板前,需要先安装 Docker:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **应用** > **原生应用**
|
||||
2. 找到 Docker,点击 **安装**
|
||||
3. 等待安装完成
|
||||
|
||||
## 模板列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **应用** 页面,点击 **容器模板** 标签查看可用模板:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 部署应用
|
||||
|
||||
点击模板卡片上的 **部署** 按钮,会启动部署向导。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步:选择部署模式
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **创建新编排**:从模板创建一个新的 Docker Compose 编排
|
||||
- **更新现有编排**:使用模板更新已有的编排配置
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:配置参数
|
||||
|
||||
根据应用需求填写配置信息:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
常见配置项:
|
||||
|
||||
- **编排名称**:用于标识这个部署
|
||||
- **自动启动**:是否在创建后自动启动容器
|
||||
- **自动防火墙**:是否自动放行端口
|
||||
- **数据库配置**:用户名、密码、地址等
|
||||
- **端口配置**:服务监听的端口
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:预览与编辑
|
||||
|
||||
预览生成的 Docker Compose 配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以在这里:
|
||||
|
||||
- 查看和编辑 **编排文件**(docker-compose.yml)
|
||||
- 查看和编辑 **环境变量**
|
||||
|
||||
### 第四步:确认部署
|
||||
|
||||
确认所有配置无误后,点击 **创建** 完成部署:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
部署完成后,应用会出现在 **容器** > **编排** 页面中进行管理。
|
||||
|
||||
## 模板 vs 手动部署
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | 使用模板 | 手动部署 |
|
||||
| ---- | ----------- | --------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 配置难度 | 简单,填写基本信息即可 | 需要编写 docker-compose.yml |
|
||||
| 灵活性 | 使用预设配置 | 完全自定义 |
|
||||
| 适用场景 | 快速部署常用应用 | 特殊需求、自定义配置 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 常用模板说明
|
||||
|
||||
### WordPress
|
||||
|
||||
开源博客和内容管理系统,适合搭建个人博客或企业网站。
|
||||
|
||||
### pgAdmin 4
|
||||
|
||||
PostgreSQL 数据库的图形化管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### phpMyAdmin
|
||||
|
||||
MySQL/MariaDB 数据库的图形化管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### Vaultwarden
|
||||
|
||||
轻量级密码管理服务器,兼容 Bitwarden 客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
### 青龙
|
||||
|
||||
定时任务管理平台,支持 Python、JavaScript、Shell 等脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenList
|
||||
|
||||
多存储聚合的文件列表程序,支持阿里云盘、OneDrive 等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 更新缓存
|
||||
|
||||
如果模板列表显示不完整或需要获取最新模板,点击页面顶部的 **更新缓存** 按钮刷新模板列表。
|
||||
231
zh_CN/advanced/backup.md
Normal file
231
zh_CN/advanced/backup.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
|
||||
# 备份
|
||||
|
||||
备份模块用于备份和恢复网站文件和数据库,支持本地备份和远程存储。
|
||||
|
||||
## 备份页面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 备份类型
|
||||
|
||||
备份模块支持以下类型的备份:
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---------- | ---------------------------- |
|
||||
| 网站 | 备份网站文件 |
|
||||
| MySQL | 备份 Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 数据库 |
|
||||
| PostgreSQL | 备份 PostgreSQL 数据库 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建备份
|
||||
|
||||
1. 选择备份类型标签(网站/MySQL/PostgreSQL)
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建备份**
|
||||
3. 选择要备份的网站或数据库
|
||||
4. 选择存储位置
|
||||
5. 点击确认
|
||||
|
||||
备份文件格式:
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:`.zip` 压缩包
|
||||
- 数据库:`.sql.zip` 压缩的 SQL 文件
|
||||
|
||||
## 备份列表
|
||||
|
||||
备份列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **文件名**:备份文件名称
|
||||
- **大小**:备份文件大小
|
||||
- **更新日期**:备份时间
|
||||
- **操作**:下载、恢复、删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 恢复备份
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在备份列表中找到要恢复的备份
|
||||
2. 点击 **恢复** 按钮
|
||||
3. 确认恢复操作
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
恢复操作会覆盖现有数据, 请确保已备份当前数据!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 上传备份
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **上传备份** 按钮可以上传本地的备份文件,用于恢复数据。
|
||||
|
||||
## 存储管理
|
||||
|
||||
切换到 **存储** 标签页管理备份存储位置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 本地存储
|
||||
|
||||
默认的存储位置,备份文件保存在服务器本地。
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程存储
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **添加存储** 可以添加远程存储,支持:
|
||||
|
||||
- **S3 兼容存储**:AWS S3、阿里云 OSS、腾讯云 COS 等
|
||||
- **FTP/SFTP**:FTP 或 SFTP 服务器
|
||||
- **WebDAV**:WebDAV 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
远程存储的优势:
|
||||
|
||||
- 异地备份,防止数据丢失
|
||||
- 不占用服务器磁盘空间
|
||||
- 便于多服务器共享备份
|
||||
|
||||
### S3 兼容存储配置
|
||||
|
||||
S3 兼容存储是最常用的远程存储方式, 大多数云存储服务商都提供 S3 兼容接口。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 配置参数
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---------- | -------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 名称 | 存储配置的名称,便于识别 |
|
||||
| 类型 | 选择 S3 |
|
||||
| Access Key | Access Key ID |
|
||||
| Secret Key | Access Key Secret |
|
||||
| 风格 | Virtual Hosted 或 Path Style |
|
||||
| 区域 | 区域代码,如 `us-east-1`、`cn-hangzhou` |
|
||||
| 端点 | S3 服务端点 URL |
|
||||
| 协议 | HTTPS(推荐)或 HTTP |
|
||||
| 存储桶 | 存储桶名称 |
|
||||
| 路径 | 备份文件存储的子路径(可选) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 访问风格说明
|
||||
|
||||
S3 有两种 URL 访问风格:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Virtual Hosted Style**:`https://bucket.endpoint/key`
|
||||
- 桶名作为子域名
|
||||
- AWS S3 默认使用此风格
|
||||
|
||||
- **Path Style**:`https://endpoint/bucket/key`
|
||||
- 桶名作为路径的一部分
|
||||
- 自建 MinIO 等通常使用此风格
|
||||
|
||||
#### 兼容性列表
|
||||
|
||||
| 服务商 | 文档 | 兼容访问风格 | 兼容性 |
|
||||
| ------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------- | --- |
|
||||
| 阿里云 OSS | [文档](https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/410748.html) | Virtual Hosted 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 腾讯云 COS | [文档](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/436/41284) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 七牛云 | [文档](https://developer.qiniu.com/kodo/4088/s3-access-domainname) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 百度云 BOS | [文档](https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/BOS/s/Fjwvyq9xo) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 京东云 | [文档](https://docs.jdcloud.com/cn/object-storage-service/api/regions-and-endpoints) | Virtual Hosted 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 金山云 | [文档](https://docs.ksyun.com/documents/6761) | Virtual Hosted 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 青云 QingStor | [文档](https://docsv3.qingcloud.com/storage/object-storage/s3/intro/) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 网易数帆 | [文档](https://sf.163.com/help/documents/89796157866430464) | Virtual Hosted 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| Cloudflare R2 | [文档](https://developers.cloudflare.com/r2/data-access/s3-api/) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 甲骨文云 | [文档](https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Object/Tasks/s3compatibleapi.htm) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 又拍云 | [文档](https://help.upyun.com/knowledge-base/aws-s3%E5%85%BC%E5%AE%B9/) | Virtual Hosted 风格 / Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 自建 MinIO | - | Path 风格 | ✅ |
|
||||
| 华为云 OBS | - | Virtual Hosted 风格 | ❓ |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
华为云官方文档未说明是否兼容 S3 API,但实际测试可以使用。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
#### 配置示例
|
||||
|
||||
**阿里云 OSS**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
名称: aliyun-oss
|
||||
类型: S3
|
||||
Access Key: 你的 AccessKey ID
|
||||
Secret Key: 你的 AccessKey Secret
|
||||
风格: Virtual Hosted
|
||||
区域: cn-hangzhou
|
||||
端点: oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
|
||||
协议: HTTPS
|
||||
存储桶: your-bucket-name
|
||||
路径: backup(可选)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**腾讯云 COS**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
名称: tencent-cos
|
||||
类型: S3
|
||||
Access Key: 你的 SecretId
|
||||
Secret Key: 你的 SecretKey
|
||||
风格: Virtual Hosted
|
||||
区域: ap-guangzhou
|
||||
端点: cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com
|
||||
协议: HTTPS
|
||||
存储桶: your-bucket-name
|
||||
路径: backup(可选)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Cloudflare R2**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
名称: cloudflare-r2
|
||||
类型: S3
|
||||
Access Key: 你的 Access Key ID
|
||||
Secret Key: 你的 Secret Access Key
|
||||
风格: Path Style
|
||||
区域: auto
|
||||
端点: <account-id>.r2.cloudflarestorage.com
|
||||
协议: HTTPS
|
||||
存储桶: your-bucket-name
|
||||
路径: backup(可选)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**自建 MinIO**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
名称: minio
|
||||
类型: S3
|
||||
Access Key: minioadmin
|
||||
Secret Key: minioadmin
|
||||
风格: Path Style
|
||||
区域: us-east-1
|
||||
端点: minio.example.com:9000
|
||||
协议: HTTP 或 HTTPS
|
||||
存储桶: backup
|
||||
路径:(可选)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
|
||||
- 请确保存储桶已创建且有正确的访问权限
|
||||
- 建议为备份创建专用的访问密钥,并限制权限范围
|
||||
- 部分服务商的 Endpoint 需要包含区域信息
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 定时备份
|
||||
|
||||
结合 [计划任务](./task/schedule) 功能,可以设置定时自动备份:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **任务** > **计划任务**
|
||||
2. 创建新任务
|
||||
3. 选择备份类型
|
||||
4. 设置执行周期
|
||||
5. 选择存储位置
|
||||
|
||||
## 备份策略建议
|
||||
|
||||
### 备份频率
|
||||
|
||||
| 数据类型 | 建议频率 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------- |
|
||||
| 数据库 | 每天 |
|
||||
| 网站文件 | 每周 |
|
||||
| 配置文件 | 修改后立即备份 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 保留策略
|
||||
|
||||
- 保留最近 7 天的每日备份
|
||||
- 保留最近 4 周的每周备份
|
||||
- 保留最近 3 个月的每月备份
|
||||
|
||||
### 存储位置
|
||||
|
||||
- 至少保留一份本地备份
|
||||
- 重要数据应同时备份到远程存储
|
||||
- 定期验证备份文件的完整性
|
||||
81
zh_CN/advanced/cert.md
Normal file
81
zh_CN/advanced/cert.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
# 证书
|
||||
|
||||
证书模块用于管理 SSL/TLS 证书,支持通过 ACME 协议自动申请免费证书,也支持上传自有证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能概览
|
||||
|
||||
证书模块分为三个部分:
|
||||
|
||||
| 功能 | 说明 |
|
||||
| -------------------- | ------------- |
|
||||
| [证书](./cert/cert) | 管理 SSL 证书 |
|
||||
| [账户](./cert/account) | 管理 ACME 账户 |
|
||||
| [DNS](./cert/dns) | 管理 DNS API 配置 |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 证书类型
|
||||
|
||||
### 免费证书
|
||||
|
||||
通过 ACME 协议从 Let's Encrypt 等 CA 自动申请免费证书:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Let's Encrypt**:最流行的免费证书颁发机构
|
||||
- **LiteSSL**:TrustAsia 提供的免费证书服务
|
||||
- **Google**:谷歌的免费证书服务
|
||||
- **GoogleCN**:AcePanel 提供的谷歌证书服务镜像
|
||||
- **ZeroSSL**:另一个免费证书选项
|
||||
- **Buypass**:挪威的免费证书服务
|
||||
|
||||
免费证书有效期通常为 90 天,AcePanel 支持自动续签。
|
||||
|
||||
### 付费证书
|
||||
|
||||
从商业 CA 购买的证书,通常有效期为 1 年或更长:
|
||||
|
||||
- 更长的有效期
|
||||
- 更高的信任度
|
||||
- 提供保险和技术支持
|
||||
|
||||
如有证书购买需求,可通过本页顶部的「证书」链接联系我们。
|
||||
|
||||
## 验证方式
|
||||
|
||||
申请证书时需要验证域名所有权, 支持以下方式:
|
||||
|
||||
### HTTP 验证
|
||||
|
||||
在网站根目录放置验证文件,CA 通过 HTTP 访问验证。
|
||||
|
||||
要求:
|
||||
|
||||
- 域名已解析到服务器
|
||||
- 80 端口可访问
|
||||
|
||||
### DNS 验证
|
||||
|
||||
在域名 DNS 中添加 TXT 记录验证。
|
||||
|
||||
要求:
|
||||
|
||||
- 有域名 DNS 管理权限
|
||||
- 配置 DNS API(用于自动验证)
|
||||
|
||||
DNS 验证的优势:
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持申请泛域名证书(\*.example.com)
|
||||
- 不需要 80 端口可访问
|
||||
- 适合内网服务器
|
||||
|
||||
## 快速开始
|
||||
|
||||
1. 创建 ACME 账户(首次使用)
|
||||
2. 如需 DNS 验证,配置 DNS API
|
||||
3. 创建证书,选择验证方式
|
||||
4. 将证书应用到网站
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [证书管理](./cert/cert) - 了解如何申请和管理证书
|
||||
- [账户管理](./cert/account) - 了解如何管理 ACME 账户
|
||||
- [DNS 配置](./cert/dns) - 了解如何配置 DNS API
|
||||
84
zh_CN/advanced/cert/account.md
Normal file
84
zh_CN/advanced/cert/account.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
# 账户管理
|
||||
|
||||
账户管理页面用于管理 ACME 账户, ACME 账户用于向证书颁发机构申请证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 账户列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **证书** > **账户** 标签页查看账户列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **邮箱**:账户邮箱
|
||||
- **CA**:证书颁发机构
|
||||
- **密钥类型**:账户密钥类型
|
||||
- **操作**:修改、删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建账户
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建账户** 按钮
|
||||
2. 填写配置:
|
||||
- **邮箱**:用于接收证书相关通知
|
||||
- **CA**:选择证书颁发机构
|
||||
- **密钥类型**:选择密钥算法
|
||||
- **KID**:可选,部分 CA 需要提供 KID
|
||||
- **HMAC**:可选,部分 CA 需要提供 HMAC 密钥
|
||||
3. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
### 证书颁发机构(CA)
|
||||
|
||||
| CA | 说明 |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------------------- |
|
||||
| Let's Encrypt | 最流行的免费 CA,证书有效期 90 天 |
|
||||
| LiteSSL | TrustAsia 提供的免费证书服务 |
|
||||
| Google | 谷歌的免费证书服务 |
|
||||
| GoogleCN | AcePanel 提供的谷歌证书服务镜像 |
|
||||
| ZeroSSL | 免费 CA,证书有效期 90 天 |
|
||||
| Buypass | 挪威免费 CA,证书有效期 180 天 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 密钥类型
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ----------------------------- | --------------- |
|
||||
| P256 (ECC) | 推荐,密钥更短,性能更好 |
|
||||
| P384 (ECC) | 更高安全性的 ECC 密钥 |
|
||||
| RSA 2048 | 传统 RSA 密钥,兼容性最好 |
|
||||
| RSA 4096 | 更高安全性的 RSA 密钥 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 推荐
|
||||
一般情况下推荐使用 P256 (ECC) 密钥,兼顾安全性和性能。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 修改账户
|
||||
|
||||
点击账户右侧的 **修改** 按钮可以修改账户邮箱。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
修改邮箱后,证书相关通知将发送到新邮箱。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除账户
|
||||
|
||||
点击账户右侧的 **删除** 按钮删除账户。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
删除账户后,使用该账户申请的证书将无法续签。 请先将证书迁移到其他账户或删除相关证书。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 账户用途
|
||||
|
||||
ACME 账户用于:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 向 CA 证明你的身份
|
||||
2. 接收证书到期提醒
|
||||
3. 管理已申请的证书
|
||||
4. 撤销证书
|
||||
|
||||
## 多账户
|
||||
|
||||
你可以创建多个账户:
|
||||
|
||||
- 不同 CA 需要不同账户
|
||||
- 可以为不同项目使用不同账户
|
||||
- 便于管理和区分证书
|
||||
103
zh_CN/advanced/cert/cert.md
Normal file
103
zh_CN/advanced/cert/cert.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
# 证书管理
|
||||
|
||||
证书管理页面用于申请、上传和管理 SSL/TLS 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 证书列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **证书** 页面,默认显示证书列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **域名**:证书包含的域名
|
||||
- **类型**:证书类型(ACME/上传)
|
||||
- **关联账户**:使用的 ACME 账户
|
||||
- **颁发者**:证书颁发机构
|
||||
- **过期时间**:证书到期时间
|
||||
- **下次续签时间**:自动续签时间
|
||||
- **自动续签**:是否启用自动续签
|
||||
- **操作**:续签、下载、删除等
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建证书
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **创建证书** 按钮申请新证书。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **域名**:要申请证书的域名,支持多个域名
|
||||
- **密钥类型**:RSA 或 ECC
|
||||
- **网站**:该证书关联的网站
|
||||
- **账户**:该证书关联的 ACME 账户
|
||||
- **DNS**:该证书关联的 DNS API
|
||||
|
||||
### 域名格式
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
example.com # 单个域名
|
||||
www.example.com # 子域名
|
||||
*.example.com # 泛域名(需要 DNS 验证)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
泛域名证书(\*.example.com)只能通过 DNS 验证方式申请。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 上传证书
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **上传证书** 按钮上传已有证书。
|
||||
|
||||
需要提供:
|
||||
|
||||
- **证书文件**:PEM 格式的证书(.crt 或 .pem),请包含完整证书链
|
||||
- **私钥文件**:PEM 格式的私钥(.key)
|
||||
|
||||
## 应用证书
|
||||
|
||||
申请或上传证书后,需要在网站设置中启用 HTTPS 并选择证书。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入网站编辑页面
|
||||
2. 切换到 **HTTPS** 标签
|
||||
3. 启用 HTTPS
|
||||
4. 选择证书
|
||||
5. 保存配置
|
||||
|
||||
## 自动续签
|
||||
|
||||
ACME 证书支持自动续签:
|
||||
|
||||
- 证书签发后通过 ARI 获取建议的续签时间
|
||||
- 系统会在续签时间前自动尝试续签
|
||||
- 续签成功后自动更新网站配置
|
||||
- 续签失败会发送通知
|
||||
|
||||
## 证书操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 手动续签
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **续签** 按钮手动触发证书续签。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载证书
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **下载** 按钮下载证书文件,包含:
|
||||
|
||||
- 完整证书链(.crt)
|
||||
- 私钥文件(.key)
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除证书
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **删除** 按钮删除证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 申请失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查域名是否正确解析到服务器
|
||||
- 检查 80 端口是否可访问(HTTP 验证)
|
||||
- 检查 DNS API 配置是否正确(DNS 验证)
|
||||
|
||||
### 续签失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查域名解析是否变更
|
||||
- 检查 DNS API 是否过期
|
||||
- 查看面板日志了解详细错误
|
||||
99
zh_CN/advanced/cert/dns.md
Normal file
99
zh_CN/advanced/cert/dns.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# DNS 配置
|
||||
|
||||
DNS 配置页面用于管理 DNS API,用于通过 DNS 验证方式申请证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## DNS 列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **证书** > **DNS** 标签页查看 DNS 配置列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **备注名称**:配置名称
|
||||
- **类型**:DNS 提供商类型
|
||||
- **操作**:修改、删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建 DNS 配置
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建 DNS** 按钮
|
||||
2. 选择 DNS 提供商
|
||||
3. 填写 API 凭证
|
||||
4. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持的 DNS 提供商
|
||||
|
||||
### 国内提供商
|
||||
|
||||
| 提供商 | 所需凭证 |
|
||||
| ---------- | ----------------------------- |
|
||||
| 阿里云 DNS | AccessKey ID、AccessKey Secret |
|
||||
| 腾讯云 DNSPod | SecretId、SecretKey |
|
||||
| 华为云 DNS | AccessKeyId、SecretAccessKey |
|
||||
| 西部数码 DNS | Username、API Password |
|
||||
|
||||
### 国际提供商
|
||||
|
||||
| 提供商 | 所需凭证 |
|
||||
| ---------- | --------------------- |
|
||||
| Cloudflare | API Token |
|
||||
| Gcore DNS | API Key |
|
||||
| Porkbun | API Key、Secret Key |
|
||||
| NameSilo | API Token |
|
||||
| ClouDNS | Auth ID、Auth Password |
|
||||
|
||||
## 获取 API 凭证
|
||||
|
||||
### 阿里云
|
||||
|
||||
1. 登录阿里云控制台
|
||||
2. 进入 **AccessKey 管理**
|
||||
3. 创建 AccessKey
|
||||
4. 记录 AccessKey ID 和 AccessKey Secret
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 安全提示
|
||||
建议创建子账号并只授予 DNS 管理权限, 避免使用主账户的 AccessKey。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 腾讯云
|
||||
|
||||
1. 登录腾讯云控制台
|
||||
2. 进入 **访问管理** > **API 密钥管理**
|
||||
3. 创建密钥
|
||||
4. 记录 SecretId 和 SecretKey
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloudflare
|
||||
|
||||
1. 登录 Cloudflare 控制台
|
||||
2. 进入 **My Profile** > **API Tokens**
|
||||
3. 创建 Token,选择 **Edit zone DNS** 模板
|
||||
4. 记录生成的 Token
|
||||
|
||||
## DNS 验证原理
|
||||
|
||||
1. 申请证书时,CA 要求在域名 DNS 中添加特定的 TXT 记录
|
||||
2. AcePanel 通过 DNS API 自动添加验证记录
|
||||
3. CA 验证 TXT 记录存在
|
||||
4. 验证通过后颁发证书
|
||||
5. AcePanel 自动删除验证记录
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用场景
|
||||
|
||||
DNS 验证适用于:
|
||||
|
||||
- 申请泛域名证书(\*.example.com)
|
||||
- 服务器 80 端口不可访问
|
||||
- 内网服务器
|
||||
- CDN 后的源站
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查 API 凭证是否正确
|
||||
- 检查 API 权限是否足够
|
||||
- 检查域名是否在该 DNS 提供商管理
|
||||
|
||||
### DNS 传播延迟
|
||||
|
||||
DNS 记录添加后需要一定时间传播,通常几分钟到几小时不等。 如果验证失败,可以稍后重试。
|
||||
56
zh_CN/advanced/container.md
Normal file
56
zh_CN/advanced/container.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
# 容器
|
||||
|
||||
容器模块提供了完整的 Docker 容器管理功能,包括容器、编排、镜像、网络和卷的管理。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
使用容器功能前,需要先安装 Docker 或 Podman:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **应用** > **原生应用**
|
||||
2. 找到 Docker 或 Podman,点击 **安装**
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能概览
|
||||
|
||||
容器模块分为五个部分:
|
||||
|
||||
| 功能 | 说明 |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------- |
|
||||
| [容器](./container/container) | 管理运行中的容器实例 |
|
||||
| [编排](./container/compose) | 使用 Docker Compose 管理多容器应用 |
|
||||
| [镜像](./container/image) | 管理本地镜像 |
|
||||
| [网络](./container/network) | 管理 Docker 网络 |
|
||||
| [卷](./container/volume) | 管理数据卷 |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 快速开始
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建容器
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **容器** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建容器**
|
||||
3. 填写镜像名称(如 `nginx:latest`)
|
||||
4. 配置端口映射、卷挂载等
|
||||
5. 点击 **创建**
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用容器模板
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想快速部署常用应用,推荐使用 [容器模板](./app/template),无需手动配置即可一键部署。
|
||||
|
||||
## 容器 vs 原生应用
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | 容器 | 原生应用 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------- | ------ |
|
||||
| 隔离性 | 完全隔离 | 共享系统环境 |
|
||||
| 性能 | 略有损耗 | 原生性能 |
|
||||
| 部署 | 标准化、可移植 | 依赖系统环境 |
|
||||
| 资源占用 | 较高 | 较低 |
|
||||
| 版本管理 | 方便切换 | 需要手动管理 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [容器管理](./container/container) - 了解如何管理容器
|
||||
- [编排管理](./container/compose) - 了解如何使用 Docker Compose
|
||||
- [镜像管理](./container/image) - 了解如何管理镜像
|
||||
- [网络管理](./container/network) - 了解如何管理网络
|
||||
- [卷管理](./container/volume) - 了解如何管理数据卷
|
||||
108
zh_CN/advanced/container/compose.md
Normal file
108
zh_CN/advanced/container/compose.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
# 编排
|
||||
|
||||
编排功能基于 Docker Compose,用于定义和运行多容器应用。 通过一个 YAML 文件描述应用的服务、网络和卷,然后一键启动整个应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 编排列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **容器** > **编排** 标签页查看编排列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:编排项目名称
|
||||
- **目录**:docker-compose.yml 文件所在目录
|
||||
- **状态**:运行状态
|
||||
- **创建时间**:创建时间
|
||||
- **操作**:启动、停止、编辑等
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建编排
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建编排** 按钮
|
||||
2. 输入编排名称
|
||||
3. 编写或粘贴 docker-compose.yml 内容
|
||||
4. 配置环境变量(可选)
|
||||
5. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### docker-compose.yml 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: '3'
|
||||
services:
|
||||
web:
|
||||
image: nginx:latest
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "80:80"
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- app
|
||||
app:
|
||||
image: php:8.4-fpm
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./html:/var/www/html
|
||||
db:
|
||||
image: mysql:8.4
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: your_password
|
||||
MYSQL_DATABASE: myapp
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
db_data:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 编排操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动编排
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **启动** 按钮会弹出确认对话框:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **强制拉取镜像**:勾选后会在启动前拉取最新镜像
|
||||
|
||||
点击确认后,会显示启动进度:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启动编排会创建并启动所有定义的服务容器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 停止编排
|
||||
|
||||
停止编排会停止所有相关容器,但不会删除容器和数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除编排
|
||||
|
||||
删除编排会停止并删除所有相关容器。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
删除编排不会删除数据卷, 如需删除数据卷请在 **卷** 页面手动删除。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 编辑编排
|
||||
|
||||
点击编排列表中的 **编辑** 按钮,可以修改 docker-compose.yml 文件内容和环境变量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
修改后需要重新启动编排才能生效。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用场景
|
||||
|
||||
编排适合以下场景:
|
||||
|
||||
- **多容器应用**:如 Web 应用 + 数据库 + 缓存
|
||||
- **开发环境**:快速搭建一致的开发环境
|
||||
- **微服务架构**:管理多个相互依赖的服务
|
||||
|
||||
## 与容器模板的区别
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | 编排 | 容器模板 |
|
||||
| ---- | --------------- | ---------- |
|
||||
| 配置方式 | 手写 YAML | 图形界面 |
|
||||
| 灵活性 | 完全自定义 | 使用预设配置+自定义 |
|
||||
| 适用场景 | 自定义复杂应用 | 快速部署常用应用 |
|
||||
| 学习成本 | 需要了解 Compose 语法 | 无需学习 |
|
||||
93
zh_CN/advanced/container/container.md
Normal file
93
zh_CN/advanced/container/container.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
# 容器管理
|
||||
|
||||
容器是 Docker 的核心概念,是镜像的运行实例。 通过容器管理页面,你可以创建、启动、停止和管理容器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 容器列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **容器** 页面,默认显示容器列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **容器名称**:容器的名称
|
||||
- **状态**:运行状态开关
|
||||
- **镜像**:容器使用的镜像
|
||||
- **端口**:端口映射(主机端口 -> 容器端口)
|
||||
- **运行状态**:详细的运行状态信息
|
||||
- **操作**:终端、日志、重命名等
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建容器
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **创建容器** 按钮打开创建对话框。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 基本设置
|
||||
|
||||
- **容器名称**:可选,留空则自动生成
|
||||
- **镜像**:Docker 镜像名称,如 `nginx:latest`、`mysql:8.0`
|
||||
- **网络**:选择容器使用的网络
|
||||
- **重启策略**:容器退出后的重启行为
|
||||
- 无:不自动重启
|
||||
- always:总是重启
|
||||
- 编排启动失败
|
||||
- unless-stopped:除非手动停止,否则重启
|
||||
|
||||
### 高级选项
|
||||
|
||||
- **TTY (-t)**:分配伪终端
|
||||
- **STDIN (-i)**:保持标准输入打开
|
||||
- **自动移除**:容器停止后自动删除
|
||||
- **特权模式**:赋予容器完整的系统权限(谨慎使用)
|
||||
|
||||
### 端口被占用:修改映射端口
|
||||
|
||||
将容器内部端口映射到主机端口,格式:`主机端口:容器端口`
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
例如:`8080:80` 表示将容器的 80 端口映射到主机的 8080 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 卷挂载
|
||||
|
||||
将主机目录或数据卷挂载到容器内,格式:`主机路径:容器路径`
|
||||
|
||||
例如:`/opt/ace/data:/data` 表示将主机的 `/opt/ace/data` 目录挂载到容器的 `/data` 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 资源限制
|
||||
|
||||
限制容器可使用的 CPU 和内存资源。
|
||||
|
||||
### 环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
设置容器的环境变量,格式:`KEY=VALUE`
|
||||
|
||||
## 容器操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 批量操作
|
||||
|
||||
勾选多个容器后,可以进行批量操作:
|
||||
|
||||
- **启动**:启动选中的容器
|
||||
- **停止**:停止选中的容器
|
||||
- **重启**:重启选中的容器
|
||||
- **强制停止**:强制停止选中的容器
|
||||
- **暂停**:暂停选中的容器
|
||||
- **恢复**:恢复暂停的容器
|
||||
- **删除**:删除选中的容器
|
||||
|
||||
### 单个容器操作
|
||||
|
||||
- **终端**:打开容器的终端,可以在容器内执行命令
|
||||
- 查看容器日志
|
||||
- **重命名**:修改容器名称
|
||||
- **更多**:查看详情、导出等操作
|
||||
|
||||
## 清理容器
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **清理容器** 可以删除所有已停止的容器,释放系统资源。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
清理操作不可恢复, 请确保已停止的容器不再需要。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
77
zh_CN/advanced/container/image.md
Normal file
77
zh_CN/advanced/container/image.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# 镜像
|
||||
|
||||
镜像是容器的模板,包含了运行应用所需的所有文件和配置。 通过镜像管理页面,你可以拉取、查看和删除本地镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
## 镜像列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **容器** > **镜像** 标签页查看本地镜像列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **ID**:镜像 ID
|
||||
- **容器数量**:使用该镜像的容器数量
|
||||
- **镜像**:镜像名称和标签
|
||||
- **大小**:镜像占用的磁盘空间
|
||||
- **创建时间**:镜像创建时间
|
||||
- **操作**:删除等
|
||||
|
||||
## 拉取镜像
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **拉取镜像** 按钮
|
||||
2. 输入镜像名称,如 `nginx:latest`、`mysql:8.4`
|
||||
3. 点击确认开始拉取
|
||||
|
||||
镜像名称格式:`[仓库地址/]镜像名[:标签]`
|
||||
|
||||
- `nginx` - 拉取官方 nginx 镜像的 latest 标签
|
||||
- `nginx:1.28` - 拉取指定版本
|
||||
- `mysql:8.4` - 拉取 MySQL 8.4 版本
|
||||
- `registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xxx/yyy:latest` - 从阿里云镜像仓库拉取
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
国内服务器拉取 Docker Hub 镜像可能较慢, 建议配置镜像加速器或使用国内镜像源。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除镜像
|
||||
|
||||
选中镜像后点击 **删除** 按钮删除镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
如果镜像正在被容器使用,需要先删除相关容器才能删除镜像。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 清理镜像
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **清理镜像** 可以删除所有未被使用的镜像,释放磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
清理操作会删除:
|
||||
|
||||
- 悬空镜像(dangling images)
|
||||
- 未被任何容器使用的镜像
|
||||
|
||||
## 镜像来源
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Hub
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 官方镜像仓库,包含大量官方和社区镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
常用官方镜像:
|
||||
|
||||
- `nginx` - Web 服务器
|
||||
- `mysql` / `mariadb` - 数据库
|
||||
- `redis` - 缓存
|
||||
- `postgres` - PostgreSQL 数据库
|
||||
- `node` - Node.js 运行环境
|
||||
- `python` - Python 运行环境
|
||||
|
||||
### 国内镜像源
|
||||
|
||||
- 阿里云:`registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com`
|
||||
- 腾讯云:`ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com`
|
||||
- 华为云:`swr.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com`
|
||||
|
||||
### 私有仓库
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有私有镜像仓库,可以直接使用完整的镜像地址拉取。
|
||||
76
zh_CN/advanced/container/network.md
Normal file
76
zh_CN/advanced/container/network.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
# 网络
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 网络用于容器之间的通信。 通过网络管理页面,你可以创建、查看和删除网络。
|
||||
|
||||
## 网络列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **容器** > **网络** 标签页查看网络列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:网络名称
|
||||
- **驱动**:网络驱动类型
|
||||
- **范围**:网络范围
|
||||
- **子网**:网络的子网地址
|
||||
- **网关**:网络的网关地址
|
||||
- **创建时间**:创建时间
|
||||
- **操作**:删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 默认网络
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 安装后会自动创建以下网络:
|
||||
|
||||
| 网络名称 | 驱动 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ------ | ------ | -------------------- |
|
||||
| bridge | bridge | 默认网络,容器通过 NAT 访问外部网络 |
|
||||
| host | host | 容器直接使用主机网络,无网络隔离 |
|
||||
| none | null | 无网络,容器完全隔离 |
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 还会创建 `acepanel-network` 网络,用于面板编排模版部署的容器, 请勿删除。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建网络
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建网络** 按钮
|
||||
2. 输入网络名称
|
||||
3. 选择网络驱动
|
||||
4. 配置子网和网关(可选)
|
||||
5. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
### 网络驱动
|
||||
|
||||
- **bridge**:桥接网络,最常用的网络类型。 容器通过虚拟网桥连接,可以相互通信。
|
||||
- **host**:主机网络,容器直接使用主机的网络栈,性能最好但无隔离。
|
||||
- **overlay**:覆盖网络,用于跨主机的容器通信(Swarm 模式)。
|
||||
- **macvlan**:MAC VLAN 网络,为容器分配独立的 MAC 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
## 网络使用
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建容器时指定网络
|
||||
|
||||
创建容器时,在 **网络** 选项中选择要使用的网络。
|
||||
|
||||
### 容器间通信
|
||||
|
||||
同一网络中的容器可以通过容器名称相互访问。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,在 `acepanel-network` 网络中:
|
||||
|
||||
- 容器 A 名称为 `web`
|
||||
- 容器 B 名称为 `db`
|
||||
- 容器 A 可以通过 `db:3306` 访问容器 B 的数据库
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除网络
|
||||
|
||||
选中网络后点击 **删除** 按钮删除网络。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
|
||||
- 默认网络(bridge、host、none)和 `acepanel-network` 不能删除
|
||||
- 如果网络中有容器,需要先删除或断开容器才能删除网络
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 清理网络
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **清理网络** 可以删除所有未被使用的自定义网络。
|
||||
77
zh_CN/advanced/container/volume.md
Normal file
77
zh_CN/advanced/container/volume.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# 卷
|
||||
|
||||
卷(Volume)是 Docker 管理的数据存储,用于持久化容器数据。 与直接挂载主机目录相比,卷由 Docker 管理,更加安全和便携。
|
||||
|
||||
## 卷列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **容器** > **卷** 标签页查看卷列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:卷名称
|
||||
- **驱动**:存储驱动
|
||||
- **范围**:卷的范围
|
||||
- **挂载点**:卷在主机上的实际存储路径
|
||||
- **创建时间**:创建时间
|
||||
- **操作**:删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建卷
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建卷** 按钮
|
||||
2. 输入卷名称
|
||||
3. 选择驱动(默认 local)
|
||||
4. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用卷
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建容器时挂载卷
|
||||
|
||||
创建容器时,在 **卷** 选项中添加卷挂载:
|
||||
|
||||
- **卷名称:容器路径** - 使用命名卷
|
||||
- **主机路径:容器路径** - 直接挂载主机目录
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
- `mysql_data:/var/lib/mysql` - 将 mysql_data 卷挂载到容器的 /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
- `/opt/ace/data:/data` - 将主机的 /opt/ace/data 目录挂载到容器的 /data
|
||||
|
||||
### 卷 vs 绑定挂载
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | 卷(Volume) | 绑定挂载(Bind Mount) |
|
||||
| ---- | -------------- | ---------------- |
|
||||
| 管理方式 | Docker 管理 | 用户管理 |
|
||||
| 存储位置 | Docker 数据目录 | 任意主机路径 |
|
||||
| 备份 | 需要通过 Docker 命令 | 直接备份目录 |
|
||||
| 可移植性 | 高 | 依赖主机路径 |
|
||||
| 适用场景 | 数据库等需要持久化的数据 | 配置文件、代码目录 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除卷
|
||||
|
||||
选中卷后点击 **删除** 按钮删除卷。
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
删除卷会永久删除卷中的所有数据, 此操作不可恢复!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
如果卷正在被容器使用,需要先删除相关容器才能删除卷。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 清理卷
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **清理卷** 可以删除所有未被使用的卷,释放磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
清理前请确认未使用的卷中没有重要数据。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据备份
|
||||
|
||||
卷数据存储在 Docker 数据目录中(通常是 `/var/lib/docker/volumes/`), 可以通过以下方式备份:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用 `docker run` 创建临时容器挂载卷并导出数据
|
||||
2. 直接备份 Docker 数据目录(需要停止 Docker 服务)
|
||||
3. (开发中)使用 AcePanel 的 [备份功能](../backup) 进行备份
|
||||
77
zh_CN/advanced/database.md
Normal file
77
zh_CN/advanced/database.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
数据库模块用于管理 MySQL、MariaDB、PostgreSQL 等数据库。 支持创建数据库、管理用户和配置数据库服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
使用数据库功能前,需要先安装数据库软件:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **应用** > **原生应用**
|
||||
2. 安装 Percona、MySQL、MariaDB 或 PostgreSQL
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能概览
|
||||
|
||||
数据库模块分为三个部分:
|
||||
|
||||
| 功能 | 说明 |
|
||||
| -------------------------- | ---------- |
|
||||
| [数据库](./database/database) | 创建和管理数据库 |
|
||||
| [用户](./database/user) | 管理数据库用户和权限 |
|
||||
| [服务器](./database/server) | 管理数据库服务器连接 |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 支持的数据库
|
||||
|
||||
| 数据库 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---------- | ---------------------- |
|
||||
| Percona | MySQL 的高性能分支,适合高负载场景 |
|
||||
| MySQL | 世界上最流行的开源关系型数据库 |
|
||||
| MariaDB | MySQL 的开源分支,完全兼容 MySQL |
|
||||
| PostgreSQL | 功能强大的开源对象关系型数据库 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 快速开始
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建数据库
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **数据库** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建数据库**
|
||||
3. 选择数据库类型和服务器
|
||||
4. 输入数据库名称
|
||||
5. 选择是否创建用户并设置权限
|
||||
6. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建用户
|
||||
|
||||
1. 切换到 **用户** 标签
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建用户**
|
||||
3. 输入用户名和密码
|
||||
4. 设置访问权限
|
||||
5. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
## 连接数据库
|
||||
|
||||
### 本地连接
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
主机:127.0.0.1 或 localhost
|
||||
端口:Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 3306,PostgreSQL 5432
|
||||
Socket:Percona/MySQL/MariaDB /tmp/mysql.sock,PostgreSQL /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程连接
|
||||
|
||||
如需远程连接数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在防火墙中开放数据库端口
|
||||
2. 创建允许远程访问的用户(主机设为 `%`)
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 安全提示
|
||||
不建议将数据库端口暴露到公网, 如需远程管理建议使用 SSH 隧道或 VPN。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [数据库管理](./database/database) - 了解如何创建和管理数据库
|
||||
- [用户管理](./database/user) - 了解如何管理数据库用户
|
||||
- [服务器管理](./database/server) - 了解如何管理数据库服务器
|
||||
58
zh_CN/advanced/database/database.md
Normal file
58
zh_CN/advanced/database/database.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
# 数据库管理
|
||||
|
||||
数据库管理页面用于创建、查看和删除数据库, AcePanel 已全面默认使用 UTF-8 编码创建数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据库列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **数据库** 页面,默认显示数据库列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **类型**:数据库类型(MySQL/PostgreSQL)
|
||||
- **数据库名称**:数据库名称
|
||||
- **服务器**:所属的数据库服务器
|
||||
- **编码**:字符编码
|
||||
- **注释**:备注信息(PostgreSQL 支持)
|
||||
- **操作**:删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建数据库
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建数据库** 按钮
|
||||
2. 填写配置:
|
||||
- **服务器**:选择数据库服务器
|
||||
- **数据库名称**:只能使用字母、数字和下划线
|
||||
3. 选择是否创建用户并设置权限(可选)
|
||||
4. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据库备份
|
||||
|
||||
点击数据库右侧的 **删除** 按钮删除数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
删除数据库会永久删除该数据库中的所有数据, 此操作不可恢复! 请务必提前备份重要数据。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据库命名规范
|
||||
|
||||
- 只能使用字母、数字和下划线
|
||||
- 不能以数字开头
|
||||
- 避免使用数据库保留字
|
||||
- 建议使用有意义的名称,如 `wordpress`、`myapp_production`
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建数据库失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查数据库名称是否符合命名规范
|
||||
- 检查是否已存在同名数据库
|
||||
- 检查数据库服务是否运行
|
||||
|
||||
### 数据库常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
如果出现乱码,检查:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 数据库编码是否正确
|
||||
2. 连接时是否指定了正确的编码
|
||||
3. 应用程序的编码设置
|
||||
86
zh_CN/advanced/database/server.md
Normal file
86
zh_CN/advanced/database/server.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
# 服务器管理
|
||||
|
||||
服务器管理页面用于管理数据库服务器连接,支持本地和远程数据库服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 服务器列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **数据库** > **服务器** 标签页查看服务器列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **类型**:数据库类型(MySQL/PostgreSQL)
|
||||
- **名称**:服务器名称
|
||||
- **用户名**:管理员用户名
|
||||
- **密码**:管理员密码
|
||||
- **主机**:服务器地址和端口
|
||||
- **注释**:备注信息
|
||||
- **状态**:连接状态
|
||||
- **更新日期**:最后更新时间
|
||||
- **操作**:终端、同步、修改、删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 本地服务器
|
||||
|
||||
安装数据库软件后,AcePanel 会自动添加本地服务器, 此类服务器不支持自行删除:
|
||||
|
||||
- **local_mysql**:本地 Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 服务器
|
||||
- **local_postgresql**:本地 PostgreSQL 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
## 添加远程服务器
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **添加服务器** 按钮
|
||||
2. 填写配置:
|
||||
- **类型**:选择数据库类型
|
||||
- **名称**:服务器名称(用于标识)
|
||||
- **主机**:服务器地址
|
||||
- **端口**:数据库端口
|
||||
- **用户名**:管理员用户名
|
||||
- **密码**:管理员密码
|
||||
3. 点击添加
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程服务器使用场景
|
||||
|
||||
- 连接云数据库(如阿里云 RDS、腾讯云 CDB)
|
||||
- 连接容器中的数据库服务
|
||||
- 连接其他服务器上的数据库
|
||||
- 数据库读写分离架构
|
||||
|
||||
## 服务器操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 终端
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **终端** 按钮打开数据库命令行终端,可以直接执行 SQL 语句。
|
||||
|
||||
### 同步
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **同步** 按钮同步数据库和用户信息。 当直接在数据库中创建了数据库或用户时,可以使用此功能同步到面板。
|
||||
|
||||
### 修改
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **修改** 按钮可以修改服务器连接信息,如密码、主机地址等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **删除** 按钮删除服务器配置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
删除服务器配置不会删除实际的数据库服务,只是从面板中移除该服务器的管理。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 连接测试
|
||||
|
||||
添加或修改服务器后,系统会自动测试连接。 如果连接失败,请检查:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 服务器地址和端口是否正确
|
||||
2. 用户名和密码是否正确
|
||||
3. 防火墙是否允许连接
|
||||
4. 数据库服务是否正常运行
|
||||
5. 数据库用户是否允许从当前主机连接
|
||||
|
||||
## 默认端口
|
||||
|
||||
| 数据库 | 默认端口 |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ---- |
|
||||
| Percona/MySQL/MariaDB | 3306 |
|
||||
| PostgreSQL | 5432 |
|
||||
83
zh_CN/advanced/database/user.md
Normal file
83
zh_CN/advanced/database/user.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
# 用户管理
|
||||
|
||||
用户管理页面用于创建和管理数据库用户,设置用户权限。
|
||||
|
||||
## 用户列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **数据库** > **用户** 标签页查看用户列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示所有面板用户的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **类型**:数据库类型
|
||||
- 用户名
|
||||
- 用户邮箱,用于找回密码等功能
|
||||
- **主机**:允许连接的主机
|
||||
- **服务器**:所属的数据库服务器
|
||||
- **权限**:用户拥有权限的数据库
|
||||
- **注释**:备注信息
|
||||
- **邮箱**:用户邮箱地址
|
||||
- **更新日期**:最后更新时间
|
||||
- **操作**:修改、删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建用户
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建用户** 按钮添加新用户:
|
||||
2. 填写配置:
|
||||
- **服务器**:选择数据库服务器
|
||||
- **用户名**:登录用户名
|
||||
- **密码**:登录密码
|
||||
- **主机**:允许连接的主机地址
|
||||
- **权限**:选择用户可以访问的数据库
|
||||
3. 创建时间
|
||||
|
||||
### 主机设置
|
||||
|
||||
| 值 | 说明 |
|
||||
| --------------- | ----------- |
|
||||
| `localhost` | 只允许本地连接 |
|
||||
| `127.0.0.1` | 只允许本地 IP 连接 |
|
||||
| `%` | 允许任意主机连接 |
|
||||
| `192.168.1.%` | 允许指定网段连接 |
|
||||
| `192.168.1.100` | 只允许指定 IP 连接 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 安全建议
|
||||
生产环境不建议使用 `%` 允许任意主机连接, 应限制为具体的 IP 地址或网段。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 用户操作
|
||||
|
||||
登录用户名,可直接在表格中修改
|
||||
|
||||
- 更改密码
|
||||
- 修改允许连接的主机
|
||||
- 修改数据库权限
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除用户
|
||||
|
||||
点击用户右侧的 **删除** 按钮删除用户。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
删除用户后,使用该用户连接数据库的应用将无法正常工作。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 权限说明
|
||||
|
||||
### Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 权限
|
||||
|
||||
创建用户时可以选择授予权限的数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
- 选择具体数据库:用户只能访问选中的数据库
|
||||
- 不选择:用户没有任何数据库权限
|
||||
|
||||
### PostgreSQL 权限
|
||||
|
||||
PostgreSQL 的权限管理更加细粒度, 可以自行针对数据库、模式、表等设置不同权限, 面板仅支持授予数据库访问权限。
|
||||
|
||||
## 密码安全
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用强密码,包含大小写字母、数字和特殊字符
|
||||
- 密码长度建议 16 位以上
|
||||
- 不同应用使用不同的数据库用户
|
||||
- 定期更换密码
|
||||
206
zh_CN/advanced/file.md
Normal file
206
zh_CN/advanced/file.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
|
||||
# 文件
|
||||
|
||||
文件模块提供了功能强大的图形化文件管理器, 设计理念是尽可能还原 Windows 资源管理器的操作体验,支持右键菜单、拖拽上传、快捷键等特性。
|
||||
|
||||
## 文件管理器
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 核心特性
|
||||
|
||||
### 类 Windows 操作体验
|
||||
|
||||
- **右键菜单**:右键点击文件或目录弹出操作菜单
|
||||
- **拖拽上传**:直接将本地文件拖拽到浏览器窗口即可上传
|
||||
- **多选操作**:支持 Ctrl+点击 多选,Shift+点击 范围选择
|
||||
- **快捷键支持**:常用操作都有对应的快捷键
|
||||
|
||||
### 快捷键
|
||||
|
||||
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
|
||||
| -------- | --- |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+C` | 复制 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+X` | 剪切 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+V` | 粘贴 |
|
||||
| `Delete` | 删除 |
|
||||
| `F2` | 重命名 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+A` | 全选 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 导航
|
||||
|
||||
### 路径导航
|
||||
|
||||
顶部显示当前路径的面包屑导航, 点击可以快速跳转到任意上级目录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 快捷按钮
|
||||
|
||||
- **后退**:返回上一个访问的目录
|
||||
- **前进**:前进到下一个目录
|
||||
- **上级目录**:返回上级目录
|
||||
- **刷新**:刷新当前目录
|
||||
- **主目录**:返回默认目录
|
||||
|
||||
## 文件列表
|
||||
|
||||
文件列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
| 列 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ----- | ------------------ |
|
||||
| 名称 | 文件或目录名称 |
|
||||
| 大小 | 文件大小,目录显示「计算」可点击计算 |
|
||||
| 权限 | 文件权限(如 0755) |
|
||||
| 所有者/组 | 文件的所有者和所属组 |
|
||||
| 修改时间 | 最后修改时间 |
|
||||
| 操作 | 打开、压缩、重命名、删除、更多 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择文件
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择文件后,顶部会显示批量操作按钮:
|
||||
|
||||
- **复制**:复制选中的文件
|
||||
- **移动**:移动选中的文件
|
||||
- **压缩**:压缩选中的文件
|
||||
- **权限**:修改权限
|
||||
- **删除**:删除选中的文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 更多操作
|
||||
|
||||
点击文件行的 **更多** 按钮,显示更多操作选项:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **复制**:复制文件到其他目录
|
||||
- **移动**:移动文件到其他目录
|
||||
- **权限**:修改文件权限和所有者
|
||||
- **压缩**:压缩文件
|
||||
- **复制路径**:复制文件的完整路径
|
||||
- **属性**:查看文件详细属性
|
||||
|
||||
## 工具栏
|
||||
|
||||
### 新建
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **新建** 按钮可以:
|
||||
|
||||
- 新建文件
|
||||
- 新建目录
|
||||
|
||||
### 上传
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **上传** 按钮上传本地文件到服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
支持的上传方式:
|
||||
|
||||
- 点击选择文件上传
|
||||
- **拖拽上传**:直接将文件拖拽到页面即可上传
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程下载
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **远程下载** 按钮,输入 URL 地址,将远程文件下载到当前目录。
|
||||
|
||||
适用场景:
|
||||
|
||||
- 下载软件安装包
|
||||
- 下载远程备份文件
|
||||
- 从其他服务器获取文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 搜索
|
||||
|
||||
在搜索框输入关键词搜索文件:
|
||||
|
||||
- 默认搜索当前目录
|
||||
- 勾选 **包括子目录** 可以递归搜索
|
||||
|
||||
### 终端
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **终端** 按钮可以在当前目录打开终端,方便执行命令行操作。
|
||||
|
||||
### 排序
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **排序** 按钮可以按不同字段排序文件列表。
|
||||
|
||||
## 文件编辑器
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 内置了功能强大的代码编辑器,基于 Monaco Editor(VS Code 同款编辑器内核)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 编辑器特性
|
||||
|
||||
- **语法高亮**:支持各种编程语言的语法高亮
|
||||
- **代码折叠**:支持代码块折叠
|
||||
- **行号显示**:显示行号,方便定位
|
||||
- **小地图**:右侧显示代码缩略图
|
||||
- **自动换行**:可切换自动换行模式
|
||||
- **多文件编辑**:支持同时打开多个文件,标签页切换
|
||||
|
||||
### 编辑器快捷键
|
||||
|
||||
| 快捷键 | 功能 |
|
||||
| -------------- | ------ |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+S` | 保存当前文件 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+Shift+S` | 保存所有文件 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+F` | 搜索 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+H` | 替换 |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+G` | 转到指定行 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 编辑器工具栏
|
||||
|
||||
- **保存**:保存当前文件
|
||||
- **保存所有**:保存所有修改的文件
|
||||
- **刷新**:重新加载文件内容
|
||||
- **搜索**:打开搜索面板
|
||||
- **替换**:打开替换面板
|
||||
- **转到**:跳转到指定行
|
||||
- **字体大小**:调整编辑器字体大小
|
||||
- **切换自动换行**:开启/关闭自动换行
|
||||
- **切换小地图**:显示/隐藏右侧小地图
|
||||
- **设置**:编辑器设置
|
||||
|
||||
### 全屏模式
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **最大化** 按钮可以全屏编辑,获得更大的编辑空间:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 侧边栏文件树
|
||||
|
||||
编辑器左侧显示当前目录的文件树,可以:
|
||||
|
||||
- 快速切换编辑其他文件
|
||||
- 新建文件
|
||||
- 搜索文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 状态栏
|
||||
|
||||
编辑器底部状态栏显示:
|
||||
|
||||
- 文件完整路径
|
||||
- 换行符类型(LF/CRLF)
|
||||
- 光标位置(行、列)
|
||||
- 缩进设置(空格/Tab)
|
||||
- 文件语言类型
|
||||
|
||||
## 权限说明
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 文件权限由三组数字表示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 权限 | 数字 | 说明 |
|
||||
| -- | -- | -- |
|
||||
| r | 4 | 读取 |
|
||||
| w | 2 | 写入 |
|
||||
| x | 1 | 执行 |
|
||||
|
||||
例如 `0755`:
|
||||
|
||||
- 所有者:7 (4+2+1) = 读+写+执行
|
||||
- 所属组:5 (4+1) = 读+执行
|
||||
- 其他用户:5 (4+1) = 读+执行
|
||||
|
||||
常用权限:
|
||||
|
||||
- `0644`:普通文件
|
||||
- `0755`:可执行文件和目录
|
||||
- `0600`:私密文件(如密钥)
|
||||
105
zh_CN/advanced/monitor.md
Normal file
105
zh_CN/advanced/monitor.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
# 监控
|
||||
|
||||
监控模块用于记录和查看服务器的性能数据,包括 CPU、内存、磁盘 I/O 和网络流量。
|
||||
|
||||
## 监控页面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 监控设置
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用监控
|
||||
|
||||
开启 **启用监控** 开关后,系统会定期采集性能数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### 保存天数
|
||||
|
||||
设置监控数据的保留时间,默认 30 天。 超过保留时间的数据会自动清理。
|
||||
|
||||
### 清除监控记录
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **清除监控记录** 按钮可以手动清除所有历史监控数据。
|
||||
|
||||
## 监控指标
|
||||
|
||||
### 负载(Load Average)
|
||||
|
||||
系统负载反映了 CPU 的繁忙程度:
|
||||
|
||||
- **1 分钟负载**:最近 1 分钟的平均负载
|
||||
- **5 分钟负载**:最近 5 分钟的平均负载
|
||||
- **15 分钟负载**:最近 15 分钟的平均负载
|
||||
|
||||
负载值的参考:
|
||||
|
||||
- 负载 < CPU 核心数:系统运行流畅
|
||||
- 负载 = CPU 核心数:系统满负荷运行
|
||||
- 负载 > CPU 核心数:系统过载,可能出现卡顿
|
||||
|
||||
### CPU 使用率
|
||||
|
||||
显示 CPU 的使用百分比,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用户态使用率
|
||||
- 系统态使用率
|
||||
- 空闲率
|
||||
|
||||
### 内存使用
|
||||
|
||||
显示内存的使用情况:
|
||||
|
||||
- 已使用内存
|
||||
- 可用内存
|
||||
- 缓存/缓冲区
|
||||
|
||||
### 磁盘 I/O
|
||||
|
||||
显示磁盘的读写速度:
|
||||
|
||||
- 读取速度(KB/s 或 MB/s)
|
||||
- 写入速度(KB/s 或 MB/s)
|
||||
|
||||
可以选择要监控的磁盘设备。
|
||||
|
||||
### 网络流量
|
||||
|
||||
显示网络接口的流量:
|
||||
|
||||
- 发送速度
|
||||
- 接收速度
|
||||
|
||||
可以选择要监控的网络接口。
|
||||
|
||||
## 时间范围
|
||||
|
||||
每个监控图表都支持选择时间范围:
|
||||
|
||||
- **昨天**:查看昨天的数据
|
||||
- **今天**:查看今天的数据
|
||||
- **近 7 天**:查看最近一周的数据
|
||||
- **自定义**:选择任意时间范围
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用场景
|
||||
|
||||
### 性能分析
|
||||
|
||||
通过监控数据分析服务器性能瓶颈:
|
||||
|
||||
- CPU 持续高负载:考虑优化程序或升级 CPU
|
||||
- 内存不足:考虑增加内存或优化内存使用
|
||||
- 磁盘 I/O 高:考虑使用 SSD 或优化数据库查询
|
||||
- 网络带宽不足:考虑升级带宽
|
||||
|
||||
### 故障排查
|
||||
|
||||
出现问题时,查看历史监控数据定位问题发生的时间和原因。
|
||||
|
||||
### 容量规划
|
||||
|
||||
根据历史数据趋势,预测未来的资源需求,提前进行扩容。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
- 监控数据会占用一定的磁盘空间
|
||||
- 保存天数越长,占用空间越大
|
||||
- 建议根据实际需求设置合适的保存天数
|
||||
156
zh_CN/advanced/project.md
Normal file
156
zh_CN/advanced/project.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
||||
# 项目
|
||||
|
||||
项目模块用于管理后端应用程序,支持 Go、Java、Node.js、PHP、Python 等多种语言。 项目会作为系统服务运行,支持自动重启、开机自启等功能。
|
||||
|
||||
## 项目类型
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 说明 | 适用场景 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------- | -------------------------- | ----------------------- |
|
||||
| [Go](./project/go) | Go 语言项目 | Gin、Echo、Fiber 等框架 |
|
||||
| [Java](./project/java) | Java 项目 | Spring Boot、Tomcat 等 |
|
||||
| [Node.js](./project/nodejs) | Node.js 项目 | Express、Koa、NestJS 等 |
|
||||
| [PHP](./project/php) | PHP 项目 | Laravel Octane、Swoole 等 |
|
||||
| [Python](./project/python) | Python 项目 | Django、Flask、FastAPI 等 |
|
||||
| [通用](./project/general) | 其他类型项目 | 任意可执行程序 |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 项目 vs 网站
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | 项目 | 网站 |
|
||||
| ---- | -------- | ----------- |
|
||||
| 运行方式 | 独立进程 | 依赖 Web 服务器 |
|
||||
| 进程管理 | 项目自动重启 | 由 Web 服务器管理 |
|
||||
| 适用场景 | 后端服务、API | 传统 Web 应用 |
|
||||
| 对外访问 | 反向代理配置 | 直接访问 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建项目
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **项目** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建项目**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **项目名**:项目标识,用作服务名称
|
||||
- **项目目录**:项目文件所在目录
|
||||
- **运行用户**:运行项目的系统用户,默认 www
|
||||
- **启动命令**:启动项目的命令
|
||||
- 创建项目时开启「反向代理」,会自动创建一个反向代理网站。
|
||||
|
||||
## 项目管理
|
||||
|
||||
项目列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:项目名称
|
||||
- **描述**:项目描述
|
||||
- **类型**:项目类型(Go/Java/Node.js 等)
|
||||
- **状态**:运行状态
|
||||
- **自启动**:是否开机自启
|
||||
- **目录**:项目目录
|
||||
- **操作**:启动、停止、重启、日志等
|
||||
|
||||
### 项目操作
|
||||
|
||||
- **启动**:启动项目
|
||||
- **停止**:停止项目
|
||||
- **重启**:重启项目
|
||||
- 查看项目日志
|
||||
- **编辑**:修改项目配置
|
||||
- **删除**:删除项目
|
||||
|
||||
## 编辑项目
|
||||
|
||||
点击项目列表中的 **编辑** 按钮,可以修改项目配置。 编辑对话框包含多个标签页:
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本设置
|
||||
|
||||
配置项目的基本信息:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **项目名**:项目标识,用作服务名称
|
||||
- **描述**:项目描述信息
|
||||
- **项目目录**:项目文件所在目录
|
||||
- **工作目录**:程序运行时的工作目录,默认为项目目录
|
||||
- **运行用户**:运行项目的系统用户
|
||||
|
||||
### 在「运行设置」中配置:
|
||||
|
||||
配置项目的运行参数:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **启动命令**:启动项目的命令
|
||||
- 预启动命令
|
||||
- **启动后命令**:启动后运行的命令(可选)
|
||||
- **停止命令**:自定义停止命令(可选)
|
||||
- **重载命令**:自定义重载命令(可选)
|
||||
- **重启策略**:失败时重启 / 总是重启 / 不重启
|
||||
- **重启间隔**:两次重启之间的等待时间
|
||||
- **最大重启次数**:防止无限重启
|
||||
- 在项目启动前执行,如安装依赖:
|
||||
- lsof -i:3000 # 查看占用端口的进程
|
||||
- **标准输出**:标准输出的处理方式
|
||||
- **标准错误**:标准错误的处理方式
|
||||
- **环境变量**:设置项目运行时的环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
### 依赖
|
||||
|
||||
配置服务依赖关系以控制启动顺序:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Requires**:强依赖,如果这些服务不可用,项目将会失败
|
||||
- **Wants**:弱依赖,如果这些服务失败,项目仍然会启动
|
||||
- **After**:在指定服务之后启动此项目
|
||||
- **Before**:在指定服务之前启动此项目
|
||||
|
||||
常见服务:`network.target`、`mysqld.service`、`postgresql.service`、`redis.service`
|
||||
|
||||
### 资源限制
|
||||
|
||||
设置资源限制以防止服务消耗过多系统资源:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **内存限制**:限制项目使用的最大内存,0 表示无限制
|
||||
- **CPU 配额**:限制 CPU 使用率,100% = 1 个 CPU 核心
|
||||
|
||||
### 安全设置
|
||||
|
||||
增强服务隔离的安全选项:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **没有新权限**:防止进程获取新的权限
|
||||
- **保护 /tmp**:为服务创建私有的 /tmp 目录
|
||||
- **保护 /home**:限制对 /home 目录的访问
|
||||
- **保护系统**:设置系统目录的只读保护级别
|
||||
- `true`:/usr、/boot 为只读
|
||||
- `full`:+ /etc 为只读
|
||||
- `strict`:整个文件系统为只读
|
||||
- **读写路径**:服务可以读写的路径
|
||||
- **只读路径**:服务只能读取的路径
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
安全设置可能会影响某些功能, 请在启用之前进行充分测试。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 进程管理
|
||||
|
||||
项目使用 systemd 进行进程管理,具有以下特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 项目启动失败
|
||||
- **开机自启**:系统启动时自动启动项目
|
||||
- **日志管理**:自动记录标准输出和错误输出
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [Go 项目](./project/go) - 部署 Go 应用
|
||||
- [Java 项目](./project/java) - 部署 Java 应用
|
||||
- [Node.js 项目](./project/nodejs) - 部署 Node.js 应用
|
||||
- [PHP 项目](./project/php) - 部署 PHP 应用
|
||||
- [Python 项目](./project/python) - 部署 Python 应用
|
||||
- [通用项目](./project/general) - 部署其他类型应用
|
||||
132
zh_CN/advanced/project/general.md
Normal file
132
zh_CN/advanced/project/general.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
# 通用项目
|
||||
|
||||
通用项目用于部署任意类型的可执行程序,不限于特定编程语言。
|
||||
|
||||
## 适用场景
|
||||
|
||||
- Rust 应用
|
||||
- C/C++ 应用
|
||||
- Shell 脚本
|
||||
- 其他编译型语言应用
|
||||
- 自定义启动脚本
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建通用项目
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **项目** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建项目**
|
||||
3. 填写配置:
|
||||
- **项目名**:项目标识
|
||||
- **项目目录**:可执行文件所在目录
|
||||
- **启动命令**:启动程序的命令
|
||||
4. 根据需要开启 **反向代理**
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust 应用
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 运行编译好的二进制文件
|
||||
./myapp
|
||||
|
||||
# 带参数运行
|
||||
./myapp --config config.toml --port 8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Shell 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 运行脚本
|
||||
/bin/bash start.sh
|
||||
|
||||
# 或直接运行(需要 shebang 和执行权限)
|
||||
./start.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 自定义启动脚本
|
||||
|
||||
创建 `start.sh`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
export ENV=production
|
||||
./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`/bin/bash start.sh`
|
||||
|
||||
## 环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
可以在启动命令中设置环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 单个环境变量
|
||||
ENV=production ./myapp
|
||||
|
||||
# 多个环境变量
|
||||
ENV=production PORT=8080 ./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或直接编辑项目,在 **运行设置** 中添加环境变量。
|
||||
|
||||
## 工作目录
|
||||
|
||||
项目会在指定的项目目录下运行,相对路径会基于该目录解析。
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要切换目录,可以在启动命令中使用 `cd`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp/bin && ./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 权限设置
|
||||
|
||||
确保可执行文件有执行权限:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
chmod +x myapp
|
||||
chmod +x start.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 运行用户
|
||||
|
||||
默认使用 `www` 用户运行项目。 如果程序需要特殊权限,可以选择其他用户。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
使用 root 用户运行可能带来安全风险,请谨慎选择。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 日志输出
|
||||
|
||||
程序的标准输出(stdout)和标准错误(stderr)会被记录到日志中,可以在项目管理页面查看。
|
||||
|
||||
建议程序将日志输出到标准输出,而非写入文件,便于统一管理。
|
||||
|
||||
## 信号处理
|
||||
|
||||
项目停止时会发送 SIGTERM 信号, 程序应正确处理该信号以实现优雅关闭:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// Rust 示例
|
||||
use signal_hook::{consts::SIGTERM, iterator::Signals};
|
||||
|
||||
fn main() {
|
||||
let mut signals = Signals::new(&[SIGTERM]).unwrap();
|
||||
// 处理 SIGTERM 信号
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// C 示例
|
||||
#include <signal.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void handle_sigterm(int sig) {
|
||||
// 清理资源
|
||||
exit(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
signal(SIGTERM, handle_sigterm);
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
120
zh_CN/advanced/project/go.md
Normal file
120
zh_CN/advanced/project/go.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
# Go 项目
|
||||
|
||||
Go 项目用于部署使用 Go 语言开发的后端应用,如 Gin、Echo、Fiber 等框架。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 Go 运行环境:**应用** > **运行环境** > **Go**
|
||||
2. 编译好的 Go 可执行文件或源代码
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署方式
|
||||
|
||||
### 方式一:部署编译好的二进制文件
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在本地编译 Go 项目:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 交叉编译为 Linux amd64
|
||||
GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 上传二进制文件到服务器
|
||||
3. 创建项目,启动命令填写:`./myapp`
|
||||
|
||||
### 方式二:在服务器上编译
|
||||
|
||||
1. 上传源代码到服务器
|
||||
2. 在终端中编译:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
go build -o myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 创建项目,启动命令填写:`./myapp`
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建 Go 项目
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **项目** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建项目**
|
||||
3. 填写配置:
|
||||
- **项目名**:`myapp`
|
||||
- **项目目录**:`/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **启动命令**:`./myapp` 或 `go1.24 run main.go`
|
||||
4. 开启 **反向代理** 以便外部访问
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 运行编译好的二进制文件
|
||||
./myapp
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用指定版本的 Go 运行
|
||||
go1.24 run main.go
|
||||
|
||||
# 带参数运行
|
||||
./myapp -port 8080 -config ./config.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置环境变量
|
||||
GIN_MODE=release ./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常用框架
|
||||
|
||||
### Gin
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
r := gin.Default()
|
||||
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
|
||||
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": "Hello"})
|
||||
})
|
||||
r.Run(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`GIN_MODE=release ./myapp`
|
||||
|
||||
### Echo
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
e := echo.New()
|
||||
e.GET("/", func(c echo.Context) error {
|
||||
return c.String(200, "Hello")
|
||||
})
|
||||
e.Start(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Fiber
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
app := fiber.New()
|
||||
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) error {
|
||||
return c.SendString("Hello")
|
||||
})
|
||||
app.Listen(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. 确保二进制文件有执行权限:`chmod +x myapp`
|
||||
2. 生产环境建议使用编译好的二进制文件,而非 `go run`
|
||||
3. 建议使用环境变量或配置文件管理配置,避免硬编码
|
||||
111
zh_CN/advanced/project/java.md
Normal file
111
zh_CN/advanced/project/java.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
# Java 项目
|
||||
|
||||
Java 项目用于部署 Spring Boot、Tomcat 等 Java 应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 Java 运行环境:**应用** > **运行环境** > **Java**(Corretto JDK)
|
||||
2. 打包好的 JAR 文件或 WAR 文件
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署 Spring Boot 应用
|
||||
|
||||
### 打包项目
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Maven
|
||||
mvn clean package -DskipTests
|
||||
|
||||
# Gradle
|
||||
./gradlew build -x test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 上传并部署
|
||||
|
||||
1. 上传 JAR 文件到服务器(如 `/opt/ace/project/myapp/app.jar`)
|
||||
2. 创建项目:
|
||||
- **项目名**:`myapp`
|
||||
- **项目目录**:`/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **启动命令**:`java21 -jar app.jar`
|
||||
3. 开启 **反向代理**
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 基本启动
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar
|
||||
|
||||
# 指定配置文件
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置 JVM 参数
|
||||
java21 -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -jar app.jar
|
||||
|
||||
# 指定端口
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar --server.port=8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## JVM 参数建议
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 生产环境推荐配置
|
||||
java21 \
|
||||
-Xms512m \
|
||||
-Xmx1024m \
|
||||
-XX:+UseG1GC \
|
||||
-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200 \
|
||||
-jar app.jar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
常用参数说明:
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | ----------- |
|
||||
| `-Xms` | 初始堆内存大小 |
|
||||
| `-Xmx` | 最大堆内存大小 |
|
||||
| `-XX:+UseG1GC` | 使用 G1 垃圾收集器 |
|
||||
| `-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis` | 最大 GC 停顿时间 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 多版本 JDK
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 支持安装多个 JDK 版本,路径如 `/opt/ace/server/java/{version}/bin/java`,已默认链接 `java{version}` 命令方便使用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 配置文件 `application.yml` 示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
server:
|
||||
port: 8080
|
||||
|
||||
spring:
|
||||
datasource:
|
||||
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
|
||||
username: root
|
||||
password: your_password
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 内存不足
|
||||
|
||||
增加 JVM 堆内存:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
java21 -Xms1g -Xmx2g -jar app.jar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 端口冲突
|
||||
|
||||
修改启动端口:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar --server.port=8081
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动慢
|
||||
|
||||
检查是否有外部依赖连接超时,或添加以下参数加速启动:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-XX:TieredStopAtLevel=1 -noverify
|
||||
```
|
||||
135
zh_CN/advanced/project/nodejs.md
Normal file
135
zh_CN/advanced/project/nodejs.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
# Node.js 项目
|
||||
|
||||
Node.js 项目用于部署 Express、Koa、NestJS、Next.js 等 Node.js 应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 Node.js 运行环境:**应用** > **运行环境** > **Node.js**
|
||||
2. 项目源代码
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署步骤
|
||||
|
||||
1. 上传项目代码到服务器
|
||||
2. 安装依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
npm24 install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 创建项目:
|
||||
- **项目名**:`myapp`
|
||||
- **项目目录**:`/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **启动命令**:`node24 app.js`
|
||||
4. 开启 **反向代理**
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 直接运行
|
||||
node24 app.js
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 npm scripts
|
||||
npm24 start
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 npm run
|
||||
npm24 run start:prod
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置环境变量
|
||||
NODE_ENV=production node24 app.js
|
||||
|
||||
# 指定端口
|
||||
PORT=3000 node24 app.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常用框架
|
||||
|
||||
### Express
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const express = require('express');
|
||||
const app = express();
|
||||
|
||||
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
|
||||
res.send('Hello World');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
app.listen(3000);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`node24 app.js`
|
||||
|
||||
### NestJS
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 构建
|
||||
npm24 run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`node24 dist/main.js`
|
||||
|
||||
### Next.js
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 构建
|
||||
npm24 run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`npm24 start`
|
||||
|
||||
### Nuxt.js
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 构建
|
||||
npm24 run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`node24 .output/server/index.mjs`
|
||||
|
||||
## 进程管理
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 使用 systemd 管理 Node.js 进程,自动处理:
|
||||
|
||||
- 进程崩溃自动重启
|
||||
- 开机自动启动
|
||||
- 日志记录
|
||||
|
||||
## 环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
推荐使用 `.env` 文件管理环境变量:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# .env
|
||||
NODE_ENV=production
|
||||
PORT=3000
|
||||
DATABASE_URL=mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `dotenv` 包加载:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
require('dotenv').config();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 依赖安装失败
|
||||
|
||||
尝试清除缓存重新安装:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json
|
||||
npm24 install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 内存不足
|
||||
|
||||
增加 Node.js 内存限制:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096" node24 app.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 端口被占用
|
||||
|
||||
修改应用监听的端口,或检查是否有其他进程占用。
|
||||
97
zh_CN/advanced/project/php.md
Normal file
97
zh_CN/advanced/project/php.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
# PHP 网站
|
||||
|
||||
PHP 网站用于运行 PHP 程序,如 WordPress、Laravel、ThinkPHP 等。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 警告
|
||||
传统的 PHP-FPM 应用(如 WordPress、Laravel)应使用 [PHP 网站](../website/php) 方式部署,而非项目。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 适用场景
|
||||
|
||||
- Laravel Octane(Swoole/RoadRunner)
|
||||
- Swoole 应用
|
||||
- Workerman 应用
|
||||
- ReactPHP 应用
|
||||
- 其他需要常驻进程的 PHP 应用
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
1. **PHP 运行环境**:在 **应用** > **运行环境** 中安装所需的 PHP 版本
|
||||
2. 根据需要安装 Swoole 等模块
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署 Laravel Octane
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建项目
|
||||
|
||||
1. 创建项目:
|
||||
- **项目名**:`myapp`
|
||||
- **项目目录**:`/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **启动命令**:`php84 artisan octane:start --host=0.0.0.0 --port=8000`
|
||||
2. 开启 **反向代理**
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Laravel Octane (Swoole)
|
||||
php84 artisan octane:start --host=0.0.0.0 --port=8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Laravel Octane (RoadRunner)
|
||||
php84 artisan octane:start --server=roadrunner --host=0.0.0.0 --port=8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Swoole HTTP Server
|
||||
php84 server.php
|
||||
|
||||
# Workerman
|
||||
php84 start.php start
|
||||
|
||||
# Laravel Queue Worker
|
||||
php84 artisan queue:work --daemon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Swoole 应用示例
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
$server = new Swoole\HTTP\Server("0.0.0.0", 9501);
|
||||
|
||||
$server->on("request", function ($request, $response) {
|
||||
$response->header("Content-Type", "text/plain");
|
||||
$response->end("Hello World");
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
$server->start();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`php84 server.php`
|
||||
|
||||
## Workerman 应用示例
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
|
||||
|
||||
use Workerman\Worker;
|
||||
|
||||
$worker = new Worker("http://0.0.0.0:8080");
|
||||
$worker->onMessage = function($connection, $request) {
|
||||
$connection->send("Hello World");
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Worker::runAll();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:`php84 start.php start`
|
||||
|
||||
## 队列处理
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel 队列 Worker 也可以作为项目运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
php84 artisan queue:work --daemon --tries=3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意
|
||||
|
||||
1. 常驻进程的 PHP 应用需要注意内存泄漏问题
|
||||
2. 代码更新后需要重启项目才能生效
|
||||
3. 建议配置进程监控,异常时自动重启
|
||||
149
zh_CN/advanced/project/python.md
Normal file
149
zh_CN/advanced/project/python.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
# Python 项目
|
||||
|
||||
Python 项目用于部署 Django、Flask、FastAPI 等 Python Web 应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 Python 运行环境:**应用** > **运行环境** > **Python**
|
||||
2. 项目源代码
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署步骤
|
||||
|
||||
1. 上传项目代码到服务器
|
||||
2. 创建虚拟环境并安装依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
python3.13 -m venv venv
|
||||
source venv/bin/activate
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 创建项目:
|
||||
- **项目名**:`myapp`
|
||||
- **项目目录**:`/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **启动命令**:见下方示例
|
||||
4. 开启 **反向代理**
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
### Django
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 开发服务器(不推荐生产使用)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 Gunicorn(推荐)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn myproject.wsgi:application -b 0.0.0.0:8000 -w 4
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 uWSGI
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/uwsgi --http 0.0.0.0:8000 --module myproject.wsgi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Flask
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 开发服务器(不推荐生产使用)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/python app.py
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 Gunicorn(推荐)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn app:app -b 0.0.0.0:8000 -w 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 使用 Uvicorn
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 Gunicorn + Uvicorn Workers(推荐)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn main:app -b 0.0.0.0:8000 -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常用框架配置
|
||||
|
||||
### Django 生产配置
|
||||
|
||||
`settings.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
DEBUG = False
|
||||
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['your-domain.com']
|
||||
STATIC_ROOT = '/opt/ace/project/myapp/static/'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
收集静态文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/python manage.py collectstatic
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### FastAPI 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Gunicorn 配置
|
||||
|
||||
创建 `gunicorn.conf.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bind = "0.0.0.0:8000"
|
||||
workers = 4
|
||||
worker_class = "sync" # 或 "uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker" for FastAPI
|
||||
timeout = 30
|
||||
keepalive = 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn -c gunicorn.conf.py myproject.wsgi:application
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 虚拟环境
|
||||
|
||||
强烈建议使用虚拟环境隔离项目依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 创建虚拟环境
|
||||
python3.13 -m venv venv
|
||||
|
||||
# 激活虚拟环境
|
||||
source venv/bin/activate
|
||||
|
||||
# 安装依赖
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# 退出虚拟环境
|
||||
deactivate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 依赖安装失败
|
||||
|
||||
某些包需要编译,确保安装了必要的系统依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# AlmaLinux/Rocky Linux
|
||||
yum install gcc python3-devel
|
||||
|
||||
# Ubuntu/Debian
|
||||
apt install gcc python3-dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 静态文件 404
|
||||
|
||||
Django 生产环境需要配置 Nginx 直接提供静态文件,或使用 WhiteNoise。
|
||||
|
||||
### 数据库连接问题
|
||||
|
||||
检查数据库配置和网络连接,确保数据库服务正常运行。
|
||||
29
zh_CN/advanced/security.md
Normal file
29
zh_CN/advanced/security.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
# 安全建议
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站安全
|
||||
|
||||
大多数入侵和挂马事件源于程序漏洞,与面板或环境无关。
|
||||
|
||||
- 不使用盗版程序,因为无法确认是否被篡改
|
||||
- 及时更新网站程序和运行环境
|
||||
- 后台密码使用随机生成的 20 位以上混合字符,启用两步验证
|
||||
- 配置定时备份
|
||||
- 保留 PHP 默认禁用的高危函数(`disable_functions`)
|
||||
|
||||
## 系统安全
|
||||
|
||||
- 定期更新系统:`dnf update` 或 `apt upgrade`
|
||||
- SSH 禁用默认 22 端口,使用强密码或密钥认证
|
||||
- 安装 Fail2ban 防止暴力破解
|
||||
- 不随意设置 777 权限或给 www 用户执行权限
|
||||
- 有 VNC 的情况下可考虑关闭 SSH
|
||||
|
||||
## 面板安全
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 拥有 root 权限,需重点保护。
|
||||
|
||||
- 保持面板和应用更新
|
||||
- 修改默认端口,使用强密码
|
||||
- 启用安全入口,开启 HTTPS
|
||||
- 内部服务端口(Redis 6379、MySQL 3306、PostgreSQL 5432 等) 不要对外开放
|
||||
- 高安全要求场景可在不使用时停止面板进程,不影响已部署的服务
|
||||
58
zh_CN/advanced/setting/basic.md
Normal file
58
zh_CN/advanced/setting/basic.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
# 基本设置
|
||||
|
||||
基本设置页面用于配置面板的基础参数。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 面板名称
|
||||
|
||||
自定义面板显示的名称,默认为「AcePanel」。 修改后刷新页面会显示在浏览器标题和面板左上角。
|
||||
|
||||
## 语言
|
||||
|
||||
选择面板界面语言:
|
||||
|
||||
- 简体中文
|
||||
- 繁体中文
|
||||
- English
|
||||
|
||||
## 更新渠道
|
||||
|
||||
选择面板更新的版本渠道:
|
||||
|
||||
- **稳定版**:经过充分测试的正式版本,推荐生产环境使用
|
||||
- **测试版**:包含最新功能但可能存在问题,适合尝鲜用户
|
||||
|
||||
## 端口
|
||||
|
||||
面板的访问端口,默认为 8888。 修改端口后需要:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 确保新端口未被占用
|
||||
2. 在服务器安全组中开放新端口
|
||||
3. 保存后面板会自动重启
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
修改端口前请确保服务器安全组已开放新端口,否则可能无法访问面板。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 默认目录
|
||||
|
||||
配置各类资源的默认存储路径:
|
||||
|
||||
| 设置项 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ------ | ----------------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 默认网站目录 | /opt/ace/sites | 网站文件存放目录 |
|
||||
| 默认备份目录 | /opt/ace/backup | 备份文件存放目录 |
|
||||
| 默认项目目录 | /opt/ace/projects | 项目文件存放目录 |
|
||||
|
||||
修改目录后,新创建的网站/备份/项目会使用新目录,已有的不受影响。
|
||||
|
||||
## 自定义 Logo
|
||||
|
||||
输入图片的完整 URL 地址,可以替换面板左上角的 Logo。 支持 PNG、JPG、SVG 等格式。
|
||||
|
||||
## 隐藏菜单
|
||||
|
||||
选择要隐藏的菜单项。 隐藏后的菜单不会显示在左侧导航栏中,但功能仍然可用(通过直接访问 URL)。
|
||||
|
||||
适用于简化界面或限制普通用户可见的功能范围。
|
||||
101
zh_CN/advanced/setting/safe.md
Normal file
101
zh_CN/advanced/setting/safe.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
# 安全设置
|
||||
|
||||
安全设置页面用于配置面板的安全相关选项,保护面板免受未授权访问。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 登录超时
|
||||
|
||||
设置登录会话的有效时间,单位为分钟。 超过该时间未操作将自动退出登录,需要重新认证。
|
||||
|
||||
默认值为 120 分钟。
|
||||
|
||||
## 访问入口
|
||||
|
||||
设置面板的访问路径, 设置访问入口后需要通过 `https://IP:端口/入口路径` 才能访问。
|
||||
|
||||
例如设置为 `/admin`,则访问地址变为 `https://IP:端口/admin`。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个简单但有效的安全措施,可以防止面板被扫描器发现。
|
||||
|
||||
## 入口错误页
|
||||
|
||||
当访问错误的入口路径时返回的 HTTP 状态码:
|
||||
|
||||
- **418 I'm a teapot**:返回一个有趣的错误码与错误页
|
||||
- **Nginx 404**:返回 Nginx 同款 404 页面
|
||||
- **关闭连接**:直接关闭连接不返回任何内容
|
||||
|
||||
## 登录验证码
|
||||
|
||||
开启后登录时多次输入错误密码会触发验证码,防止暴力破解。
|
||||
|
||||
## 请求 IP 头
|
||||
|
||||
当面板部署在反向代理(如 Nginx、CDN)后面时,需要设置正确的 IP 头才能获取真实的客户端 IP。
|
||||
|
||||
常用值:
|
||||
|
||||
- `X-Real-IP`:Nginx 默认使用
|
||||
- `X-Forwarded-For`:标准代理头
|
||||
- `CF-Connecting-IP`:Cloudflare 使用
|
||||
|
||||
## 绑定域名
|
||||
|
||||
限制只能通过指定域名访问面板。 添加域名后,通过 IP 或其他域名将无法访问。
|
||||
|
||||
适用于:
|
||||
|
||||
- 提高安全性
|
||||
- 配合 SSL 证书使用
|
||||
|
||||
## 绑定 IP
|
||||
|
||||
限制只能从指定 IP 地址访问面板。 可以添加多个 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
适用于:
|
||||
|
||||
- 固定办公网络
|
||||
- 跳板机访问
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
绑定 IP 前请确保你的 IP 地址是固定的,否则可能导致无法访问面板。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 绑定 UA
|
||||
|
||||
限制只能使用指定 User-Agent 的浏览器访问面板。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个高级安全选项,可以配合自定义浏览器插件使用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 离线模式
|
||||
|
||||
开启后面板将不会连接外部网络,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查更新
|
||||
- 下载应用
|
||||
- 同步缓存数据
|
||||
|
||||
适用于内网环境或有严格网络限制的场景。
|
||||
|
||||
## 自动更新
|
||||
|
||||
开启后面板会每日自动检查并安装更新。 建议保持开启以获取最新的安全修复。
|
||||
|
||||
## 面板 HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
为面板启用 HTTPS 加密访问:
|
||||
|
||||
- **禁用**:使用 HTTP 访问
|
||||
- **ACME(自动)**:自动申请和续签 Let's Encrypt 证书,需要 IP 支持 80 端口访问
|
||||
- **自定义证书**:使用自己的 SSL 证书
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 推荐
|
||||
生产环境建议启用 HTTPS,保护登录凭据和敏感数据的传输安全。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 面板公网 IP
|
||||
|
||||
配置面板的公网 IP 地址,目前主要用于向 Let's Encrypt 申请 IP 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
支持 IPv4 和 IPv6 地址。
|
||||
74
zh_CN/advanced/setting/user.md
Normal file
74
zh_CN/advanced/setting/user.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
# 用户管理
|
||||
|
||||
用户管理页面用于管理面板的登录用户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 用户列表
|
||||
|
||||
列表显示所有面板用户的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
| 字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---- | --------------- |
|
||||
| 用户名 | 登录用户名,可直接在表格中修改 |
|
||||
| 邮箱 | 用户邮箱,用于找回密码等功能 |
|
||||
| 两步验证 | 是否启用 TOTP 两步验证 |
|
||||
| 创建时间 | 用户创建时间 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建用户
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **创建用户** 按钮添加新用户:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
填写以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **用户名**:登录用户名
|
||||
- **密码**:登录密码
|
||||
- **邮箱**:用户邮箱地址
|
||||
|
||||
## 用户操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 访问令牌
|
||||
|
||||
生成 API 访问令牌,用于通过 API 接口访问面板功能。
|
||||
|
||||
令牌具有与用户相同的权限,请妥善保管。
|
||||
|
||||
### 更改密码
|
||||
|
||||
修改用户的登录密码。 建议定期更换密码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除用户
|
||||
|
||||
删除用户账号。 删除后该用户将无法登录面板。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
至少需要保留一个用户,无法删除最后一个用户。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 两步验证
|
||||
|
||||
两步验证(2FA)为账号提供额外的安全保护。 启用后登录时除了密码还需要输入动态验证码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用两步验证
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击两步验证开关
|
||||
2. 使用 Google Authenticator、Microsoft Authenticator 等应用扫描二维码
|
||||
3. 输入应用显示的 6 位验证码确认
|
||||
|
||||
### 支持的验证器应用
|
||||
|
||||
- Google Authenticator
|
||||
- Microsoft Authenticator
|
||||
- Authy
|
||||
- 1Password
|
||||
- 其他支持 TOTP 的应用
|
||||
|
||||
## 安全建议
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用强密码,包含大小写字母、数字和特殊字符
|
||||
2. 启用两步验证
|
||||
3. 定期更换密码
|
||||
4. 不要共享账号
|
||||
5. 及时删除不再使用的账号
|
||||
96
zh_CN/advanced/ssh.md
Normal file
96
zh_CN/advanced/ssh.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
# 终端
|
||||
|
||||
终端模块提供了基于 Web 的 SSH 终端,可以直接在浏览器中连接服务器执行命令。
|
||||
|
||||
## 终端页面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 创建主机
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **创建主机** 按钮添加 SSH 连接:
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:连接名称,用于标识
|
||||
- **主机**:服务器 IP 地址或域名
|
||||
- **端口**:SSH 端口,默认 22
|
||||
- **认证方式**:密码或密钥
|
||||
- **用户名**:SSH 用户名
|
||||
- **密码/密钥**:认证凭证
|
||||
- **备注**:可选备注
|
||||
|
||||
### 认证方式
|
||||
|
||||
| 方式 | 说明 |
|
||||
| -- | ----------- |
|
||||
| 密码 | 使用用户名和密码认证 |
|
||||
| 密钥 | 使用 SSH 私钥认证 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 推荐
|
||||
生产环境建议使用密钥认证,更加安全。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 连接服务器
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在左侧主机列表中选择要连接的主机
|
||||
2. 点击主机名称打开终端
|
||||
3. 开始执行命令
|
||||
|
||||
## 终端功能
|
||||
|
||||
### 多标签
|
||||
|
||||
支持同时打开多个终端标签,方便在多个会话间切换。
|
||||
|
||||
### 复制粘贴
|
||||
|
||||
- **复制**:选中文本后自动复制,或使用 `Ctrl+Shift+C`
|
||||
- **粘贴**:右键粘贴,或使用 `Ctrl+Shift+V`
|
||||
|
||||
### 全屏模式
|
||||
|
||||
点击全屏按钮可以进入全屏模式,获得更大的终端空间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 字体设置
|
||||
|
||||
可以调整终端的字体大小和字体类型。
|
||||
|
||||
## 本地终端
|
||||
|
||||
默认会显示本地服务器的终端连接,可以直接连接到当前服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 远程主机
|
||||
|
||||
可以添加多个远程主机,方便管理多台服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **创建主机**
|
||||
2. 填写远程服务器信息
|
||||
3. 保存后在列表中选择连接
|
||||
|
||||
## 安全建议
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用强密码或密钥认证
|
||||
2. 修改默认 SSH 端口
|
||||
3. 限制 SSH 访问的 IP 地址
|
||||
4. 定期更换密码或密钥
|
||||
5. 使用非 root 用户登录
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 连接超时
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查服务器 IP 和端口是否正确
|
||||
- 检查防火墙是否允许 SSH 连接
|
||||
- 检查 SSH 服务是否正常运行
|
||||
|
||||
### 认证失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查用户名和密码是否正确
|
||||
- 检查密钥格式是否正确
|
||||
- 检查用户是否有 SSH 登录权限
|
||||
|
||||
### 中文乱码
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查服务器的 locale 设置
|
||||
- 确保服务器编码为 UTF-8
|
||||
89
zh_CN/advanced/task/panel.md
Normal file
89
zh_CN/advanced/task/panel.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
# 面板任务
|
||||
|
||||
面板任务显示 AcePanel 执行的后台任务,如应用安装、环境安装等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 任务列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **任务** > **面板任务** 标签页查看面板任务列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **任务名称**:任务描述
|
||||
- **状态**:运行中/已完成/失败
|
||||
- **创建时间**:任务开始时间
|
||||
- **完成时间**:任务结束时间
|
||||
- **操作**:查看日志、删除
|
||||
|
||||
## 任务状态
|
||||
|
||||
| 状态 | 说明 |
|
||||
| --- | ------ |
|
||||
| 运行中 | 任务正在执行 |
|
||||
| 已完成 | 任务执行成功 |
|
||||
| 失败 | 任务执行失败 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见任务类型
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用安装
|
||||
|
||||
安装原生应用时会创建安装任务:
|
||||
|
||||
- 安装应用 Nginx
|
||||
- 安装应用 MySQL
|
||||
- 安装应用 Docker
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用卸载
|
||||
|
||||
卸载应用时会创建卸载任务:
|
||||
|
||||
- 卸载应用 MariaDB
|
||||
- 卸载应用 Redis
|
||||
|
||||
### 环境安装
|
||||
|
||||
安装运行环境时会创建安装任务:
|
||||
|
||||
- 安装环境 PHP 8.4
|
||||
- 安装环境 Node.js 20
|
||||
- 安装环境 Go 1.24
|
||||
|
||||
## 查看日志
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **日志** 按钮查看任务的详细执行日志,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令输出
|
||||
- 错误信息
|
||||
|
||||
日志对于排查任务失败原因非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除任务
|
||||
|
||||
已完成或失败的任务可以删除。 运行中的任务无法删除。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
删除任务只是从列表中移除记录,不会影响已安装的应用或环境。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 任务失败处理
|
||||
|
||||
如果无法启动,尝试修复:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **日志** 查看错误信息
|
||||
2. 根据错误信息排查问题
|
||||
3. 解决问题后重新执行操作
|
||||
|
||||
常见失败原因:
|
||||
|
||||
- 网络问题导致下载失败
|
||||
- 磁盘空间不足
|
||||
- 依赖包缺失
|
||||
- 端口被占用
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装任务可能需要较长时间,请耐心等待
|
||||
2. 任务执行期间可以关闭浏览器
|
||||
3. 如果任务长时间无响应,可以刷新页面查看状态
|
||||
4. 建议定期清理已完成的任务记录
|
||||
118
zh_CN/advanced/task/schedule.md
Normal file
118
zh_CN/advanced/task/schedule.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
|
||||
# 计划任务
|
||||
|
||||
计划任务用于设置定时执行的任务,如定时备份、定时执行脚本等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 任务列表
|
||||
|
||||
进入 **任务** 页面,默认显示计划任务列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **任务名称**:任务名称
|
||||
- **任务类型**:Shell/备份等
|
||||
- **已启用**:是否启用
|
||||
- **任务周期**:执行周期
|
||||
- **创建时间**:创建时间
|
||||
- **最后更新时间**:最后执行时间
|
||||
- **操作**:编辑、执行、删除等
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建任务
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **创建任务** 按钮创建新的计划任务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 任务类型
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ----- | -------------- |
|
||||
| 运行脚本 | 执行 Shell 命令或脚本 |
|
||||
| 备份网站 | 定时备份网站文件 |
|
||||
| 备份数据库 | 定时备份数据库 |
|
||||
| 日志切割 | 定时切割日志文件 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 执行周期
|
||||
|
||||
支持多种周期设置:
|
||||
|
||||
- **每分钟**:每分钟执行一次
|
||||
- **每小时**:每小时执行一次
|
||||
- **每天**:每天指定时间执行
|
||||
- **每周**:每周指定日期和时间执行
|
||||
- **每月**:每月指定日期和时间执行
|
||||
- **自定义**:使用 Cron 表达式
|
||||
|
||||
### Cron 表达式
|
||||
|
||||
Cron 表达式格式:`分 时 日 月 周`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
* * * * *
|
||||
│ │ │ │ │
|
||||
│ │ │ │ └── 周几 (0-7, 0和7都是周日)
|
||||
│ │ │ └─────── 月份 (1-12)
|
||||
│ │ └──────────── 日期 (1-31)
|
||||
│ └───────────────── 小时 (0-23)
|
||||
└────────────────────── 分钟 (0-59)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
常用示例:
|
||||
|
||||
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------- |
|
||||
| `0 2 * * *` | 每天凌晨 2 点 |
|
||||
| `0 */6 * * *` | 每 6 小时 |
|
||||
| `0 0 * * 0` | 每周日凌晨 |
|
||||
| `0 0 1 * *` | 每月 1 号凌晨 |
|
||||
| `*/5 * * * *` | 每 5 分钟 |
|
||||
|
||||
不会写? 直接找个 AI 描述清楚需求让它帮你生成一个。
|
||||
|
||||
## Shell 任务示例
|
||||
|
||||
### 清理临时文件
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
find /tmp -type f -mtime +7 -delete
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 重启服务
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
systemctl restart nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 同步时间
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 任务操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用/禁用
|
||||
|
||||
通过开关控制任务是否启用。 禁用的任务不会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 立即执行
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **运行** 按钮可以立即执行任务,不等待计划时间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 查看日志
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **日志** 按钮查看任务的执行日志。
|
||||
|
||||
### 编辑任务
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **编辑** 按钮修改任务配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除任务
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **删除** 按钮删除任务。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. 任务执行时间基于服务器时区
|
||||
2. 长时间运行的任务可能影响下次执行
|
||||
3. 建议为重要任务设置通知提醒
|
||||
4. 定期检查任务执行状态
|
||||
27
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox.md
Normal file
27
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
# 工具箱
|
||||
|
||||
工具箱提供了一系列系统管理工具,包括进程管理、系统信息、SSH 配置、磁盘管理等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能列表
|
||||
|
||||
| 功能 | 说明 |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------- |
|
||||
| [进程](./toolbox/process) | 查看和管理系统进程 |
|
||||
| [系统](./toolbox/system) | 查看系统信息和配置 |
|
||||
| [SSH](./toolbox/ssh) | SSH 服务配置 |
|
||||
| [磁盘](./toolbox/disk) | 磁盘使用情况和管理 |
|
||||
| [日志清理](./toolbox/log) | 清理系统日志 |
|
||||
| [Web 钩子](./toolbox/webhook) | 配置 Webhook 通知 |
|
||||
| [跑分](./toolbox/benchmark) | 服务器性能测试 |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [进程管理](./toolbox/process) - 查看和管理系统进程
|
||||
- [系统信息](./toolbox/system) - 查看系统配置
|
||||
- [SSH 配置](./toolbox/ssh) - 配置 SSH 服务
|
||||
- [磁盘管理](./toolbox/disk) - 管理磁盘空间
|
||||
- [日志清理](./toolbox/log) - 清理系统日志
|
||||
- [Web 钩子](./toolbox/webhook) - 配置通知
|
||||
- [跑分测试](./toolbox/benchmark) - 测试服务器性能
|
||||
46
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/benchmark.md
Normal file
46
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/benchmark.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
# 跑分测试
|
||||
|
||||
跑分功能用于测试服务器的 CPU、内存和磁盘性能,帮助你了解服务器的实际性能表现。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 测试项目
|
||||
|
||||
### CPU 测试
|
||||
|
||||
测试 CPU 的计算能力,通过执行大量数学运算来评估处理器性能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 内存测试
|
||||
|
||||
测试内存的读写速度,评估内存子系统的性能表现。
|
||||
|
||||
### 磁盘测试
|
||||
|
||||
测试磁盘的读写速度,评估存储设备的 I/O 性能。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用方法
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **开始跑分** 按钮,系统会依次执行 CPU、内存和磁盘测试。 测试完成后会显示各项得分。
|
||||
|
||||
## 结果说明
|
||||
|
||||
跑分结果以数值形式展示,数值越高表示性能越好。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
跑分结果仅供参考。 由于系统资源调度、缓存和其他因素的影响,测试结果可能与实际使用中的性能有所差异。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试建议
|
||||
|
||||
1. 测试前关闭不必要的服务和进程
|
||||
2. 避免在业务高峰期进行测试
|
||||
3. 多次测试取平均值更准确
|
||||
4. 不同时间段的测试结果可能有波动
|
||||
|
||||
## 性能优化参考
|
||||
|
||||
如果跑分结果不理想,可以考虑:
|
||||
|
||||
- **CPU 性能低**:检查是否有进程占用过高 CPU
|
||||
- **内存性能低**:检查内存使用情况,是否存在内存泄漏
|
||||
- **磁盘性能低**:检查磁盘健康状态,考虑升级到 SSD
|
||||
120
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/disk.md
Normal file
120
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/disk.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
# 磁盘
|
||||
|
||||
磁盘页面提供磁盘分区管理和 LVM 逻辑卷管理功能。
|
||||
|
||||
## 磁盘管理
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 磁盘信息
|
||||
|
||||
页面顶部显示每个磁盘的基本信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **磁盘名**:如 vda、sda
|
||||
- **类型**:系统盘或数据盘
|
||||
- **大小**:磁盘总容量
|
||||
- **分区数**:分区数量
|
||||
- **磁盘类型**:HDD、SSD 等
|
||||
|
||||
### 分区列表
|
||||
|
||||
每个磁盘下显示其分区信息:
|
||||
|
||||
| 列 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------------ |
|
||||
| 分区名 | 分区设备名,如 vda1、vda2 |
|
||||
| 大小 | 分区容量 |
|
||||
| 已用 | 已使用空间 |
|
||||
| 可用 | 可用空间 |
|
||||
| 使用率 | 使用百分比 |
|
||||
| 挂载点 | 挂载目录,如 `/`、`/data` |
|
||||
| 文件系统 | 文件系统类型,如 ext4、xfs |
|
||||
| 操作 | 卸载等操作 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 挂载分区
|
||||
|
||||
将未挂载的分区挂载到指定目录:
|
||||
|
||||
- **分区**:选择要挂载的分区
|
||||
- **挂载路径**:挂载目录,如 `/mnt/data`
|
||||
- **挂载选项**:挂载参数,如 `defaults,noatime`
|
||||
- **启动时自动挂载**:是否写入 fstab 开机自动挂载
|
||||
|
||||
### 格式化分区
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
格式化将清除分区上的所有数据!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
- **分区**:选择要格式化的分区
|
||||
- **文件系统类型**:ext4、xfs、btrfs 等
|
||||
|
||||
### 初始化磁盘
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
初始化将删除磁盘上的所有分区和数据!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
将整个磁盘初始化为单个分区:
|
||||
|
||||
- **磁盘**:选择要初始化的磁盘
|
||||
- **文件系统类型**:ext4、xfs、btrfs 等
|
||||
|
||||
### 自动挂载配置(fstab)
|
||||
|
||||
显示 `/etc/fstab` 中的挂载配置:
|
||||
|
||||
- **设备**:设备名或 UUID
|
||||
- **挂载点**:挂载目录
|
||||
- **文件系统**:文件系统类型
|
||||
- **选项**:挂载选项
|
||||
- **操作**:移除配置
|
||||
|
||||
## LVM 管理
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
LVM(Logical Volume Manager)提供灵活的磁盘空间管理,支持动态调整分区大小。
|
||||
|
||||
### 物理卷(PV)
|
||||
|
||||
物理卷是 LVM 的基础,通常是一个磁盘分区或整个磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
**创建物理卷**:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 选择设备(未使用的分区或磁盘)
|
||||
2. 点击 **创建物理卷**
|
||||
|
||||
### 卷组(VG)
|
||||
|
||||
卷组由一个或多个物理卷组成,是存储池的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
**创建卷组**:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 输入卷组名
|
||||
2. 选择要加入的物理卷
|
||||
3. 点击 **创建卷组**
|
||||
|
||||
### 逻辑卷(LV)
|
||||
|
||||
逻辑卷从卷组中分配空间,相当于传统的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
**创建逻辑卷**:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 输入逻辑卷名
|
||||
2. 选择卷组
|
||||
3. 设置大小(GB)
|
||||
4. 点击 **创建逻辑卷**
|
||||
|
||||
### 扩展逻辑卷
|
||||
|
||||
动态扩展逻辑卷的大小:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 选择要扩展的逻辑卷
|
||||
2. 输入扩展大小(GB)
|
||||
3. 勾选 **自动调整文件系统大小**(推荐)
|
||||
4. 点击 **扩展逻辑卷**
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
LVM 的优势在于可以在线扩展逻辑卷,无需卸载分区或重启系统。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
79
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/log.md
Normal file
79
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/log.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
# 日志清理
|
||||
|
||||
日志清理功能用于扫描和清理系统及应用产生的日志文件,释放磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 功能概览
|
||||
|
||||
页面顶部提供批量操作按钮:
|
||||
|
||||
- **扫描所有**:扫描所有类型的日志
|
||||
- **清理所有**:清理所有已扫描的日志
|
||||
|
||||
## 日志类型
|
||||
|
||||
### 面板日志
|
||||
|
||||
面板运行产生的日志文件。
|
||||
|
||||
- 点击 **扫描** 检查日志大小
|
||||
- 点击 **清理** 删除日志文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 网站日志
|
||||
|
||||
网站的访问日志和错误日志,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- Nginx 访问日志(access.log)
|
||||
- Nginx 错误日志(error.log)
|
||||
- 各网站的独立日志
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
网站日志通常是占用空间最大的日志类型,建议定期清理。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### MySQL 日志
|
||||
|
||||
Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 数据库的日志文件:
|
||||
|
||||
- 慢查询日志(slow query log)
|
||||
- 二进制日志(binlog)
|
||||
- 错误日志
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
二进制日志用于数据恢复和主从复制,清理前请确认不再需要。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 相关的日志和未使用资源:
|
||||
|
||||
- 容器日志
|
||||
- 未使用的镜像
|
||||
- 构建缓存
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统日志
|
||||
|
||||
系统级别的日志文件:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemd journal 日志
|
||||
- `/var/log` 下的系统日志
|
||||
- 内核日志
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用方法
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击各类型的 **扫描** 按钮,查看日志占用空间
|
||||
2. 确认要清理的日志类型
|
||||
3. 点击 **清理** 按钮删除日志
|
||||
|
||||
或者:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **扫描所有** 一次性扫描所有日志
|
||||
2. 查看各类型的占用情况
|
||||
3. 点击 **清理所有** 批量清理
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. 清理操作不可恢复,请确认日志不再需要
|
||||
2. 重要日志建议先备份
|
||||
3. 生产环境建议保留最近的日志用于问题排查
|
||||
61
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/process.md
Normal file
61
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/process.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
# 进程管理
|
||||
|
||||
进程管理页面用于查看和管理系统中运行的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
## 进程列表
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
页面以表格形式展示所有运行中的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **PID**:进程 ID
|
||||
- **名称**:进程名称
|
||||
- **父进程 PID**:父进程的 PID
|
||||
- **线程**:线程数量
|
||||
- **用户**:运行进程的用户
|
||||
- **状态**:进程状态
|
||||
- **CPU**:CPU 使用率
|
||||
- **内存**:内存使用量
|
||||
- **启动时间**:进程启动时间
|
||||
|
||||
## 进程状态
|
||||
|
||||
| 状态 | 说明 |
|
||||
| --- | ---------- |
|
||||
| 运行中 | 进程正在执行 |
|
||||
| 睡眠 | 进程等待事件 |
|
||||
| 空闲 | 内核线程空闲 |
|
||||
| 停止 | 进程已停止 |
|
||||
| 僵尸 | 进程已结束但未被回收 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 搜索和筛选
|
||||
|
||||
- **搜索**:按 PID 或进程名称搜索
|
||||
- **状态筛选**:筛选特定状态的进程
|
||||
|
||||
## 进程操作
|
||||
|
||||
右键点击进程可以:
|
||||
|
||||
- **结束进程**:发送 SIGTERM 信号
|
||||
- **强制结束**:发送 SIGKILL 信号
|
||||
- **查看详情**:查看进程详细信息
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见进程
|
||||
|
||||
| 进程 | 说明 |
|
||||
| -------- | ----------------- |
|
||||
| nginx | Nginx Web 服务器 |
|
||||
| php-fpm | PHP FastCGI 进程管理器 |
|
||||
| mysqld | MySQL 数据库服务 |
|
||||
| postgres | PostgreSQL 数据库服务 |
|
||||
| dockerd | Docker 守护进程 |
|
||||
| ace | AcePanel 面板进程 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. 结束系统关键进程可能导致系统不稳定
|
||||
2. 结束面板进程会导致面板无法访问
|
||||
3. 建议只结束确认无用的进程
|
||||
81
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/ssh.md
Normal file
81
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/ssh.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
# 远程主机
|
||||
|
||||
SSH 页面用于管理服务器的 SSH 服务配置,包括服务状态、认证方式和 Root 账户设置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 运行状态
|
||||
|
||||
显示 SSH 服务的当前状态,并提供以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
- **启动**:启动 SSH 服务
|
||||
- **停止**:停止 SSH 服务
|
||||
- **重启**:重启 SSH 服务
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
停止 SSH 服务后将无法通过 SSH 远程连接服务器, 请确保有其他方式访问服务器(如 VNC、带外管理)后再操作。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## SSH 设置
|
||||
|
||||
### SSH 密码登录
|
||||
|
||||
控制是否允许使用密码进行 SSH 认证。
|
||||
|
||||
- **开启**:允许使用密码登录
|
||||
- **关闭**:禁止密码登录,只能使用密钥
|
||||
|
||||
### SSH 密钥登录
|
||||
|
||||
控制是否允许使用 SSH 密钥进行认证。
|
||||
|
||||
- **开启**:允许使用密钥登录
|
||||
- **关闭**:禁止密钥登录
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 安全建议
|
||||
推荐开启密钥登录并关闭密码登录,可以有效防止暴力破解攻击。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### SSH 端口
|
||||
|
||||
修改 SSH 服务监听的端口,默认为 `22`。
|
||||
|
||||
修改端口后:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击 **保存** 按钮
|
||||
2. 确保防火墙已放行新端口
|
||||
3. 使用新端口连接测试
|
||||
4. 确认可以连接后再关闭旧端口
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
修改端口前请确保新端口已在防火墙中放行,否则可能导致无法连接。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Root 设置
|
||||
|
||||
### Root 密码登录设置
|
||||
|
||||
控制 Root 用户的 SSH 登录权限:
|
||||
|
||||
- **允许 SSH 登录**:Root 可以通过 SSH 登录
|
||||
- **禁止 SSH 登录**:Root 无法通过 SSH 登录
|
||||
- **仅允许密钥登录**:Root 只能使用密钥登录
|
||||
|
||||
### Root 密码
|
||||
|
||||
重置 Root 用户的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
- 输入新密码后点击 **重置** 按钮
|
||||
- 建议使用包含大小写字母、数字和特殊字符的复杂密码
|
||||
- 刷新页面将清除密码输入框
|
||||
|
||||
### Root 密钥
|
||||
|
||||
管理 Root 用户的 SSH 密钥:
|
||||
|
||||
- **查看密钥**:查看当前配置的公钥
|
||||
- **下载**:下载私钥文件
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 安全建议
|
||||
推荐使用密钥登录并禁用密码,可以显著提高服务器安全性。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
101
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/system.md
Normal file
101
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/system.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
# 系统
|
||||
|
||||
系统页面提供服务器基础配置的管理功能,包括 DNS、SWAP、主机名和时间设置。
|
||||
|
||||
## DNS
|
||||
|
||||
配置系统的 DNS 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **DNS1**:主 DNS 服务器地址
|
||||
- **DNS2**:辅 DNS 服务器地址
|
||||
|
||||
### 常用 DNS 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
| 服务商 | DNS1 | DNS2 |
|
||||
| ---------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 阿里云 | 223.5.5.5 | 223.6.6.6 |
|
||||
| 腾讯云 | 119.29.29.29 | 119.28.28.28 |
|
||||
| 114 DNS | 114.114.114.114 | 114.114.115.115 |
|
||||
| Google | 8.8.8.8 | 8.8.4.4 |
|
||||
| Cloudflare | 1.1.1.1 | 1.0.0.1 |
|
||||
|
||||
## SWAP
|
||||
|
||||
管理系统的 SWAP 交换空间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
页面显示当前 SWAP 使用情况:
|
||||
|
||||
- 系统总计
|
||||
- 已使用
|
||||
- 可用
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置面板 SWAP
|
||||
|
||||
设置面板管理的 SWAP 文件大小(单位:MB)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 设置为 `0` 表示禁用面板 SWAP
|
||||
- 建议根据服务器内存大小设置,通常为内存的 1-2 倍
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 提示
|
||||
SWAP 可以在物理内存不足时提供额外的虚拟内存,但性能低于物理内存。 对于内存充足的服务器,可以不启用 SWAP。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Host
|
||||
|
||||
配置系统主机名和 Hosts 文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 系统主机名
|
||||
|
||||
修改服务器的主机名,例如 `myserver`、`web-01` 等。
|
||||
|
||||
### Hosts
|
||||
|
||||
编辑系统的 `/etc/hosts` 文件,用于配置本地域名解析。
|
||||
|
||||
常见用途:
|
||||
|
||||
- 屏蔽特定域名
|
||||
- 配置本地开发域名
|
||||
- 加速特定域名的解析
|
||||
|
||||
## 时间
|
||||
|
||||
配置系统时区和时间同步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 选择时区
|
||||
|
||||
从下拉列表中选择服务器所在的时区,例如 `Asia/Shanghai`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 修改时间
|
||||
|
||||
手动设置系统时间。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
手动更改时间后,系统自动时间同步可能仍会覆盖设置。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### NTP 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
配置 NTP 时间同步服务器。 留空则使用系统默认服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
常用 NTP 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
- `ntp.aliyun.com` - 阿里云
|
||||
- `ntp.tencent.com` - 腾讯云
|
||||
- `cn.pool.ntp.org` - 中国 NTP 池
|
||||
|
||||
### 操作按钮
|
||||
|
||||
- **配置默认服务器**:恢复使用系统默认的 NTP 服务器
|
||||
- **保存**:保存时区和时间设置
|
||||
- **同步时间**:立即与 NTP 服务器同步时间
|
||||
80
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/webhook.md
Normal file
80
zh_CN/advanced/toolbox/webhook.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
# Web 钩子
|
||||
|
||||
Web 钩子(Webhook)允许你通过 HTTP 请求触发服务器上的脚本执行,实现自动化部署、CI/CD 集成等功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 创建 Web 钩子
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **创建 Web 钩子** 按钮,填写以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:Web 钩子的名称,用于标识用途
|
||||
- **用户**:执行脚本的系统用户,默认为 root
|
||||
- **原始输出**:开启后返回脚本的原始输出,关闭则返回 JSON 格式
|
||||
- **脚本**:要执行的 Shell 脚本内容
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用方式
|
||||
|
||||
创建完成后,系统会生成一个唯一的 Key。 通过访问以下 URL 即可触发脚本执行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
https://your-panel-domain/api/webhook/{key}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
支持 GET 和 POST 请求。
|
||||
|
||||
## 适用场景
|
||||
|
||||
### Git 自动部署
|
||||
|
||||
配合 GitHub/GitLab 的 Webhook 功能,实现代码推送后自动部署:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/projects/myproject
|
||||
git pull origin main
|
||||
npm install
|
||||
npm run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 定时任务触发
|
||||
|
||||
通过外部服务(如监控系统)触发特定操作:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# 清理临时文件
|
||||
rm -rf /tmp/cache/*
|
||||
# 重启服务
|
||||
systemctl restart myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### CI/CD 集成
|
||||
|
||||
在 CI/CD 流水线中调用 Webhook 完成部署:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 在 CI 脚本中
|
||||
curl -X POST https://panel.example.com/api/webhook/your-key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 列表说明
|
||||
|
||||
| 字段 | 说明 |
|
||||
| ---- | --------------- |
|
||||
| 名称 | Web 钩子名称 |
|
||||
| Key | 唯一标识,用于构建调用 URL |
|
||||
| 运行用户 | 执行脚本的系统用户 |
|
||||
| 原始输出 | 是否返回原始文本输出 |
|
||||
| 已启用 | 是否启用该 Web 钩子 |
|
||||
| 调用次数 | 累计被调用的次数 |
|
||||
| 最后调用 | 最后一次调用时间 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. Key 是敏感信息,不要泄露给不信任的人
|
||||
2. 脚本以指定用户身份执行,注意权限控制
|
||||
3. 建议在脚本中添加必要的错误处理
|
||||
4. 可以通过禁用开关临时停用 Web 钩子
|
||||
66
zh_CN/advanced/website.md
Normal file
66
zh_CN/advanced/website.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
# 网站常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
网站模块用于管理 Web 服务器上的站点配置。 AcePanel 支持三种类型的网站:反向代理、PHP 和纯静态。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
使用网站功能前,需要先安装 Web 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **应用** > **原生应用**
|
||||
2. 安装 Nginx、OpenResty 或 Apache
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站类型
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 说明 | 适用场景 |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | ---------- | ----------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [反向代理](./website/proxy) | 将请求转发到后端服务 | Node.js、Go、Java 等应用 |
|
||||
| [PHP](./website/php) | 运行 PHP 程序 | WordPress、Laravel 等 |
|
||||
| [纯静态](./website/static) | 托管静态文件 | HTML、Vue/React 构建产物 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站列表
|
||||
|
||||
网站列表显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- **网站名称**:站点的唯一标识
|
||||
- **运行中**:站点是否启用
|
||||
- **目录**:网站文件所在目录
|
||||
- **HTTPS**:是否启用 HTTPS
|
||||
- **证书有效期**:SSL 证书的到期时间
|
||||
- **备注**:自定义备注信息
|
||||
- **操作**:管理、删除等
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建网站
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **网站** 页面
|
||||
2. 选择网站类型标签(反向代理/PHP/纯静态)
|
||||
3. 点击 **创建网站**
|
||||
4. 填写网站信息
|
||||
5. 点击创建
|
||||
|
||||
### 通用配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:网站的唯一标识,只能使用英文,创建后不可修改
|
||||
- **域名**:绑定的域名,可添加多个
|
||||
- **端口**:监听的端口,默认 80
|
||||
- **备注**:可选的备注信息
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站管理
|
||||
|
||||
点击网站的 **管理** 按钮进入管理页面,可以进行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
- 修改域名和端口
|
||||
- SSL 证书申请失败
|
||||
- 设置伪静态规则
|
||||
- 配置防盗链
|
||||
- 查看访问日志
|
||||
- 查看 Nginx 错误日志
|
||||
|
||||
## 批量创建
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **批量创建网站** 可以一次创建多个网站,适合需要快速部署多个站点的场景。
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
- [反向代理](./website/proxy) - 了解如何创建反向代理网站
|
||||
- [PHP 网站](./website/php) - 了解如何创建 PHP 网站
|
||||
- [纯静态网站](./website/static) - 了解如何创建静态网站
|
||||
123
zh_CN/advanced/website/php.md
Normal file
123
zh_CN/advanced/website/php.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
# PHP 网站
|
||||
|
||||
PHP 网站用于运行 PHP 程序,如 WordPress、Laravel、ThinkPHP 等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前置要求
|
||||
|
||||
创建 PHP 网站前,需要先安装:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Web 服务器**:Nginx、OpenResty 或 Apache
|
||||
2. **PHP 运行环境**:在 **应用** > **运行环境** 中安装所需的 PHP 版本
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建 PHP 网站
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **网站** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **PHP** 标签
|
||||
3. 点击 **创建网站**
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:网站标识,如 `wordpress`
|
||||
- **域名**:绑定的域名,如 `blog.example.com`
|
||||
- **端口**:监听端口,默认 80
|
||||
- **PHP 版本**:选择已安装的 PHP 版本
|
||||
- **网站目录**:网站文件存放路径
|
||||
- **备注**:可选备注
|
||||
|
||||
## 编辑 PHP 网站
|
||||
|
||||
点击网站列表中的 **编辑** 按钮进入编辑页面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 域名和监听
|
||||
|
||||
配置网站的域名和监听端口。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 基本设置
|
||||
|
||||
配置网站目录、PHP 版本等基本信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **网站目录**:网站文件存放的绝对路径
|
||||
- **运行目录**:Laravel 等框架需要设置运行目录
|
||||
- **默认文档**:默认首页文件,如 `index.php`、`index.html`
|
||||
- **PHP 版本**:选择已安装的 PHP 版本
|
||||
- **防跨站攻击**:启用后限制 PHP 只能访问网站目录内的文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 伪静态配置
|
||||
|
||||
伪静态用于 URL 重写,支持常见 PHP 程序的预设规则。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击预设下拉框可以选择常见程序的伪静态规则:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
支持的预设包括:WordPress、Laravel、ThinkPHP、Discuz、Drupal、ECShop 等常见 PHP 程序。
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站目录结构
|
||||
|
||||
创建网站后,默认目录结构:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/opt/ace/sites/网站名称/public
|
||||
├── index.php # 入口文件
|
||||
├── .user.ini # PHP 配置
|
||||
└── ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## PHP 版本切换
|
||||
|
||||
在网站编辑页面的 **基本设置** 中可以切换 PHP 版本:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入网站编辑页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **基本设置** 标签
|
||||
3. 在 **PHP 版本** 下拉框中选择新版本
|
||||
4. 点击 **保存**
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
切换 PHP 版本可能导致程序不兼容, 请先在测试环境验证。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## PHP 配置
|
||||
|
||||
### php.ini 配置
|
||||
|
||||
在 **应用** > **原生应用** > **PHP** 管理页面可以修改 php.ini 配置。
|
||||
|
||||
常用配置项:
|
||||
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
upload_max_filesize = 50M # 最大上传文件大小
|
||||
post_max_size = 50M # POST 数据最大大小
|
||||
max_execution_time = 300 # 最大执行时间
|
||||
memory_limit = 256M # 内存限制
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 禁用函数
|
||||
|
||||
PHP 默认禁用了一些危险函数,如 `exec`、`system`、`passthru` 等。 如需启用,请在 php.ini 中修改 `disable_functions` 配置。
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
启用危险函数可能带来安全风险, 请谨慎操作。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 502 Bad Gateway
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查 PHP-FPM 是否正常运行
|
||||
- 检查 PHP 版本是否正确配置
|
||||
|
||||
### 文件上传失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查 `upload_max_filesize` 和 `post_max_size` 配置
|
||||
- 检查目录权限
|
||||
|
||||
### 页面空白
|
||||
|
||||
- 开启 PHP 错误显示
|
||||
- 查看 PHP 错误日志
|
||||
135
zh_CN/advanced/website/proxy.md
Normal file
135
zh_CN/advanced/website/proxy.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
# 反向代理
|
||||
|
||||
反向代理网站用于将外部请求转发到后端服务,常用于部署 Node.js、Go、Java、Python 等应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 工作原理
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
用户请求 -> Nginx (反向代理) -> 后端应用 (如 localhost:3000)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx 接收用户的 HTTP/HTTPS 请求,然后将请求转发到指定的后端地址。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建反向代理网站
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **网站** 页面
|
||||
2. 确保选中 **反向代理** 标签
|
||||
3. 点击 **创建网站**
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:网站标识,如 `myapp`
|
||||
- **域名**:绑定的域名,如 `app.example.com`
|
||||
- **端口**:监听端口,默认 80
|
||||
- **代理目标**:后端服务地址,如 `http://127.0.0.1:3000`
|
||||
- **备注**:可选备注
|
||||
|
||||
### 代理目标格式
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://127.0.0.1:3000 # 本地服务
|
||||
http://localhost:8080 # 本地服务
|
||||
http://172.18.0.2:80 # Docker 容器
|
||||
https://backend.internal # 内部 HTTPS 服务
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 编辑反向代理网站
|
||||
|
||||
点击网站列表中的 **编辑** 按钮进入编辑页面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 域名和监听
|
||||
|
||||
配置网站的域名和监听端口,支持添加多个域名和端口。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **域名**:可添加多个域名
|
||||
- **监听地址**:可配置多个端口,支持 HTTPS 和 QUIC(HTTP3)
|
||||
|
||||
### 上游配置
|
||||
|
||||
上游(Upstream)定义了后端服务器地址,支持配置多个后端实现负载均衡。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **上游名称**:上游的标识名称
|
||||
- **负载均衡算法**:支持轮询(默认)、IP Hash 等算法
|
||||
- **保持活动连接**:与后端保持的长连接数量
|
||||
- **DNS 解析器**:自定义 DNS 解析器
|
||||
|
||||
点击 **添加服务器** 按钮可以添加后端服务器:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **服务器地址**:后端服务器地址,如 `127.0.0.1:8080`
|
||||
- **选项**:可选参数,如 `weight=5`(权重)、`backup`(备用服务器)等
|
||||
|
||||
### 代理配置
|
||||
|
||||
配置代理行为和请求头传递。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **匹配类型**:匹配类型,如前缀匹配、正则匹配等
|
||||
- **匹配表达式**:匹配的 URL 表达式
|
||||
- **代理目标**:填写上游名称或直接填写后端地址
|
||||
- **启用缓存**:是否启用代理缓存
|
||||
- **启用缓冲区**:是否启用缓冲区,AI 应用建议关闭否则可能影响流式输出
|
||||
- **代理 SNI**:是否启用 SNI(仅 HTTPS 代理有效)
|
||||
- **自定义请求头**:添加或修改传递给后端的请求头
|
||||
- **响应内容替换**:可替换响应内容中的字符串
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用场景
|
||||
|
||||
### Node.js 应用
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 启动 Node.js 应用
|
||||
node app.js # 监听 3000 端口
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
代理目标:`http://127.0.0.1:3000`
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker 容器
|
||||
|
||||
如果后端是 Docker 容器,可以使用容器的 IP 地址或容器名称(同一网络内)。
|
||||
|
||||
代理目标:`http://容器名:端口` 或 `http://容器IP:端口`
|
||||
|
||||
### 多个后端(负载均衡)
|
||||
|
||||
在上游配置中添加多个后端地址,实现负载均衡。
|
||||
|
||||
代理目标:`http://上游名称`
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见配置
|
||||
|
||||
### WebSocket 支持
|
||||
|
||||
反向代理默认支持 WebSocket,无需额外配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 传递真实 IP
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 会自动配置以下请求头,将用户真实 IP 传递给后端:
|
||||
|
||||
- `X-Real-IP`
|
||||
- `X-Forwarded-For`
|
||||
- `X-Forwarded-Proto`
|
||||
|
||||
### 自定义配置
|
||||
|
||||
在网站管理页面可以编辑 Nginx 配置,添加自定义配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
|
||||
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
|
||||
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
|
||||
proxy_buffer_size 64k;
|
||||
proxy_buffers 4 64k;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. 确保后端服务已启动并监听指定端口
|
||||
2. 如果后端是 Docker 容器,确保端口已正确映射或使用 Docker 网络
|
||||
3. 后端服务崩溃时,Nginx 会返回 502 错误
|
||||
119
zh_CN/advanced/website/static.md
Normal file
119
zh_CN/advanced/website/static.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
# 纯静态网站
|
||||
|
||||
纯静态网站用于托管 HTML、CSS、JavaScript 等静态文件,适合部署前端项目构建产物、文档站点等。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建静态网站
|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入 **网站** 页面
|
||||
2. 点击 **纯静态** 标签
|
||||
3. 点击 **创建网站**
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置项
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:网站标识,如 `docs`
|
||||
- **域名**:绑定的域名,如 `docs.example.com`
|
||||
- **端口**:监听端口,默认 80
|
||||
- **网站目录**:静态文件存放路径
|
||||
- **备注**:可选备注
|
||||
|
||||
## 编辑静态网站
|
||||
|
||||
点击网站列表中的 **编辑** 按钮进入编辑页面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 域名和监听
|
||||
|
||||
配置网站的域名和监听端口。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 高级设置
|
||||
|
||||
配置网站日志、默认文档等高级选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **网站目录**:静态文件存放的绝对路径
|
||||
- **默认文档**:默认首页文件,如 `index.html`
|
||||
|
||||
### 自定义配置(伪静态)
|
||||
|
||||
在 **自定义配置** 标签中可以添加 Nginx 配置,用于 URL 重写等功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击 **添加自定义配置** 按钮可以添加配置:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:配置名称,支持字母、数字、下划线、破折号
|
||||
- **范围**:配置生效范围,可选择「此网站」或「全局」
|
||||
- **内容**:Nginx 配置内容,如 `location` 块
|
||||
|
||||
## 适用场景
|
||||
|
||||
### 前端项目
|
||||
|
||||
Vue、React、Angular 等前端框架的构建产物:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Vue 项目
|
||||
npm run build
|
||||
# 将 dist 目录内容上传到网站目录
|
||||
|
||||
# React 项目
|
||||
npm run build
|
||||
# 将 build 目录内容上传到网站目录
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 文档站点
|
||||
|
||||
VitePress、Docusaurus、Hugo 等静态站点生成器:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# VitePress
|
||||
npm run docs:build
|
||||
# 将 .vitepress/dist 目录内容上传到网站目录
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 单页应用(SPA)
|
||||
|
||||
单页应用需要配置伪静态规则,将所有路由指向 index.html。 在 **自定义配置** 中添加:
|
||||
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 目录结构
|
||||
|
||||
典型的静态网站目录结构:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/opt/ace/sites/网站名称/public
|
||||
├── index.html # 首页
|
||||
├── assets/ # 静态资源
|
||||
│ ├── css/
|
||||
│ ├── js/
|
||||
│ └── images/
|
||||
├── favicon.ico # 网站图标
|
||||
└── ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 404 错误
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查文件是否存在于网站目录
|
||||
- 检查文件名大小写(Linux 区分大小写)
|
||||
- 单页应用需要配置伪静态规则
|
||||
|
||||
### 资源加载失败
|
||||
|
||||
- 检查资源路径是否正确
|
||||
- 检查是否使用了绝对路径
|
||||
- 检查 CORS 配置
|
||||
|
||||
### 中文文件名乱码
|
||||
|
||||
- 确保文件使用 UTF-8 编码
|
||||
356
zh_CN/cert.md
Normal file
356
zh_CN/cert.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,356 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar: false
|
||||
aside: false
|
||||
prev: false
|
||||
next: false
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<style>
|
||||
.cert-hero {
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
padding: 40px 0 60px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-hero h1 {
|
||||
font-size: 36px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 16px;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-hero p {
|
||||
font-size: 18px;
|
||||
opacity: 0.8;
|
||||
max-width: 600px;
|
||||
margin: 0 auto;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-cards {
|
||||
display: grid;
|
||||
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
|
||||
gap: 24px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 60px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@media (max-width: 768px) {
|
||||
.cert-cards {
|
||||
grid-template-columns: 1fr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card {
|
||||
position: relative;
|
||||
padding: 32px;
|
||||
border-radius: 16px;
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-bg-soft);
|
||||
border: 1px solid var(--vp-c-divider);
|
||||
transition: all 0.3s ease;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card:hover {
|
||||
transform: translateY(-4px);
|
||||
box-shadow: 0 12px 40px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.12);
|
||||
border-color: var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card.featured {
|
||||
border: 2px solid var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card.featured::before {
|
||||
content: "推荐";
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: -12px;
|
||||
right: 24px;
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
padding: 4px 16px;
|
||||
border-radius: 20px;
|
||||
font-size: 12px;
|
||||
font-weight: 600;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card-icon {
|
||||
width: 48px;
|
||||
height: 48px;
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
font-size: 24px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 20px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card h3 {
|
||||
font-size: 22px;
|
||||
margin: 0 0 8px 0;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
padding: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card-desc {
|
||||
font-size: 14px;
|
||||
opacity: 0.7;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 24px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-price {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 24px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-price-value {
|
||||
font-size: 42px;
|
||||
font-weight: 700;
|
||||
color: var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-price-unit {
|
||||
font-size: 16px;
|
||||
opacity: 0.6;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-features {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 28px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-feature {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
gap: 12px;
|
||||
padding: 10px 0;
|
||||
border-bottom: 1px solid var(--vp-c-divider);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-feature:last-child {
|
||||
border-bottom: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-feature-check {
|
||||
width: 20px;
|
||||
height: 20px;
|
||||
border-radius: 50%;
|
||||
background: #10b981;
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
font-size: 12px;
|
||||
flex-shrink: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card a.cert-btn {
|
||||
display: block !important;
|
||||
width: 100% !important;
|
||||
padding: 14px 24px !important;
|
||||
border-radius: 8px !important;
|
||||
font-size: 16px !important;
|
||||
font-weight: 600 !important;
|
||||
text-align: center !important;
|
||||
text-decoration: none !important;
|
||||
transition: all 0.2s ease !important;
|
||||
cursor: pointer !important;
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-bg-soft) !important;
|
||||
color: var(--vp-c-text-1) !important;
|
||||
border: 1px solid var(--vp-c-divider) !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card a.cert-btn:hover {
|
||||
border-color: var(--vp-c-brand) !important;
|
||||
color: var(--vp-c-brand) !important;
|
||||
text-decoration: none !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card.featured a.cert-btn {
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-brand) !important;
|
||||
color: white !important;
|
||||
border: none !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-card.featured a.cert-btn:hover {
|
||||
opacity: 0.9 !important;
|
||||
transform: translateY(-1px) !important;
|
||||
color: white !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why {
|
||||
margin-top: 60px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why h2 {
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
font-size: 28px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 40px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-grid {
|
||||
display: grid;
|
||||
grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 1fr);
|
||||
gap: 24px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@media (max-width: 768px) {
|
||||
.cert-why-grid {
|
||||
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-item {
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
padding: 24px 16px;
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-bg-soft);
|
||||
transition: all 0.3s ease;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-item:hover {
|
||||
transform: translateY(-2px);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-icon {
|
||||
width: 56px;
|
||||
height: 56px;
|
||||
margin: 0 auto 16px;
|
||||
border-radius: 14px;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
font-size: 28px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-icon.shield { background: #3b82f6; }
|
||||
.cert-why-icon.bolt { background: #f59e0b; }
|
||||
.cert-why-icon.globe { background: #10b981; }
|
||||
.cert-why-icon.support { background: #8b5cf6; }
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-item h4 {
|
||||
font-size: 16px;
|
||||
margin: 0 0 8px 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-why-item p {
|
||||
font-size: 14px;
|
||||
opacity: 0.7;
|
||||
margin: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-contact {
|
||||
margin-top: 60px;
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
padding: 40px;
|
||||
border-radius: 16px;
|
||||
background: var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-contact h3 {
|
||||
font-size: 24px;
|
||||
margin: 0 0 12px 0;
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-contact p {
|
||||
opacity: 0.9;
|
||||
margin: 0 0 24px 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-contact-btn {
|
||||
display: inline-block;
|
||||
padding: 12px 32px;
|
||||
background: white;
|
||||
color: var(--vp-c-brand);
|
||||
border-radius: 8px;
|
||||
font-weight: 600;
|
||||
text-decoration: none;
|
||||
transition: all 0.2s ease;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.cert-contact-btn:hover {
|
||||
transform: translateY(-2px);
|
||||
box-shadow: 0 4px 12px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
</style>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="cert-hero">
|
||||
<h1>SSL 证书服务</h1>
|
||||
<p>免费证书有效期仅 3 个月且需要频繁续签, 付费证书有效期一年,省心省力</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="cert-cards">
|
||||
<div class="cert-card">
|
||||
<div class="cert-card-icon">🔒</div>
|
||||
<h3>DV 单域名证书</h3>
|
||||
<div class="cert-card-desc">适合单个网站使用</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-price"><span class="cert-price-value">¥1X</span>
|
||||
<span class="cert-price-unit"> / 年</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-features">
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>域名验证 (DV) 证书</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>保护单个域名</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>一年有效期</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>国际认可品牌</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div><a href="https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=I1oJKSTH" target="_blank" class="cert-btn cert-btn-secondary">联系购买</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="cert-card featured">
|
||||
<div class="cert-card-icon">🛡️</div>
|
||||
<h3>DV 泛域名证书</h3>
|
||||
<div class="cert-card-desc">一张证书保护所有子域名</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-price"><span class="cert-price-value">¥1XX</span>
|
||||
<span class="cert-price-unit"> / 年</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-features">
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>域名验证 (DV) 证书</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>保护所有子域名 (*.domain.com)</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>一年有效期</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-feature"><span class="cert-feature-check">✓</span>
|
||||
<span>国际认可品牌</span>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div><a href="https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=I1oJKSTH" target="_blank" class="cert-btn cert-btn-primary">联系购买</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="cert-why">
|
||||
<h2>为什么选择付费证书</h2>
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-grid">
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-item">
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-icon shield">🔐</div>
|
||||
<h4>更长有效期</h4>
|
||||
<p>一年有效期,无需频繁续签</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-item">
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-icon bolt">⚡</div>
|
||||
<h4>快速签发</h4>
|
||||
<p>付款后快速完成签发</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-item">
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-icon globe">🌐</div>
|
||||
<h4>国际品牌</h4>
|
||||
<p>全球浏览器信任</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-item">
|
||||
<div class="cert-why-icon support">💬</div>
|
||||
<h4>专业支持</h4>
|
||||
<p>遇到问题随时咨询</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="cert-contact">
|
||||
<h3>需要帮助?</h3>
|
||||
<p>如有任何问题,欢迎加入 QQ 群咨询</p><a href="https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=I1oJKSTH" target="_blank" class="cert-contact-btn">加入 QQ 群 12370907</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
73
zh_CN/faq/application.md
Normal file
73
zh_CN/faq/application.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
# 应用常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
## PHP 模块安装
|
||||
|
||||
「应用」->「运行环境」->「PHP」->「管理」->「模块」,安装需要的模块。
|
||||
|
||||
部分模块需要编译安装,耗时较长, 可在「任务」页面查看进度。
|
||||
|
||||
## PHP 函数被禁用
|
||||
|
||||
默认禁用了部分高危函数。 如需启用:
|
||||
|
||||
「应用」->「运行环境」->「PHP」->「管理」->「配置」
|
||||
|
||||
找到 `disable_functions`,删除需要启用的函数名。
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 安全提示
|
||||
`exec`、`shell_exec`、`system` 等函数有安全风险, 启用前需确认必要性。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Nginx 配置错误
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置后 Nginx 无法启动,查看错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nginx -t
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修复配置后重启:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
systemctl restart nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Supervisor 启动报错
|
||||
|
||||
### EACCES 权限错误
|
||||
|
||||
项目目录权限问题,确保目录所有者为 www:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
chown -R www:www /opt/ace/projects/项目名
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 找不到 node/npm
|
||||
|
||||
通过 nvm 安装的 Node.js 不在默认 PATH 中。
|
||||
|
||||
「应用」->「Supervisor 管理器」->「管理」->「配置」,添加:
|
||||
|
||||
```ini
|
||||
environment=PATH="/root/.nvm/versions/node/v24.0.0/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
版本号替换为实际安装的版本, 可通过 `whereis node` 查看路径。
|
||||
|
||||
## 应用安装失败
|
||||
|
||||
1. 检查网络连接
|
||||
2. 查看「任务」页面的错误信息
|
||||
3. 尝试「应用」页面点击「更新缓存」后重试
|
||||
|
||||
## 应用无法卸载
|
||||
|
||||
有依赖关系的应用需要先卸载依赖它的应用。
|
||||
|
||||
如 phpMyAdmin 依赖 Nginx,需先卸载 phpMyAdmin。
|
||||
|
||||
## 多版本 PHP 共存
|
||||
|
||||
可同时安装多个 PHP 版本, 在创建网站时选择对应版本。
|
||||
|
||||
已有网站切换版本:「编辑」->「基本设置」->「PHP 版本」。
|
||||
73
zh_CN/faq/container.md
Normal file
73
zh_CN/faq/container.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
# 容器常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
## 镜像拉取失败
|
||||
|
||||
国内服务器无法连接 Docker Hub,需配置镜像加速。
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker
|
||||
|
||||
「应用」->「Docker」->「管理」->「配置」,添加:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"registry-mirrors": [
|
||||
"https://docker.1ms.run"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Podman
|
||||
|
||||
「应用」->「Podman」->「管理」->「Registry 配置」,末尾添加:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[[registry]]
|
||||
location = "docker.io"
|
||||
[[registry.mirror]]
|
||||
location = "docker.1ms.run"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
镜像加速地址可使用 [毫秒镜像](https://1ms.run/) 或其他服务。
|
||||
|
||||
## 编排启动失败
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击「日志」查看错误信息
|
||||
2. 常见原因:
|
||||
- 端口被占用:修改映射端口
|
||||
- 镜像拉取失败:配置镜像加速
|
||||
- 配置错误:检查 docker-compose.yml 语法
|
||||
|
||||
## 容器无法访问
|
||||
|
||||
1. 检查容器是否运行:「容器」->「容器」列表查看状态
|
||||
2. 检查端口映射是否正确
|
||||
3. 检查防火墙是否放行映射的主机端口
|
||||
|
||||
## 容器内无法访问外网
|
||||
|
||||
检查 Docker 网络配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker network ls
|
||||
docker network inspect bridge
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据持久化
|
||||
|
||||
容器删除后数据会丢失。 使用卷挂载持久化数据:
|
||||
|
||||
在编排配置中添加 volumes:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./data:/app/data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 查看容器日志
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker logs 容器名或ID
|
||||
docker logs -f 容器名或ID # 实时查看
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或在面板「容器」->「容器」列表点击「日志」。
|
||||
73
zh_CN/faq/database.md
Normal file
73
zh_CN/faq/database.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
# 数据库常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
## 忘记数据库密码
|
||||
|
||||
### MySQL/MariaDB/Percona
|
||||
|
||||
在面板「数据库」->「用户」中修改用户密码。
|
||||
|
||||
如果忘记 root 密码,可前往「应用」->「MySQL/MariaDB/Percona」->「管理」中查看/重置。
|
||||
|
||||
### PostgreSQL
|
||||
|
||||
在面板「数据库」->「用户」中修改用户密码。
|
||||
|
||||
如果忘记 postgres 用户密码,可前往「应用」->「PostgreSQL」->「管理」中查看/重置。
|
||||
|
||||
## 远程连接数据库
|
||||
|
||||
默认只允许本地连接。 如需远程连接:
|
||||
|
||||
MySQL/MariaDB/Percona:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在「数据库」->「用户」中,新建一个用户主机为 `%`(允许所有 IP)或指定 IP 的用户
|
||||
2. 在防火墙放行数据库端口 3306
|
||||
|
||||
PostgreSQL:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 前往「应用」->「PostgreSQL」->「管理」中编辑主配置找到`listen_addresses`,取消注释并将其值改为 `'*'`
|
||||
2. 在同一页面编辑用户配置,添加一行:`host all 用户名 (IP地址/掩码/all) scram-sha-256` 并保存
|
||||
3. 重启 PostgreSQL 服务
|
||||
4. 在防火墙放行数据库端口 5432
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 安全提示
|
||||
不建议将数据库端口暴露到公网, 建议使用 SSH 隧道或 VPN 连接。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 连接被拒绝
|
||||
|
||||
1. 检查数据库服务是否运行
|
||||
2. 检查用户权限和主机设置
|
||||
3. 检查连接地址:本地连接用 `localhost` 或 `127.0.0.1`
|
||||
|
||||
## 导入大文件失败
|
||||
|
||||
phpMyAdmin 有上传限制。 大文件建议用命令行导入:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
mysql -u 用户名 -p 数据库名 < 文件.sql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或使用面板的文件管理上传后,在终端执行导入。
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据库备份
|
||||
|
||||
1. 「备份」->「创建备份」选择数据库
|
||||
2. 或使用命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# MySQL
|
||||
mysqldump -u 用户名 -p 数据库名 > backup.sql
|
||||
|
||||
# PostgreSQL
|
||||
pg_dump -U 用户名 数据库名 > backup.sql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 字符集问题
|
||||
|
||||
已有数据库修改字符集:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
ALTER
|
||||
DATABASE database_name CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
|
||||
```
|
||||
99
zh_CN/faq/panel.md
Normal file
99
zh_CN/faq/panel.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# 面板常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
## 面板打不开
|
||||
|
||||
SSH 登录服务器,检查面板状态:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果服务已停止,启动它:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果无法启动,尝试修复:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel fix && acepanel update
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
服务正常但仍无法访问,检查防火墙:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 检查端口是否监听
|
||||
curl -I http://127.0.0.1:面板端口/
|
||||
|
||||
# 放行端口(firewalld)
|
||||
firewall-cmd --add-port=面板端口/tcp --permanent
|
||||
firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
云服务器还需检查安全组设置。
|
||||
|
||||
查看面板日志排查问题:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
journalctl -u acepanel -n 100
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 忘记密码/用户名/地址
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel info
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出面板地址、用户名,并生成新密码。
|
||||
|
||||
## 修改面板端口
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel port 12345
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改后需在服务器安全组/防火墙放行新端口。
|
||||
|
||||
## 关闭安全入口
|
||||
|
||||
如果忘记安全入口路径:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel entrance off
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 关闭域名/IP 绑定
|
||||
|
||||
绑定后无法访问面板:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel bind-domain off
|
||||
acepanel bind-ip off
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 关闭两步验证
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel user 2fa admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 证书错误
|
||||
|
||||
面板默认使用自签名证书,浏览器会提示不安全, 点击「继续访问」即可。
|
||||
|
||||
申请正式证书:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel https generate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
需要确保服务器 IP 80 端口可直接访问。
|
||||
|
||||
## acepanel 命令无权限
|
||||
|
||||
必须以 root 用户执行,或使用 sudo:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo acepanel status
|
||||
```
|
||||
68
zh_CN/faq/project.md
Normal file
68
zh_CN/faq/project.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
# 项目常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
## 项目启动失败
|
||||
|
||||
点击「日志」查看错误信息。 常见原因:
|
||||
|
||||
### 权限问题
|
||||
|
||||
项目目录应在 `/opt/ace/projects/` 下,所有者为 www:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
chown -R www:www /opt/ace/projects/项目名
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果部署在 `/root` 下,需使用 root 用户运行(不推荐)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 找不到命令
|
||||
|
||||
如 `node: No such file or directory`,说明环境变量未配置。
|
||||
|
||||
解决方法:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在「编辑」->「依赖」中关联运行环境
|
||||
2. 或在「运行设置」->「环境变量」中添加 PATH
|
||||
|
||||
### 端口被占用
|
||||
|
||||
修改应用监听端口,或停止占用端口的进程:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
lsof -i:3000 # 查看占用端口的进程
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
「编辑」->「运行设置」->「环境变量」,点击「添加」。
|
||||
|
||||
常用配置:
|
||||
|
||||
- `NODE_ENV=production`
|
||||
- `PORT=3000`
|
||||
|
||||
## 预启动命令
|
||||
|
||||
在项目启动前执行,如安装依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
- Node.js:`npm install` 或 `yarn`
|
||||
- Python:`pip install -r requirements.txt`
|
||||
- Go:`go build`
|
||||
|
||||
## 查看项目日志
|
||||
|
||||
1. 面板:项目列表点击「日志」
|
||||
2. 命令行:`journalctl -u ace-project-项目名 -f`
|
||||
|
||||
## 项目自动重启
|
||||
|
||||
在「运行设置」中配置:
|
||||
|
||||
- **重启策略**:失败时重启 / 总是重启 / 不重启
|
||||
- **重启间隔**:两次重启之间的等待时间
|
||||
- **最大重启次数**:防止无限重启
|
||||
|
||||
## 反向代理配置
|
||||
|
||||
创建项目时开启「反向代理」,会自动创建一个反向代理网站。
|
||||
|
||||
手动配置:创建反向代理网站,上游地址填 `http://127.0.0.1:项目端口`。
|
||||
80
zh_CN/faq/website.md
Normal file
80
zh_CN/faq/website.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
# 网站常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站无法访问
|
||||
|
||||
1. 检查域名是否解析到服务器 IP
|
||||
2. 检查防火墙是否放行 80/443 端口
|
||||
3. 检查 Nginx 是否运行:「应用」->「Nginx」->「管理」
|
||||
4. 查看 Nginx 错误日志
|
||||
|
||||
## 403 Forbidden
|
||||
|
||||
通常是权限问题:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# 修复网站目录权限
|
||||
chown -R www:www /opt/ace/sites/网站名/public
|
||||
chmod -R 755 /opt/ace/sites/网站名/public
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 502 Bad Gateway
|
||||
|
||||
PHP 网站出现 502,检查 PHP 是否运行:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 「应用」->「运行环境」->「PHP」->「管理」
|
||||
2. 确认 PHP 版本与网站配置一致
|
||||
3. 查看 PHP 错误日志
|
||||
|
||||
反向代理网站出现 502,检查后端服务是否运行。
|
||||
|
||||
## 伪静态不生效
|
||||
|
||||
1. 确认在「伪静态」标签页选择了正确的预设或填写了规则
|
||||
2. 点击「保存」后 Nginx 会自动重载
|
||||
3. 清除浏览器缓存后测试
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置 QUIC (HTTP/3)
|
||||
|
||||
面板支持 QUIC,但默认不添加 `Alt-Svc` 头。 在自定义配置中添加:
|
||||
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
add_header Alt-Svc 'h3=":$server_port"; ma=2592000';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
确保服务器安全组/防火墙放行 UDP 443 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 TLSv1/TLSv1.1
|
||||
|
||||
OpenSSL 3.x 默认禁用旧协议。 如必须使用,在「HTTPS」设置中修改密码套件:
|
||||
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:DES-CBC3-SHA:@SECLEVEL=0;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 启用 IPv6
|
||||
|
||||
在「域名和监听」添加监听地址:`[::]:80` 和 `[::]:443`。
|
||||
|
||||
## CDN 回源与 HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
| CDN 回源协议 | 网站 HTTPS 配置 |
|
||||
| -------- | ------------------- |
|
||||
| HTTP | 无需开启 |
|
||||
| HTTPS | 必须开启 |
|
||||
| 协议跟随 | 必须开启,且不能开启 HTTP 重定向 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 上传文件大小限制
|
||||
|
||||
默认限制 100MB。 修改 PHP 配置:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 「应用」->「运行环境」->「PHP」->「管理」->「主配置」
|
||||
2. 修改 `upload_max_filesize` 和 `post_max_size`
|
||||
3. 保存后重启 PHP
|
||||
|
||||
## SSL 证书申请失败
|
||||
|
||||
1. 确认域名已解析到服务器
|
||||
2. 确认 80 端口可访问(Let's Encrypt 验证需要)
|
||||
3. 检查是否超过 Let's Encrypt 速率限制
|
||||
4. 尝试使用 DNS 验证方式
|
||||
5. 更换其他证书提供商
|
||||
65
zh_CN/index.md
Normal file
65
zh_CN/index.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
layout: home
|
||||
hero:
|
||||
name: "AcePanel"
|
||||
text: "简单轻量 • 高效运维"
|
||||
tagline: 全能服务器运维管理面板
|
||||
actions:
|
||||
- theme: brand
|
||||
text: 🌟 点亮 Star
|
||||
link: https://github.com/acepanel/panel
|
||||
target: _blank
|
||||
- theme: alt
|
||||
text: 快速安装
|
||||
link: /quickstart/install
|
||||
features:
|
||||
- icon: ✨
|
||||
title: 极低占用
|
||||
details: Go 语言开发,安装包小,占用低,单文件运行,不会对系统性能造成影响
|
||||
- icon: 🛠
|
||||
title: 低破坏性
|
||||
details: 设计为尽可能减少对系统的额外修改,在同类产品中,我们对系统的修改最少
|
||||
- icon: 📅
|
||||
title: 追随时代
|
||||
details: 整体设计走在时代前沿,对新系统兼容性好,在同类产品中处于领先地位
|
||||
- icon: 🚀
|
||||
title: 高效运维
|
||||
details: 功能完善,自定义能力强,既可快速部署小型网站,也可基于定制化需求部署复杂应用
|
||||
- icon: ⛓️💥
|
||||
title: 离线运行
|
||||
details: 支持离线模式,甚至可以在部署完成后停止面板进程,不会对已有服务造成任何影响
|
||||
- icon: 🛡
|
||||
title: 安全稳定
|
||||
details: 面板采用业界多种技术保障本体安全性,已在我们的多个生产环境中长期稳定运行
|
||||
- icon: 💽
|
||||
title: 全面开源
|
||||
details: 少有的全开源面板,您可以在遵守开源协议的前提下对面板自由修改、二次开发
|
||||
- icon: 🆓
|
||||
title: 永久免费
|
||||
details: 承诺面板本体未来不会引入任何收费/授权功能,永久免费使用
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 合作伙伴
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: space-around; align-items: center; flex-wrap: wrap;"><a href="https://www.weixiaoduo.com/" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/wxd.png" alt="WeiXiaoDuo">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.dkdun.cn/aff/MQZZNVHQ" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/dk.png" alt="LF Cloud">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://cloud.panguidc.com/aff/DMRRFVJX" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/pangu.png" alt="Pangu Cloud">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://waf.pro/">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/wafpro.png" alt="WAFPRO" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://scdn.ddunyun.com/">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/ddunyun.png" alt="DunYun SCDN" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://kuocai.cn/" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/kuocai.png" alt="Kuocai CDN">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://1ms.run/" style="padding: 1rem;">
|
||||
<img width="160" src="/partners/1ms.svg" alt="Millisecond Mirror">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
57
zh_CN/quickstart/cli.md
Normal file
57
zh_CN/quickstart/cli.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
# 命令行工具
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 提供命令行工具 `acepanel`,用于在无法访问 Web 界面时进行面板管理。
|
||||
|
||||
## 服务管理
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning 注意
|
||||
后台任务运行时请勿停止或重启面板,可能导致任务中断或数据丢失。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel start # 启动
|
||||
acepanel stop # 停止
|
||||
acepanel restart # 重启
|
||||
acepanel status # 查看状态
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 用户管理
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel user list # 列出所有用户
|
||||
acepanel user username <旧用户名> <新用户名> # 修改用户名
|
||||
acepanel user password <用户名> <新密码> # 修改密码
|
||||
acepanel user 2fa <用户名> # 开关两步验证
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 安全设置
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel https on|off # 开关 HTTPS
|
||||
acepanel https generate # 生成证书(自签名或 Let's Encrypt)
|
||||
acepanel entrance on|off # 开关安全入口
|
||||
acepanel port <端口号> # 修改监听端口
|
||||
acepanel bind-domain off # 解除域名绑定
|
||||
acepanel bind-ip off # 解除 IP 绑定
|
||||
acepanel bind-ua off # 解除 UA 绑定
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 维护命令
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel update # 更新面板
|
||||
acepanel fix # 修复更新问题
|
||||
acepanel sync # 同步缓存数据
|
||||
acepanel sync-time # 同步服务器时间
|
||||
acepanel clear-task # 清空任务队列
|
||||
acepanel info # 查看面板信息并重置密码
|
||||
acepanel help # 帮助
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
修改用户 `admin` 的密码为 `newpassword`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel user password admin newpassword
|
||||
```
|
||||
45
zh_CN/quickstart/first-container.md
Normal file
45
zh_CN/quickstart/first-container.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
# 第一个容器:部署 pgAdmin 4
|
||||
|
||||
本文以 pgAdmin 4 为例,演示如何通过 AcePanel 快速部署 Docker 容器。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 Docker
|
||||
|
||||
进入「应用」页面,在「原生应用」中找到 Docker 并安装。 安装进度可在「任务」页面查看。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 国内服务器
|
||||
国内服务器拉取镜像较慢, 建议配置 [毫秒镜像](https://1ms.run/) 提供的付费加速源。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署容器
|
||||
|
||||
进入「应用」->「容器模板」,找到 pgAdmin 4,点击「部署」。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择「创建新编排」后填写配置:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **编排名称**:给编排起个名字,如 `pg4admin`
|
||||
- **自动启动**:勾选后创建完成自动拉取镜像并启动
|
||||
- **自动防火墙**:勾选后自动放行端口
|
||||
- **访问端口**:容器 80 端口映射到主机端口,如 `999`
|
||||
- **管理员邮箱/密码**:pgAdmin 4 的登录凭据
|
||||
|
||||
点击「下一步」预览编排配置,确认后点击「创建」。
|
||||
|
||||
## 等待启动
|
||||
|
||||
如果勾选了「自动启动」,创建后会弹窗显示拉取和启动进度:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
也可以在「容器」->「编排」页面手动管理:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 访问服务
|
||||
|
||||
启动完成后,浏览器访问 `http://服务器IP:端口`(如 `http://x.x.x.x:999`),用之前设置的邮箱和密码登录即可。
|
||||
76
zh_CN/quickstart/first-project.md
Normal file
76
zh_CN/quickstart/first-project.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
# 第一个项目:部署 Node.js 应用
|
||||
|
||||
本文以一个简单的 Node.js HTTP 服务为例,演示如何通过 AcePanel 部署和管理项目。
|
||||
|
||||
## 准备代码
|
||||
|
||||
先准备一个简单的 Node.js 应用。 在项目目录创建 `app.js`:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const http = require('http');
|
||||
|
||||
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
|
||||
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
|
||||
res.end('Hello from AcePanel!\n');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
server.listen(3000, () => {
|
||||
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建项目
|
||||
|
||||
进入「项目」页面,点击「创建项目」。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
填写配置:
|
||||
|
||||
- **项目名**:项目标识,如 `hello-node`
|
||||
- **项目目录**:留空使用默认路径
|
||||
- **运行用户**:一般选 `www`
|
||||
- **启动命令**:`node app.js`
|
||||
- **反向代理**:如需通过域名访问,可开启自动创建反向代理
|
||||
|
||||
## 上传代码
|
||||
|
||||
项目创建后,进入「文件」页面,导航到项目目录(如 `/opt/ace/projects/hello-node`),上传 `app.js` 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
也可以通过终端用 git clone 拉取代码。
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置项目
|
||||
|
||||
在项目列表点击「编辑」,可以调整更多设置:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**运行设置**:
|
||||
|
||||
- **预启动命令**:启动前执行,如 `npm install`
|
||||
- **重启策略**:进程异常退出时的处理方式
|
||||
- **环境变量**:设置 `NODE_ENV=production` 等
|
||||
|
||||
**依赖**:可以关联 Node.js 运行环境版本。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动项目
|
||||
|
||||
回到项目列表,点击「启动」按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启动后可点击「日志」查看输出,确认服务正常运行。
|
||||
|
||||
## 访问服务
|
||||
|
||||
如果开启了反向代理,通过配置的域名访问即可。
|
||||
|
||||
如果没有,可以通过 `http://服务器IP:3000` 直接访问(需在防火墙放行 3000 端口)。
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip 生产环境
|
||||
生产环境建议:
|
||||
|
||||
- 开启「自启动」,服务器重启后自动恢复
|
||||
- 配置反向代理,通过 Nginx 转发请求
|
||||
- 在「资源限制」中设置内存上限,防止内存泄漏
|
||||
:::
|
||||
52
zh_CN/quickstart/first-website.md
Normal file
52
zh_CN/quickstart/first-website.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
# 第一个网站:部署 WordPress
|
||||
|
||||
本文以 WordPress 为例,演示如何通过 AcePanel 快速搭建 PHP 网站。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装环境
|
||||
|
||||
进入「应用」页面:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在「原生应用」中安装 Nginx 和 Percona(或 MySQL/MariaDB)
|
||||
2. 在「运行环境」中安装 PHP(建议 8.3+)
|
||||
|
||||
安装进度可在「任务」页面查看。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建网站
|
||||
|
||||
进入「网站」->「PHP」,点击「创建网站」。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
填写配置:
|
||||
|
||||
- **名称**:网站标识,如 `wordpress`,创建后不可改
|
||||
- **域名**:你的域名,没有域名可填服务器 IP
|
||||
- **根目录**:留空使用默认路径
|
||||
- **PHP 版本**:选择刚安装的版本
|
||||
- **数据库**:选择 MySQL,记下生成的数据库名、用户名、密码
|
||||
|
||||
## 上传 WordPress
|
||||
|
||||
从 [WordPress 官网](https://wordpress.org/download/) 下载安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
在网站列表点击「目录」进入文件管理,上传压缩包并解压。 进入 `wordpress` 目录,`Ctrl+A` 全选,`Ctrl+X` 剪切,返回上级目录 `Ctrl+V` 粘贴,把文件移到网站根目录。
|
||||
|
||||
## 配置伪静态
|
||||
|
||||
回到网站列表,点击「编辑」,切换到「伪静态」标签页,选择预设的 `wordpress` 规则并保存。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
:::tip HTTPS
|
||||
可在「HTTPS」标签页一键签发免费的 Let's Encrypt 证书。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 WordPress
|
||||
|
||||
浏览器访问你的域名,按提示完成安装:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 选择语言
|
||||
2. 填写站点信息(标题、管理员账号等)
|
||||
3. 数据库配置:填入之前记下的数据库信息,主机填 `localhost`
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后即可登录 WordPress 后台。
|
||||
76
zh_CN/quickstart/install.md
Normal file
76
zh_CN/quickstart/install.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
# 安装
|
||||
|
||||
## 系统要求
|
||||
|
||||
- 架构:`amd64` / `arm64`
|
||||
- 内存:≥ 512MB(建议 1GB 以上)
|
||||
- 磁盘:≥ 10GB 可用空间
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持的操作系统
|
||||
|
||||
| 系统 | 版本 | 状态 |
|
||||
| ---------------- | -- | --- |
|
||||
| AlmaLinux | 10 | 推荐 |
|
||||
| AlmaLinux | 9 | 支持 |
|
||||
| RockyLinux | 10 | 推荐 |
|
||||
| RockyLinux | 9 | 支持 |
|
||||
| Debian | 13 | 推荐 |
|
||||
| Debian | 12 | 支持 |
|
||||
| Ubuntu | 24 | 推荐 |
|
||||
| Ubuntu | 22 | 支持 |
|
||||
| OpenCloudOS | 9 | 支持 |
|
||||
| TencentOS Server | 4 | 支持 |
|
||||
| CentOS Stream | 10 | 不推荐 |
|
||||
| CentOS Stream | 9 | 不推荐 |
|
||||
|
||||
未列出的系统可自行尝试安装,但不提供技术支持。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装前准备
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用纯净系统安装,避免与已有环境冲突
|
||||
- 如需挂载数据盘,请在安装前完成,安装后不支持目录迁移
|
||||
- 确保服务器能正常访问外网
|
||||
|
||||
## 开始安装
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip AcePanel 推荐使用
|
||||
[林枫云高性能 AMD EYPC 服务器](https://www.dkdun.cn/aff/MQZZNVHQ) 服务器安装
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
以 `root` 用户登录服务器,执行:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
bash <(curl -sSLm 10 https://dl.acepanel.net/helper.sh)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装过程中请勿关闭终端。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装完成
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,终端会输出面板访问地址和初始账号密码:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
AcePanel 安装完成
|
||||
用户名:xxxxxxxx
|
||||
密码:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
|
||||
端口:xxxxx
|
||||
入口:/xxxxxx
|
||||
========================================
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
首次访问可能需在浏览器信任自签名证书。
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
**无法访问面板**
|
||||
|
||||
检查云服务器安全组和防火墙设置,确保放行面板端口。
|
||||
|
||||
**忘记用户/密码/地址**
|
||||
|
||||
使用命令行工具一键重置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel info
|
||||
```
|
||||
38
zh_CN/quickstart/introduction.md
Normal file
38
zh_CN/quickstart/introduction.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
# 产品介绍
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 是一款开源的服务器运维管理面板。
|
||||
|
||||
## 特性
|
||||
|
||||
- **极低占用**:Go 语言开发,单文件运行,资源占用极低
|
||||
- **低破坏性**:尽可能减少对系统的修改,同类产品中最少
|
||||
- **追随时代**:对新系统兼容性好,技术栈保持更新
|
||||
- **高效运维**:功能完善,自定义能力强,适用于简单到复杂的部署场景
|
||||
- **离线运行**:支持离线模式,停止面板不影响已部署的服务
|
||||
- **安全稳定**:多重安全机制,生产环境长期稳定运行
|
||||
- **完整开源**:全部代码开源,可自由修改和二次开发
|
||||
- **永久免费**:面板本体不会引入任何收费功能
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能
|
||||
|
||||
**快速建站**
|
||||
|
||||
深度集成 Nginx、MySQL、PHP 等主流服务,一键部署 LNMP 环境,支持多版本共存。
|
||||
|
||||
**文件管理**
|
||||
|
||||
类似 Windows 资源管理器的操作体验,支持快捷键、批量操作、在线编辑。
|
||||
|
||||
**备份恢复**
|
||||
|
||||
网站、数据库一键备份与恢复,支持定时备份和远程存储。
|
||||
|
||||
## 对比
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | AcePanel | 同类产品 1 | 同类产品 B |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------------------------- | ------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 用户界面 | 清爽现代 | 现代化设计 | 功能繁杂,广告较多 |
|
||||
| 开源情况 | 完整开源 | 仅开源非专业版 | 部分开源,提交记录不完整 |
|
||||
| 资源占用 | 极低,单文件运行 | core + agent 双进程 | 较高 |
|
||||
| 应用中心 | 原生应用 + 容器编排 | 仅容器编排 | 应用陈旧,更新缓慢 |
|
||||
| 技术栈 | Go 1.25 + Vue 3 | Go 1.24 + Vue 3 | Python 3.7 + Vue 3 + jQuery |
|
||||
167
zh_CN/quickstart/news/acepanel-3-release.md
Normal file
167
zh_CN/quickstart/news/acepanel-3-release.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
# AcePanel 3.0 正式发布
|
||||
|
||||
好久不见, 经过几次跳票延期,AcePanel 3.0 终于在 2026 年初完成开发, 经过了约 3 个星期的内测,现在是时候发布了。
|
||||
|
||||
## 升级全新品牌名称 AcePanel
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 原名耗子面板,是本人 2022 年底开发的服务器运维管理面板。
|
||||
|
||||
之前收到最多的一个反馈就是耗子面板这个名字不好听,于是我们现在换了更高端大气上档次的名字 - AcePanel,你也可以叫它王牌面板/艾斯面板。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
本文以下 AcePanel 均表示 AcePanel 3.0 版本
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持运行环境与项目管理
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 这次最大的更新就是新增了运行环境功能,支持一键安装与管理 Go、Java、Node.js、PHP、Python 等运行环境,支持多版本同时共存。
|
||||
|
||||
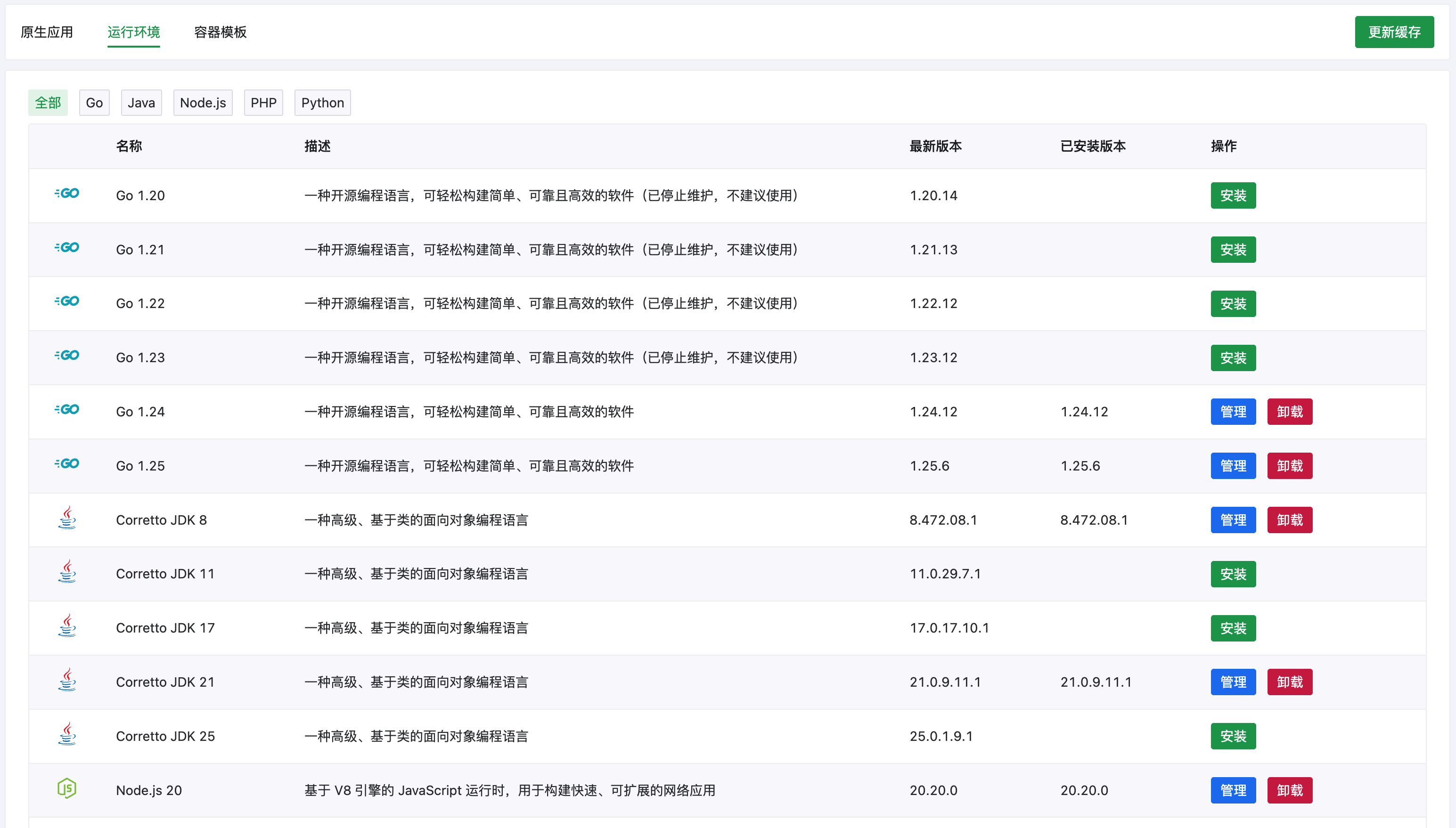
|
||||
|
||||
同时 AcePanel 基于 Linux systemd 的强大能力全新开发了项目管理功能,支持通过安装的运行环境一键创建与管理各类 Web 项目和常驻程序,可平替 PM2、Supervisor 等工具。
|
||||
|
||||
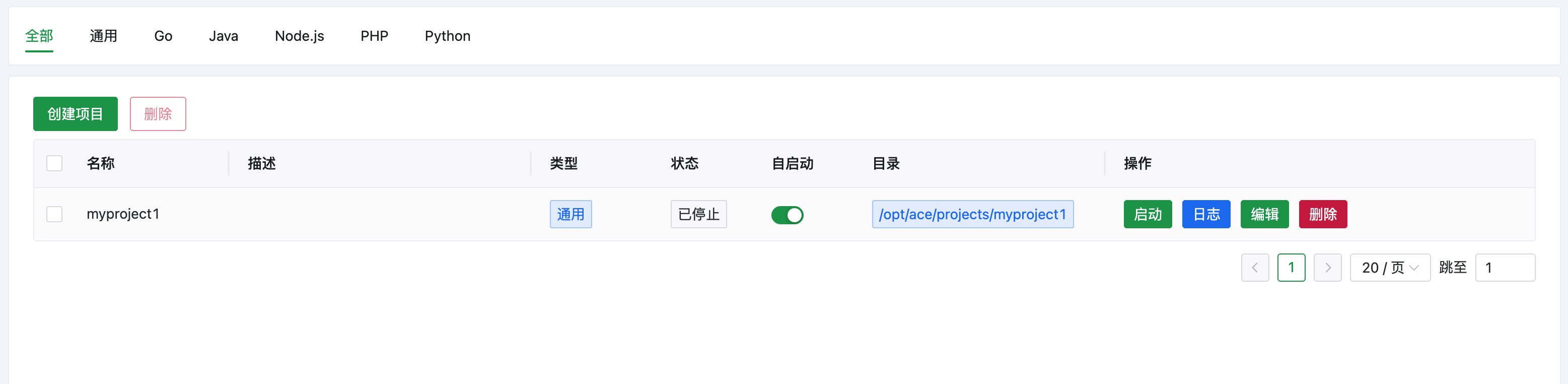
|
||||
|
||||
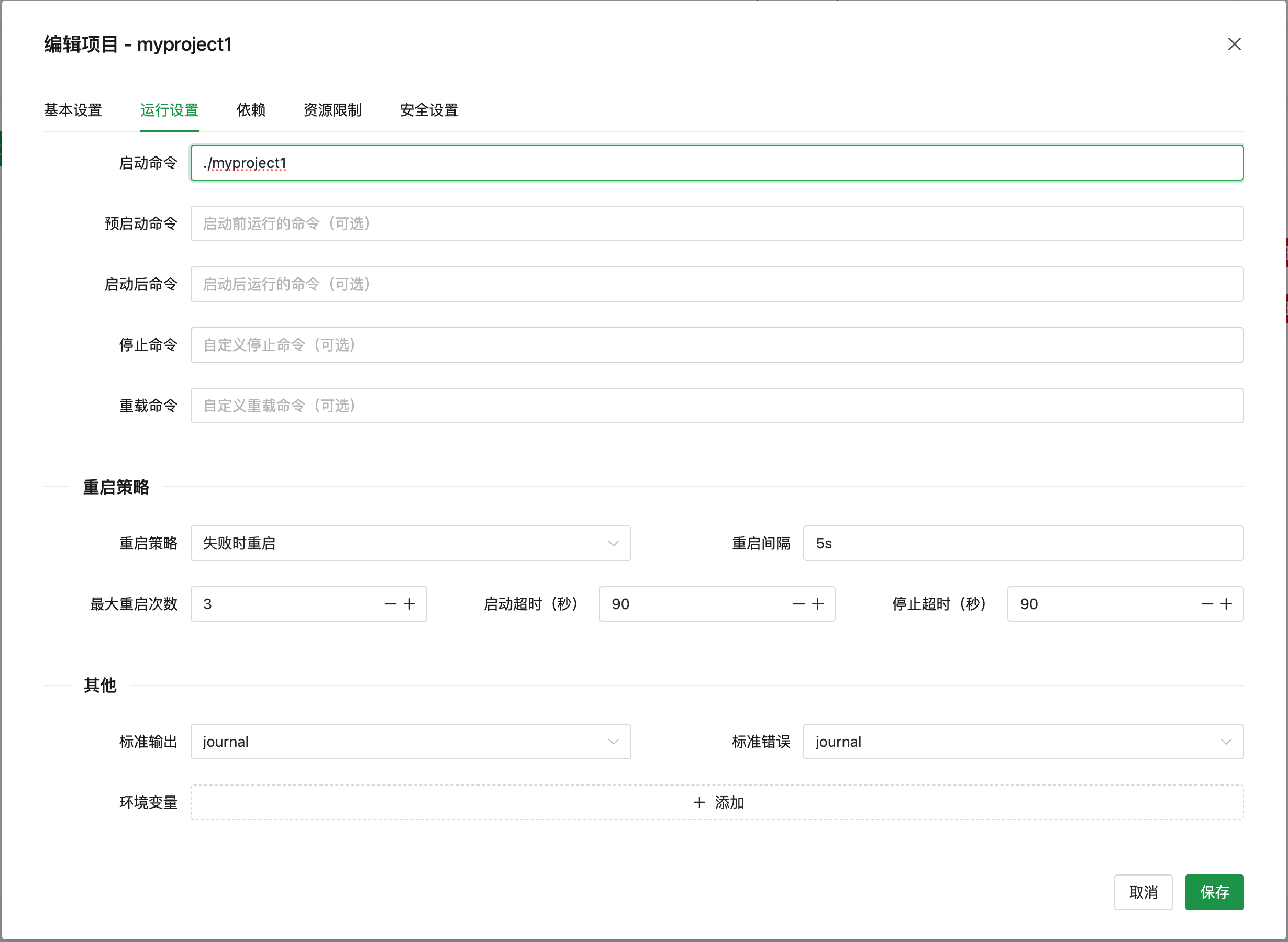
|
||||
|
||||
## 网站管理重构
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 还对网站管理功能进行了重构,重新组织了网站目录结构,支持反向代理、纯静态、PHP 3 种网站类型,并新增了多项常用配置以及自定义功能。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
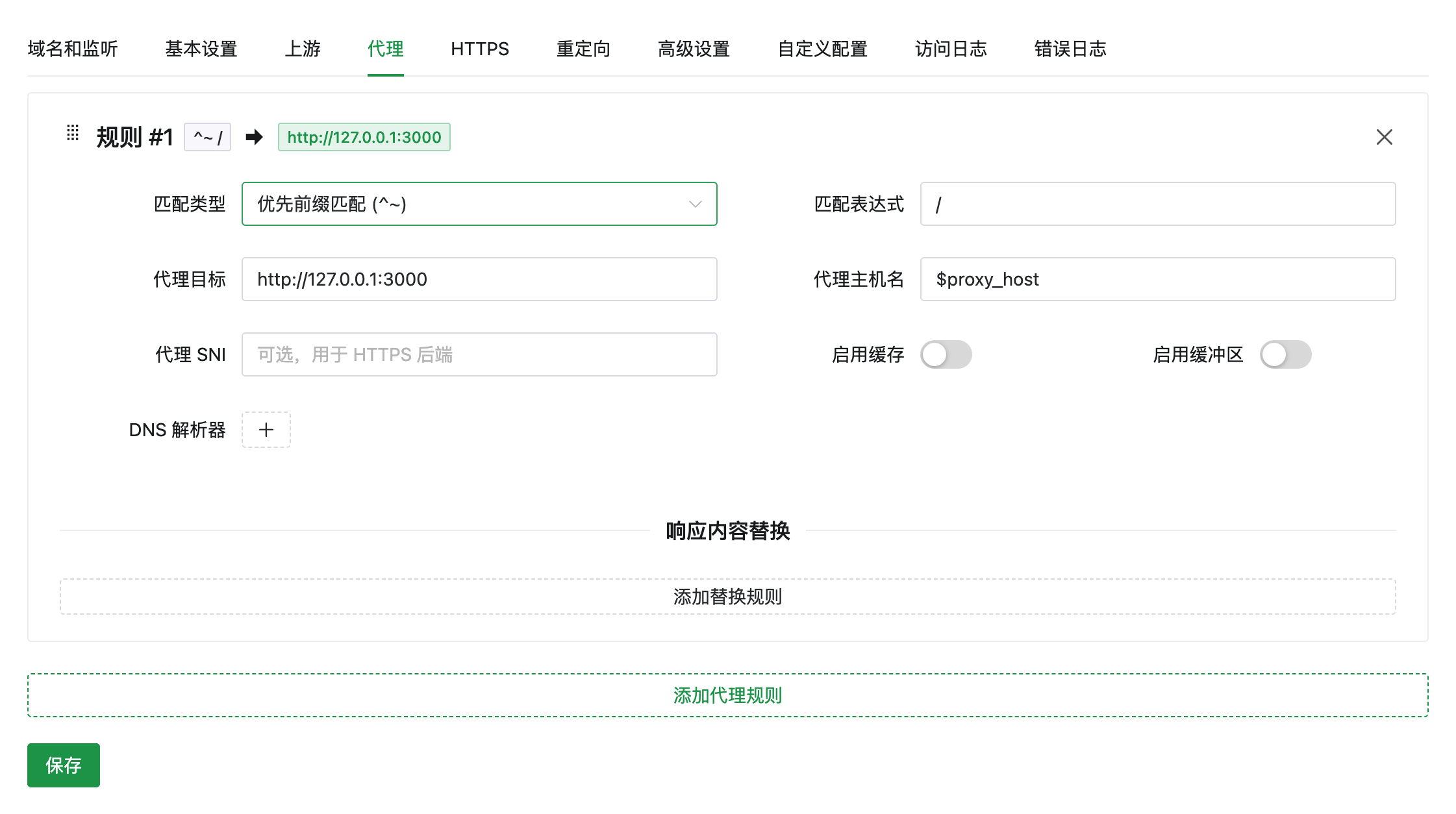
|
||||
|
||||
新的网站目录结构允许灵活添加各种自定义配置,且不易冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
## 应用中心优化
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 正式上线期待已久的容器编排模版功能,支持一键部署 WordPress、Nextcloud、GitLab 等常用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
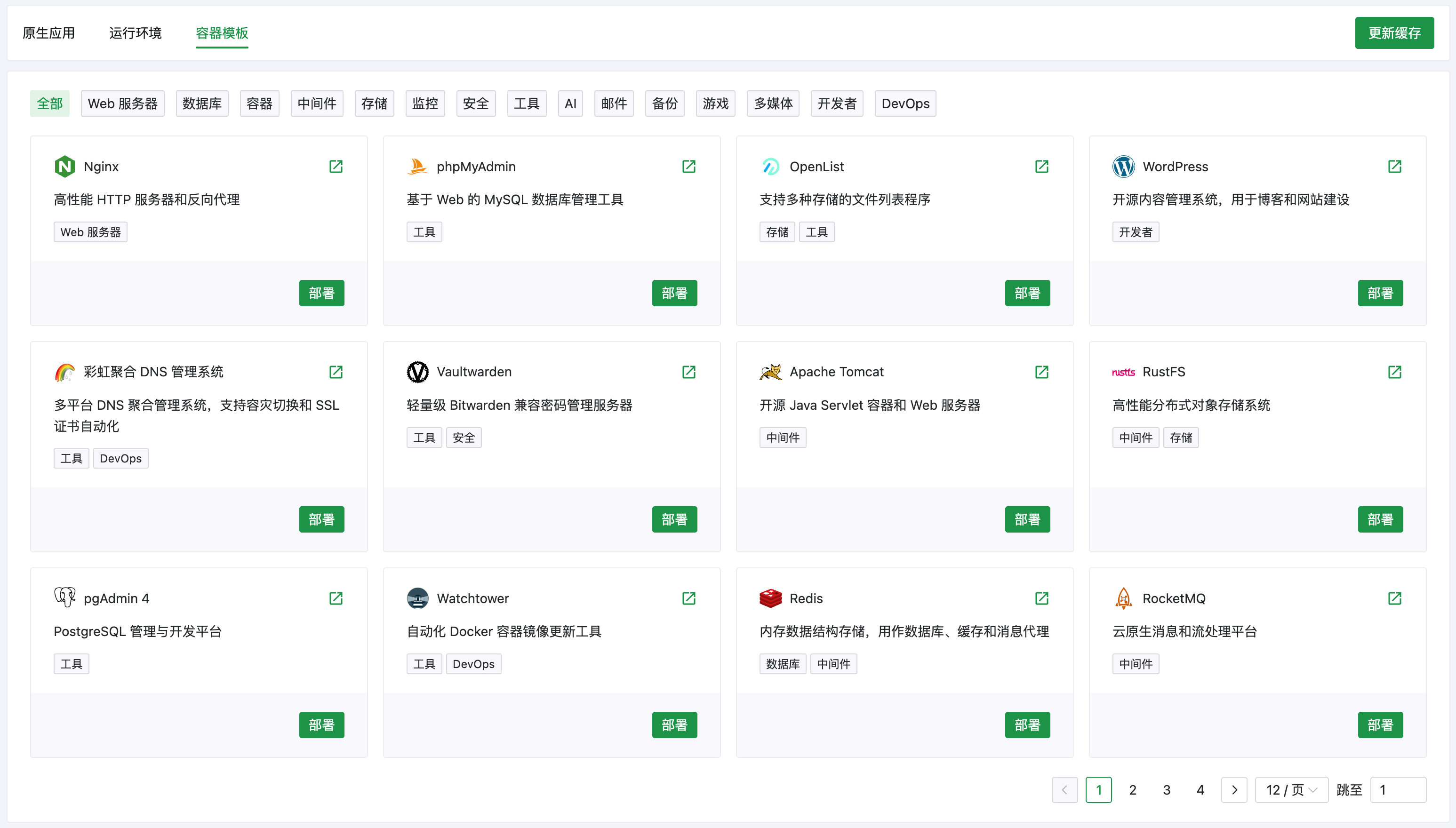
|
||||
|
||||
(缺少你想要的程序? 欢迎向 AcePanel 模版库提交 PR,方式可见文末)
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 在原有 OpenResty 与 Percona 的基础上新增 Nginx 与 MySQL、MariaDB,同时还优化了许多应用的安装流程以提高安装速度, 特别对 Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 为常用系统使用预制安装包以极大提高安装速度和成功率。
|
||||
|
||||
(实测 MySQL 通常可以在 2 分钟内完成安装)
|
||||
|
||||
## 备份优化
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 优化了备份功能,新增备份存储设置,支持添加 S3、SFTP 等常用远程存储。
|
||||
|
||||
(你可能会问为什么没有 OSS、COS? 这是因为 OSS、COS 等均提供 S3 兼容接口,可直接使用 S3 配置,因此没必要单独为它们引入依赖以及额外开发。)
|
||||
|
||||
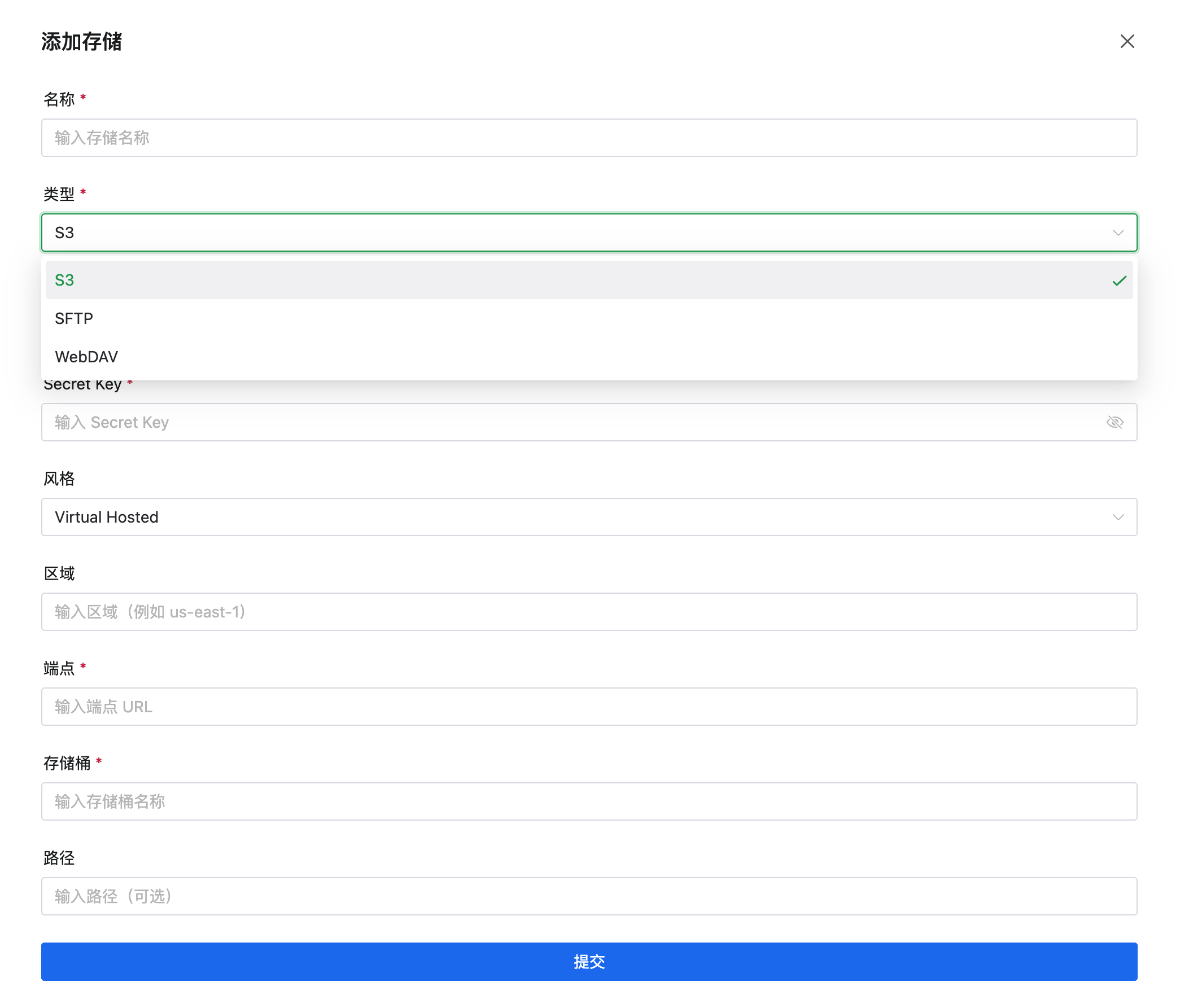
|
||||
|
||||
## 全新的面板助手
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 使用 Go 语言重写了原来基于 shell 脚本的安装器, 新的面板助手全面支持交互式安装及多语言,提供更好、更现代的用户体验。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 使用优化
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 全面优化了文件管理,还原类似 Windows 资源管理器的操作体验(支持快捷键操作)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
基于 Monaco 开发全新的文件编辑器,即是编辑器,亦可作为在线 IDE 使用(同样支持快捷键操作)。
|
||||
|
||||
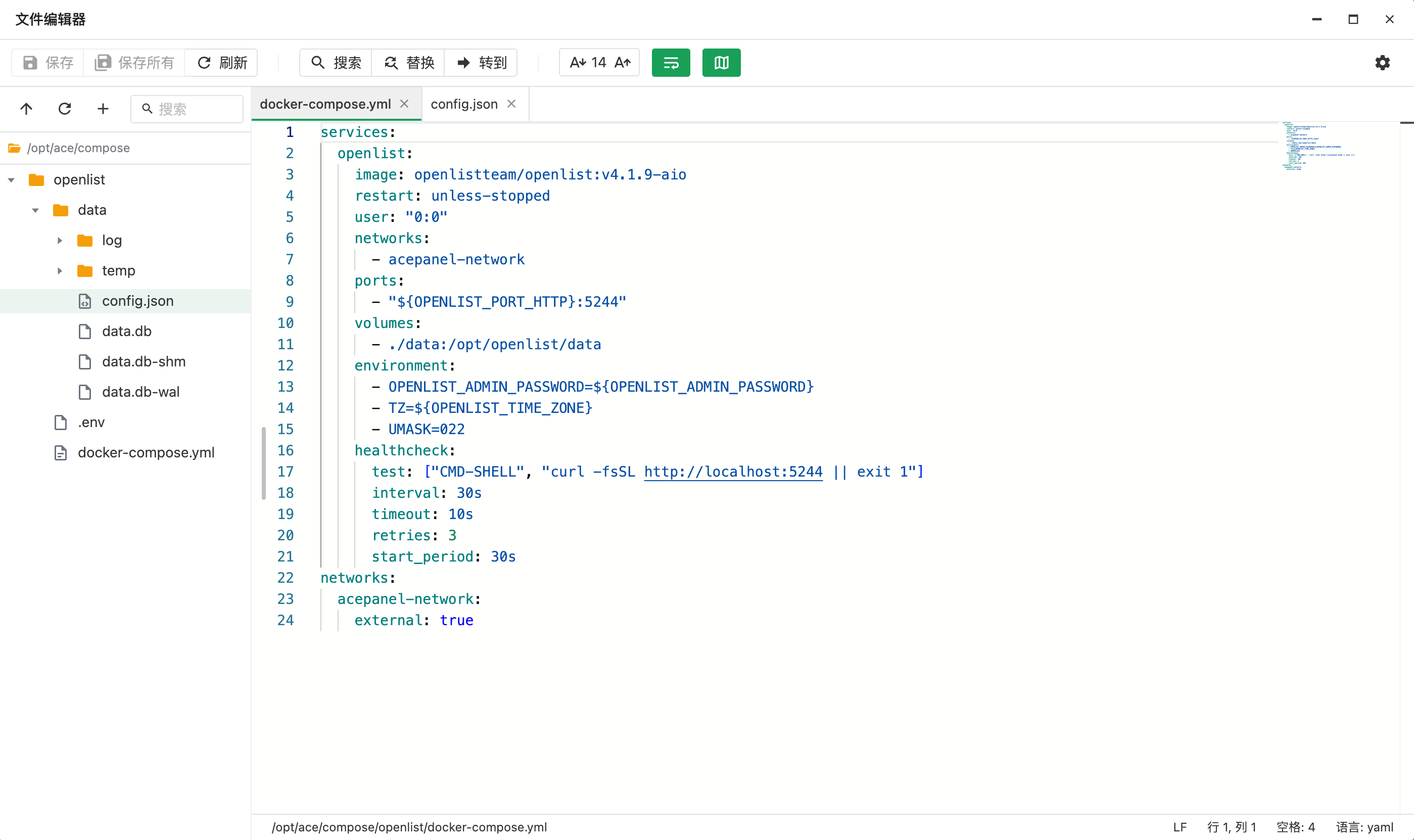
|
||||
|
||||
工具箱能力全面提升, 进程管理支持右键操作,同时新增 SSH 服务管理,磁盘管理,日志清理以及 Web 钩子等功能。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
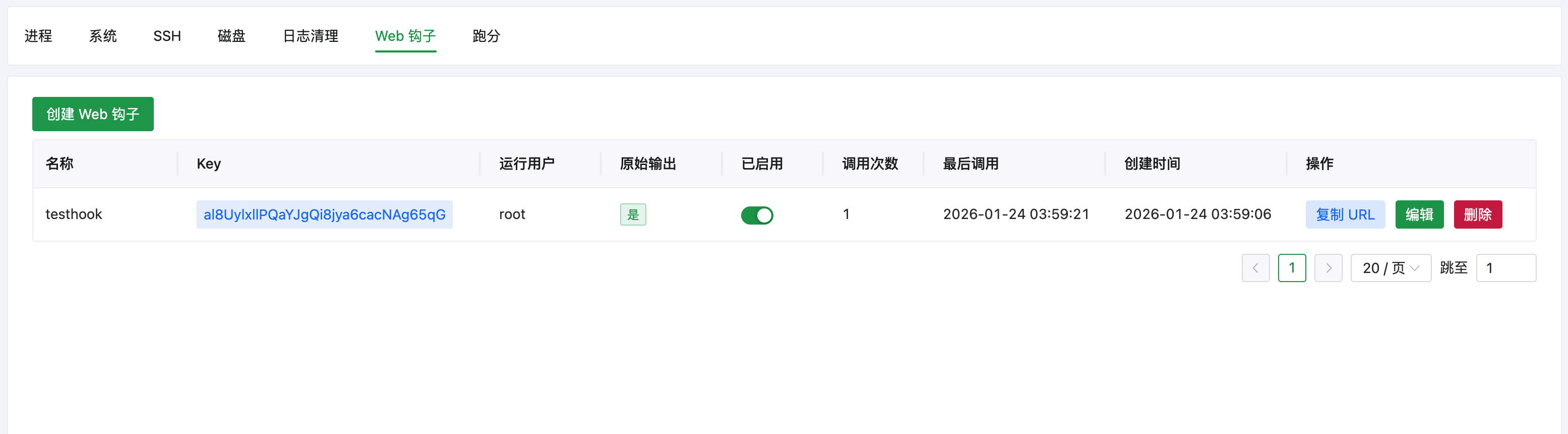
|
||||
|
||||
计划任务周期选择器重写,提供更友好的交互体验。
|
||||
|
||||
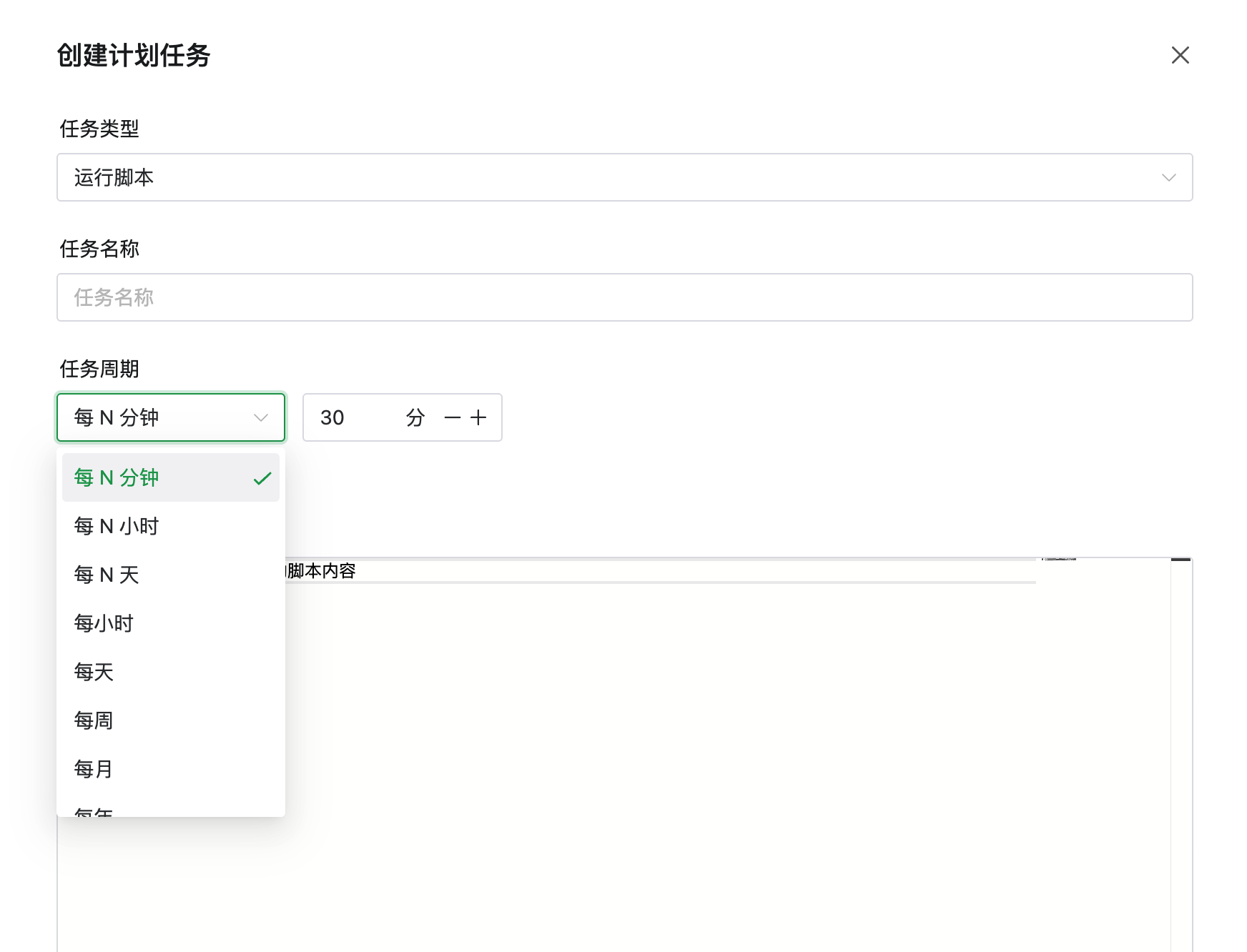
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他优化
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持使用 ACME 申请 Let's Encrypt IP 证书
|
||||
- 入口错误页支持自定义
|
||||
- 登录支持自动开启验证码
|
||||
- 自定义 Logo 与隐藏菜单支持长期保存
|
||||
- 新增操作日志记录与查看功能
|
||||
- 证书管理新增 ACME ARI 支持
|
||||
- 图标全面本地化,不再需要依赖外部 CDN
|
||||
- Nginx/OpenResty 新增 Stream 支持(四层代理)
|
||||
- 新增 PHP 8.5 支持
|
||||
- 新增 Apache Web 服务器基础支持
|
||||
- 新增 LiteSSL 证书支持
|
||||
- 容器与编排创建/启动支持实时显示进度
|
||||
- 容器支持一键进入终端
|
||||
- 资源监控支持自定义时间范围与网卡/磁盘选择
|
||||
- 首页应用支持拖拽排序
|
||||
- 文件管理支持大文件分片上传
|
||||
- 文件管理支持压缩包双击解压
|
||||
- 应用与运行环境、容器模版支持分类筛选
|
||||
- SSH 终端支持私钥登录
|
||||
- 系统工具箱 - DNS 适配现代网络管理方式
|
||||
- 支持可视化修改 Docker 基本设置
|
||||
- 数据库服务器列表支持一键进入终端
|
||||
- 部分删除操作新增 5s 倒计时确认
|
||||
|
||||
## 问题修复
|
||||
|
||||
- 修复登录超过 120 分钟后面板自动登出的问题
|
||||
- 修复 Docker 29+ 版本无法使用面板容器功能的问题
|
||||
- 修复面板偶现 ERR_CONNECTION_REFUSED 错误的问题
|
||||
- 修复面板 Websocket 会话存在资源泄露的问题
|
||||
- 修复部分情况下防火墙端口放行不生效的问题
|
||||
- 修复 PHP 设置默认 cli 版本不生效的问题
|
||||
- 修复 rsync secrets 换行符写入不正确的问题
|
||||
- 修复 fail2ban IPv6 地址显示和解封问题
|
||||
- 其他已知问题修复
|
||||
|
||||
## 兼容性变化
|
||||
|
||||
鉴于 openEuler 及 Alibaba Cloud Linux 4 和 Anolis 23 等新版信创系统把软件源改的面目全非,适配极其困难,因此 AcePanel 3.0 决定放弃对这三个发行版的支持。 建议切换到 AlmaLinux / Rocky Linux 使用, 如必须使用信创系统可考虑 OpenCloudOS 9 或 TencentOS Server 4。
|
||||
|
||||
同时 AcePanel 3.0 版本起,不再支持基于 4.x 内核的 RHEL 8-based 系统(AlmaLinux 8/Rocky Linux 8), 请升级至 9.x/10.x 使用。
|
||||
|
||||
其次为支持预制安装包以解决饱受诟病的 MySQL 编译慢问题,AcePanel 修改了默认安装目录为 `/opt/ace` 且不再允许自定义(预计影响不大,仍可在安装前挂载数据盘)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 关于旧版本升级及维护
|
||||
|
||||
计划在 AcePanel 3.0 稳定一段时间之后推出旧版耗子面板 2.x 升级至 AcePanel 3.0 的脚本, 鉴于改动较大,预计无法实现完美升级,请留意。
|
||||
|
||||
旧版耗子面板 2.x 仍将继续维护一段时间的安全更新(预计到 2026 年底), 您可在此期间自行安排时间点进行升级。
|
||||
|
||||
## 开源协议变化
|
||||
|
||||
新版本 AcePanel 决定使用更宽松的开源协议 BSD-3,希望未来能有更多的开发者参与进来,一起打造更好用的服务器面板。
|
||||
|
||||
当前可参与贡献的项目如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- [AcePanel 主程序(求star)](https://github.com/acepanel/panel)
|
||||
- [AcePanel 安装器](https://github.com/acepanel/helper)
|
||||
- [AcePanel 容器模版库](https://github.com/acepanel/templates)
|
||||
- [AcePanel 文档](https://github.com/acepanel/acepanel.github.io)
|
||||
- [AcePanel 翻译](https://zh.crowdin.com/project/acepanel)
|
||||
|
||||
不会代码? 没关系,欢迎发表使用 AcePanel 搭建各种服务、发掘不同玩法的文章,帮助推广 AcePanel。
|
||||
|
||||
## 结束语
|
||||
|
||||
写这篇文章的时候是夜里 4 点多, 转眼这个项目已经在上个月度过其 3 岁生日, 当年写下第一行代码时我还对 Go 一窍不通,如今已经成长为有些人口中的大佬。
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 是我的青春, 我希望将其写到极致而不留遗憾,因此来回重构了数次, 如果因此影响了您的使用,我在此说声道歉。 现在自己年纪也慢慢大了,加上工作与生活的琐事繁多,未来再想重构也不一定折腾得动了。
|
||||
|
||||
2026 年的 AI 已经非常强大, AcePanel 新版本中有大量复杂的交互逻辑均使用 Claude Opus 4.5 辅助开发, 我承认以我的水平难以写出这样完善的交互。 也许继续发展下去未来或将不再需要面板,而是直接对 AI 说:帮我安装 Nginx;帮我创建 xxx 项目。 谁知道呢?
|
||||
|
||||
最后,感谢赞助商微晓朵和林枫云以及参与 AcePanel 内测的所有用户, 没有你们的帮助 AcePanel 将难以如期发布。
|
||||
|
||||
附上 AcePanel 新版本的安装命令,欢迎测试体验:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash <(curl -sSLm 10 https://dl.acepanel.net/helper.sh)
|
||||
```
|
||||
17
zh_CN/quickstart/uninstall.md
Normal file
17
zh_CN/quickstart/uninstall.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
# 卸载
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger 警告
|
||||
卸载前请备份所有数据, 卸载后数据不可恢复。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 卸载步骤
|
||||
|
||||
1. 备份网站、数据库等重要数据
|
||||
2. 在面板中卸载所有已安装的应用
|
||||
3. 执行卸载命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
bash <(curl -sSLm 10 https://dl.acepanel.net/helper.sh)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
选择「卸载面板」选项完成卸载。
|
||||
33
zh_CN/quickstart/upgrade.md
Normal file
33
zh_CN/quickstart/upgrade.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
# 更新
|
||||
|
||||
## 自动更新
|
||||
|
||||
面板默认开启自动更新,每天凌晨 2 点左右会自动检测并更新。 更新期间面板会短暂不可用(通常不超过 1 分钟)。
|
||||
|
||||
关闭自动更新:「设置」->「安全」->「自动更新」。
|
||||
|
||||
## 手动更新
|
||||
|
||||
### Web 界面
|
||||
|
||||
点击首页右上角「更新」按钮, 有新版本时会弹出更新页面。
|
||||
|
||||
更新过程中请勿刷新浏览器或操作面板, 完成后页面会自动刷新。
|
||||
|
||||
### 命令行
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel update
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
适用于面板无法访问的情况。 更新过程中请勿关闭终端。
|
||||
|
||||
## 更新失败
|
||||
|
||||
如果更新后出现问题,尝试修复:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
acepanel fix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
仍有问题可到 [社区](https://tom.moe) 反馈。
|
||||
37
zh_CN/support.md
Normal file
37
zh_CN/support.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar: false
|
||||
prev: false
|
||||
next: false
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 支持
|
||||
|
||||
## 免费论坛服务
|
||||
|
||||
我们提供免费的论坛服务,您可以在论坛中提问、交流、分享面板使用中的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Moe Tom](https://tom.moe/c/technical/acepanel)
|
||||
|
||||
## 付费远程服务
|
||||
|
||||
网站报错、速度慢、被挂马? 服务器资源占用高、配置调优、入侵朔源? 我们统统一站式服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程服务价格表
|
||||
|
||||
远程服务是指我们通过远程协助的方式,帮助您解决问题。
|
||||
|
||||
| 名称 | 介绍 | 价格 |
|
||||
| ---- | ---------------- | ----- |
|
||||
| 单次服务 | 仅限一次服务,问题解决服务即结束 | ¥50 起 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 服务流程
|
||||
|
||||
1. 提前联系我们,说明问题
|
||||
2. 我们评估问题,确认是否可以解决及给出预估价格
|
||||
3. 您确认价格后,支付 50% 预付款,服务开始
|
||||
4. 服务完成后,您确认无误并支付剩余款项
|
||||
|
||||
## 联系我们
|
||||
|
||||
- [企业微信](https://work.weixin.qq.com/kfid/kfc20ea8e38b5a4e73a)
|
||||
- [QQ 826896000](https://wpa.qq.com/msgrd?v=3&uin=826896000&site=qq&menu=yes)
|
||||
8
zh_CN/version-[version].md
Normal file
8
zh_CN/version-[version].md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
# v{{ $params.version }}
|
||||
|
||||
- 版本类型:{{ $params.type == 'stable' ? '稳定版' : '测试版' }}
|
||||
- 发布时间:{{ $params.time }}
|
||||
|
||||
## 更新内容
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- @content -->
|
||||
73
zh_TW/about.md
Normal file
73
zh_TW/about.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar: false
|
||||
prev: false
|
||||
next: false
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<script setup>
|
||||
import { VPTeamMembers } from 'vitepress/theme'
|
||||
|
||||
const members = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
avatar: 'https://weavatar.com/avatar/18e77debb1bc0000c0b50757b8f1bebb2c3e4df3d494124f776c15dbc1ebe8a5',
|
||||
name: 'HaoZi',
|
||||
desc: 'Founder & CEO',
|
||||
links: [
|
||||
{ icon: 'github', link: 'https://github.com/devhaozi' },
|
||||
{ icon: 'bilibili', link: 'https://space.bilibili.com/8067' }
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
avatar: 'https://weavatar.com/avatar/f6b23deadaa481f0b3ea75ad94f246881ed2326117efebad6f2799ea165779b9',
|
||||
name: 'Liang Zai',
|
||||
desc: 'Technical Director',
|
||||
links: [
|
||||
{ icon: 'github', link: 'https://github.com/205125' }
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
|
||||
# 關於
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel is a professional server operation and maintenance management panel dedicated to providing users with simple,
|
||||
efficient, and secure server management solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
| 願景 | 使命 | 價值觀 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------- | -------------- |
|
||||
| 成為領先的伺服器管理解決方案提供商 | 讓伺服器管理變得簡單而高效 | 用戶至上、創新驅動、專業專注 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 團隊介紹
|
||||
|
||||
<VPTeamMembers size="small" :members="members" />
|
||||
|
||||
## 發展歷程
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2026 - 3.0 Era
|
||||
In 2026, We launched the highly anticipated version 3.0, introducing a revamped user interface and advanced features
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2025 - Steady Progress
|
||||
In 2025, We focused on optimizing user experience and enhancing system stability, releasing versions 2.4 series
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2024 - 全新起航
|
||||
面板得到了眾多贊助商的支持,2024 年下半年發佈了全新的 2.3 版本
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2023 - 技術積累
|
||||
使用 Go 對面板進行重寫,發佈 2.0 2.1 系列版本,積累了大量開發經驗
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::timeline 2022 - 項目立項
|
||||
2022 年中項目立項,年末發佈 1.0 版本
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 聯繫我們
|
||||
|
||||
| 名稱 | 聯繫方式 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 企業微信 | [點擊聯繫](https://work.weixin.qq.com/kfid/kfc20ea8e38b5a4e73a) |
|
||||
| QQ | [826896000](https://wpa.qq.com/msgrd?v=3&uin=826896000&site=qq&menu=yes) |
|
||||
| 電子郵件 | [haozi@loli.email](mailto:haozi@loli.email) |
|
||||
| 公司地址 | 天津市武清區黃莊街道泉里路1號智庫大廈206室 |
|
||||
661
zh_TW/advanced/api.md
Normal file
661
zh_TW/advanced/api.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,661 @@
|
||||
# API 參考文檔
|
||||
|
||||
## 概述
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel 提供了安全的 RESTful 接口,用於與面板系統進行互動。 所有 API 請求都需要進行 HMAC-SHA256 簽名認證以確保通訊的安全性和完整性。
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本信息
|
||||
|
||||
- **基本 URL**: `http(s)://your-panel-domain/{entry}/api/`
|
||||
- **內容類型**: 所有請求和響應均使用 `application/json`
|
||||
- **字符編碼**: UTF-8
|
||||
|
||||
## 身份驗證機制
|
||||
|
||||
API 使用 HMAC-SHA256 簽名算法進行身份認證。 每個請求必須包含以下 HTTP 標頭:
|
||||
|
||||
| 標頭名稱 | 描述 |
|
||||
| --------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `Content-Type` | 設置為 `application/json` |
|
||||
| `X-Timestamp` | 當前 UNIX 時間戳(秒) |
|
||||
| `Authorization` | 身份認證信息,格式為 `HMAC-SHA256 Credential={id}, Signature={signature}` |
|
||||
|
||||
## 簽名算法
|
||||
|
||||
簽名過程包含四個主要步驟:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 構造規範化請求
|
||||
|
||||
規範化請求字符串由以下部分組成,各部分之間使用換行符(\n)分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
HTTP 方法
|
||||
規範化路徑
|
||||
規範化查詢字符串
|
||||
請求體的 SHA256 哈希值
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:規範化路徑應始終使用 `/api/` 開頭的路徑部分,忽略入口前綴。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 構造待簽名字符串
|
||||
|
||||
待簽名字符串包含以下部分,各部分使用換行符(\n)分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256"
|
||||
時間戳
|
||||
規範化請求的 SHA256 哈希值
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 計算簽名
|
||||
|
||||
使用您的令牌(token)對待簽名字符串進行 HMAC-SHA256 計算,然後將結果轉換為十六進制字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 構造授權頭
|
||||
|
||||
將計算得到的簽名添加到 `Authorization` 頭:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
授權: HMAC-SHA256 Credential={id}, Signature={signature}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go 範例
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"crypto/hmac"
|
||||
"crypto/sha256"
|
||||
"encoding/hex"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
// 創建一個獲取用戶信息的請求
|
||||
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", "http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info", nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("創建請求時出錯:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 設置內容類型
|
||||
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
|
||||
|
||||
// 簽名請求 - 傳入您的用戶 ID 和 API 令牌
|
||||
if err = SignReq(req, uint(16), "YourSecretToken"); err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("簽名請求時出錯:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 發送請求
|
||||
client := &http.Client{}
|
||||
resp, err := client.Do(req)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("發送請求時出錯:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer resp.Body.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
// 處理響應
|
||||
body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("讀取響應時出錯:", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println("響應狀態:", resp.Status)
|
||||
fmt.Println("響應內容:", string(body))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SignReq 對 HTTP 請求進行簽名
|
||||
func SignReq(req *http.Request, id uint, token string) error {
|
||||
// 步驟 1:構造規範化請求
|
||||
var body []byte
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
|
||||
if req.Body != nil {
|
||||
// 讀取並保存請求體
|
||||
body, err = io.ReadAll(req.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 恢復請求體以便後續使用
|
||||
req.Body = io.NopCloser(bytes.NewReader(body))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 規範化路徑
|
||||
canonicalPath := req.URL.Path
|
||||
if !strings.HasPrefix(canonicalPath, "/api") {
|
||||
index := strings.Index(canonicalPath, "/api")
|
||||
if index != -1 {
|
||||
canonicalPath = canonicalPath[index:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
canonicalRequest := fmt.Sprintf("%s\n%s\n%s\n%s",
|
||||
req.Method,
|
||||
canonicalPath,
|
||||
req.URL.Query().Encode(),
|
||||
SHA256(string(body)))
|
||||
|
||||
// 步驟 2:設置時間戳並構造待簽名字符串
|
||||
timestamp := time.Now().Unix()
|
||||
req.Header.Set("X-Timestamp", fmt.Sprintf("%d", timestamp))
|
||||
|
||||
stringToSign := fmt.Sprintf("%s\n%d\n%s",
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256",
|
||||
timestamp,
|
||||
SHA256(canonicalRequest))
|
||||
|
||||
// 步驟 3:計算簽名
|
||||
signature := HMACSHA256(stringToSign, token)
|
||||
|
||||
// 步驟 4:設置 Authorization 頭
|
||||
authHeader := fmt.Sprintf("HMAC-SHA256 Credential=%d, Signature=%s", id, signature)
|
||||
req.Header.Set("Authorization", authHeader)
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func SHA256(str string) string {
|
||||
sum := sha256.Sum256([]byte(str))
|
||||
dst := make([]byte, hex.EncodedLen(len(sum)))
|
||||
hex.Encode(dst, sum[:])
|
||||
return string(dst)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func HMACSHA256(data string, secret string) string {
|
||||
h := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(secret))
|
||||
h.Write([]byte(data))
|
||||
return hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## PHP 範例
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* AcePanel API Request Example (PHP)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
function signRequest($method, $url, $body, $id, $token) {
|
||||
// Parse URL and get path
|
||||
$parsedUrl = parse_url($url);
|
||||
$path = $parsedUrl['path'];
|
||||
$query = isset($parsedUrl['query']) ? $parsedUrl['query'] : '';
|
||||
|
||||
// Canonical path
|
||||
$canonicalPath = $path;
|
||||
if (strpos($path, '/api') !== 0) {
|
||||
$apiPos = strpos($path, '/api');
|
||||
if ($apiPos !== false) {
|
||||
$canonicalPath = substr($path, $apiPos);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate SHA256 hash of request body
|
||||
$bodySha256 = hash('sha256', $body ?: '');
|
||||
|
||||
// Construct canonical request
|
||||
$canonicalRequest = implode("\n", [
|
||||
$method,
|
||||
$canonicalPath,
|
||||
$query,
|
||||
$bodySha256
|
||||
]);
|
||||
|
||||
// Get current timestamp
|
||||
$timestamp = time();
|
||||
|
||||
// Construct string to sign
|
||||
$stringToSign = implode("\n", [
|
||||
'HMAC-SHA256',
|
||||
$timestamp,
|
||||
hash('sha256', $canonicalRequest)
|
||||
]);
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate signature
|
||||
$signature = hash_hmac('sha256', $stringToSign, $token);
|
||||
|
||||
// Return signature and timestamp
|
||||
return [
|
||||
'timestamp' => $timestamp,
|
||||
'signature' => $signature,
|
||||
'id' => $id
|
||||
];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Example request
|
||||
$apiUrl = 'http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info';
|
||||
$method = 'GET';
|
||||
$body = ''; // For GET requests, usually no request body
|
||||
$id = 16;
|
||||
$token = 'YourSecretToken';
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate signature information
|
||||
$signingData = signRequest($method, $apiUrl, $body, $id, $token);
|
||||
|
||||
// Prepare HTTP headers
|
||||
$headers = [
|
||||
'Content-Type: application/json',
|
||||
'X-Timestamp: ' . $signingData['timestamp'],
|
||||
'Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 Credential=' . $signingData['id'] . ', Signature=' . $signingData['signature']
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
// Use cURL to send request
|
||||
$ch = curl_init($apiUrl);
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers);
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST, $method);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!empty($body)) {
|
||||
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $body);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute request and get response
|
||||
$response = curl_exec($ch);
|
||||
$statusCode = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE);
|
||||
curl_close($ch);
|
||||
|
||||
// Output results
|
||||
echo "Response Status Code: " . $statusCode . PHP_EOL;
|
||||
echo "Response Content: " . $response . PHP_EOL;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python 範例
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
import hmac
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from urllib.parse import urlparse, parse_qs
|
||||
|
||||
def sha256_hash(text):
|
||||
"""計算字符串的 SHA256 哈希值"""
|
||||
return hashlib.sha256(text.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
|
||||
|
||||
def hmac_sha256(key, message):
|
||||
"""使用 HMAC-SHA256 算法計算簽名"""
|
||||
return hmac.new(key.encode('utf-8'), message.encode('utf-8'), hashlib.sha256).hexdigest()
|
||||
|
||||
def sign_request(method, url, body, user_id, token):
|
||||
"""為 API 請求生成簽名"""
|
||||
# 解析 URL
|
||||
parsed_url = urlparse(url)
|
||||
path = parsed_url.path
|
||||
query = parsed_url.query
|
||||
|
||||
# 規範化路徑
|
||||
canonical_path = path
|
||||
if not path.startswith('/api'):
|
||||
api_pos = path.find('/api')
|
||||
if api_pos != -1:
|
||||
canonical_path = path[api_pos:]
|
||||
|
||||
# 構造規範化請求
|
||||
body_str = body if body else ""
|
||||
canonical_request = "\n".join([
|
||||
method,
|
||||
canonical_path,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
sha256_hash(body_str)
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
# 獲取當前時間戳
|
||||
timestamp = int(time.time())
|
||||
|
||||
# 構造待簽名字符串
|
||||
string_to_sign = "\n".join([
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256",
|
||||
str(timestamp),
|
||||
sha256_hash(canonical_request)
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
# 計算簽名
|
||||
signature = hmac_sha256(token, string_to_sign)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"timestamp": timestamp,
|
||||
"signature": signature,
|
||||
"id": user_id
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 範例請求
|
||||
api_url = "http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info"
|
||||
method = "GET"
|
||||
body = "" # GET 請求通常沒有請求主體
|
||||
user_id = 16
|
||||
token = "您的秘密令牌"
|
||||
|
||||
# 生成簽名信息
|
||||
signing_data = sign_request(method, api_url, body, user_id, token)
|
||||
|
||||
# 準備 HTTP 標頭
|
||||
headers = {
|
||||
"Content-Type": "application/json",
|
||||
"X-Timestamp": str(signing_data["timestamp"]),
|
||||
"Authorization": f"HMAC-SHA256 Credential={signing_data['id']}, Signature={signing_data['signature']}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 發送請求
|
||||
response = requests.request(
|
||||
method=method,
|
||||
url=api_url,
|
||||
headers=headers,
|
||||
data=body
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 輸出結果
|
||||
print(f"響應狀態碼: {response.status_code}")
|
||||
print(f"響應內容: {response.text}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Java 範例
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.net.URI;
|
||||
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
|
||||
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
|
||||
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
|
||||
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
|
||||
import java.security.MessageDigest;
|
||||
import java.time.Instant;
|
||||
import javax.crypto.Mac;
|
||||
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
|
||||
import java.util.Base64;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* AcePanel API Request Example (Java)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class AcePanelApiExample {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
// Example request
|
||||
String apiUrl = "http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info";
|
||||
String method = "GET";
|
||||
String body = ""; // For GET requests, usually no request body
|
||||
int id = 16;
|
||||
String token = "YourSecretToken";
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate signature information
|
||||
SigningData signingData = signRequest(method, apiUrl, body, id, token);
|
||||
|
||||
// Prepare HTTP request
|
||||
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
|
||||
HttpRequest.Builder requestBuilder = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
|
||||
.uri(URI.create(apiUrl))
|
||||
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
|
||||
.header("X-Timestamp", String.valueOf(signingData.timestamp))
|
||||
.header("Authorization", "HMAC-SHA256 Credential=" + signingData.id +
|
||||
", Signature=" + signingData.signature);
|
||||
|
||||
// Set request method and body
|
||||
if (method.equals("GET")) {
|
||||
requestBuilder.GET();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
requestBuilder.method(method, HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(body));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
HttpRequest request = requestBuilder.build();
|
||||
|
||||
// Send request
|
||||
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
|
||||
|
||||
// Output results
|
||||
System.out.println("Response Status Code: " + response.statusCode());
|
||||
System.out.println("Response Content: " + response.body());
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (Exception e) {
|
||||
e.printStackTrace();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static class SigningData {
|
||||
long timestamp;
|
||||
String signature;
|
||||
int id;
|
||||
|
||||
SigningData(long timestamp, String signature, int id) {
|
||||
this.timestamp = timestamp;
|
||||
this.signature = signature;
|
||||
this.id = id;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public static SigningData signRequest(String method, String url, String body, int id, String token) throws Exception {
|
||||
// Parse URL
|
||||
URI uri = new URI(url);
|
||||
String path = uri.getPath();
|
||||
String query = uri.getQuery() != null ? uri.getQuery() : "";
|
||||
|
||||
// Canonical path
|
||||
String canonicalPath = path;
|
||||
if (!path.startsWith("/api")) {
|
||||
int apiPos = path.indexOf("/api");
|
||||
if (apiPos != -1) {
|
||||
canonicalPath = path.substring(apiPos);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate SHA256 hash of request body
|
||||
String bodySha256 = sha256Hash(body != null ? body : "");
|
||||
|
||||
// Construct canonical request
|
||||
String canonicalRequest = String.join("\n",
|
||||
method,
|
||||
canonicalPath,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
bodySha256);
|
||||
|
||||
// Get current timestamp
|
||||
long timestamp = Instant.now().getEpochSecond();
|
||||
|
||||
// Construct string to sign
|
||||
String stringToSign = String.join("\n",
|
||||
"HMAC-SHA256",
|
||||
String.valueOf(timestamp),
|
||||
sha256Hash(canonicalRequest));
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate signature
|
||||
String signature = hmacSha256(token, stringToSign);
|
||||
|
||||
// Return signature and timestamp
|
||||
return new SigningData(timestamp, signature, id);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static String sha256Hash(String text) throws Exception {
|
||||
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
|
||||
byte[] hash = digest.digest(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
|
||||
return bytesToHex(hash);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static String hmacSha256(String key, String message) throws Exception {
|
||||
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
|
||||
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "HmacSHA256");
|
||||
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
|
||||
byte[] hash = mac.doFinal(message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
|
||||
return bytesToHex(hash);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
|
||||
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
|
||||
for (byte b : bytes) {
|
||||
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
|
||||
if (hex.length() == 1) {
|
||||
hexString.append('0');
|
||||
}
|
||||
hexString.append(hex);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return hexString.toString();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Node.js 範例
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const crypto = require('crypto');
|
||||
const axios = require('axios');
|
||||
const url = require('url');
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 計算字符串的 SHA256 哈希值
|
||||
* @param {string} text 待哈希的字符串
|
||||
* @returns {string} 哈希結果(十六進制)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function sha256Hash(text) {
|
||||
return crypto.createHash('sha256').update(text || '').digest('hex');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 使用 HMAC-SHA256 算法計算簽名
|
||||
* @param {string} key 密鑰
|
||||
* @param {string} message 待簽名的消息
|
||||
* @returns {string} 簽名結果(十六進制)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function hmacSha256(key, message) {
|
||||
return crypto.createHmac('sha256', key).update(message).digest('hex');
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 為 API 請求生成簽名
|
||||
* @param {string} method HTTP 方法
|
||||
* @param {string} apiUrl API 地址
|
||||
* @param {string} body 請求體
|
||||
* @param {number} id 用戶 ID
|
||||
* @param {string} token 密鑰
|
||||
* @returns {object} 包含簽名、時間戳和 ID 的對象
|
||||
*/
|
||||
function signRequest(method, apiUrl, body, id, token) {
|
||||
// 解析 URL
|
||||
const parsedUrl = new url.URL(apiUrl);
|
||||
const path = parsedUrl.pathname;
|
||||
const query = parsedUrl.search.slice(1); // 移除開頭的 '?'
|
||||
|
||||
// 規範化路徑
|
||||
let canonicalPath = path;
|
||||
if (!path.startsWith('/api')) {
|
||||
const apiPos = path.indexOf('/api');
|
||||
if (apiPos !== -1) {
|
||||
canonicalPath = path.slice(apiPos);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 構造規範化請求
|
||||
const canonicalRequest = [
|
||||
method,
|
||||
canonicalPath,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
sha256Hash(body || '')
|
||||
].join('\n');
|
||||
|
||||
// 獲取當前時間戳
|
||||
const timestamp = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
|
||||
|
||||
// 構造待簽名字符串
|
||||
const stringToSign = [
|
||||
'HMAC-SHA256',
|
||||
timestamp,
|
||||
sha256Hash(canonicalRequest)
|
||||
].join('\n');
|
||||
|
||||
// 計算簽名
|
||||
const signature = hmacSha256(token, stringToSign);
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
timestamp,
|
||||
signature,
|
||||
id
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 發送 API 請求
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async function sendApiRequest() {
|
||||
// 範例請求參數
|
||||
const apiUrl = 'http://example.com/entrance/api/user/info';
|
||||
const method = 'GET';
|
||||
const body = ''; // GET 請求通常沒有請求體
|
||||
const id = 16;
|
||||
const token = '您的秘密令牌';
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
// 生成簽名信息
|
||||
const signingData = signRequest(method, apiUrl, body, id, token);
|
||||
|
||||
// 準備 HTTP 標頭
|
||||
const headers = {
|
||||
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
|
||||
'X-Timestamp': signingData.timestamp,
|
||||
'Authorization': `HMAC-SHA256 Credential=${signingData.id}, Signature=${signingData.signature}`
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// 發送請求
|
||||
const response = await axios({
|
||||
method,
|
||||
url: apiUrl,
|
||||
headers,
|
||||
data: body || undefined
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 輸出結果
|
||||
console.log(`響應狀態碼: ${response.status}`);
|
||||
console.log(`響應內容: ${JSON.stringify(response.data)}`);
|
||||
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('請求錯誤:', error.message);
|
||||
if (error.response) {
|
||||
console.error(`響應狀態碼: ${error.response.status}`);
|
||||
console.error(`響應內容: ${JSON.stringify(error.response.data)}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 執行請求
|
||||
sendApiRequest();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 常見響應碼
|
||||
|
||||
| HTTP 狀態碼 | 描述 |
|
||||
| -------- | ------- |
|
||||
| 200 | 請求成功 |
|
||||
| 401 | 身份驗證失敗 |
|
||||
| 403 | 權限不足 |
|
||||
| 404 | 資源不存在 |
|
||||
| 422 | 請求參數錯誤 |
|
||||
| 500 | 伺服器內部錯誤 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 安全建議
|
||||
|
||||
1. **保護您的 API 令牌**:不要在客戶端代碼中硬編碼或公開您的 API 令牌
|
||||
2. **定期輪換令牌**:定期更改您的 API 令牌以提高安全性
|
||||
3. **配置 IP 白名單**:在生產環境中使用 IP 白名單限制訪問
|
||||
|
||||
## 常見問題解答
|
||||
|
||||
### 簽名驗證失敗
|
||||
|
||||
如果遇到簽名驗證失敗,請檢查:
|
||||
|
||||
- 確保使用了正確的 API 令牌和 ID
|
||||
- 檢查客戶端和伺服器時間是否準確;時間戳之間的差異超過 300 秒將導致驗證失敗
|
||||
- 確保請求主體在計算簽名前後沒有被修改
|
||||
- 確保 URL 路徑處理正確;請記住在規範化路徑時要移除入口前綴
|
||||
|
||||
### 請求超時
|
||||
|
||||
- 檢查網絡連接
|
||||
- 確認伺服器狀態
|
||||
- 考慮增加客戶端的超時設置
|
||||
40
zh_TW/advanced/app.md
Normal file
40
zh_TW/advanced/app.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
# Application
|
||||
|
||||
The application module is one of the core features of AcePanel, used to manage various software on the server. Through the application module, you can conveniently install, configure, and manage common software such as Web servers, databases, runtime environments, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Categories
|
||||
|
||||
The application module is divided into three parts:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Native Applications**: Software installed directly on the system, such as Nginx, MySQL, Redis, etc.
|
||||
- **Runtime Environments**: Runtime environments for various programming languages, such as PHP, Node.js, Python, Go, Java, etc.
|
||||
- **Container Templates**: One-click deployment templates based on Docker, for quickly deploying various applications
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Native Application vs Container Template
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Native Application | Container Template |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ---------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Performance | Higher | Slight overhead |
|
||||
| Isolation | Shared system environment | Fully isolated |
|
||||
| Deployment Difficulty | Requires configuration | One-click deployment |
|
||||
| Resource Usage | Lower | Higher |
|
||||
| Use Cases | Production environment, high performance needs | Quick testing, multiple version coexistence |
|
||||
|
||||
## Application Categories
|
||||
|
||||
Native applications are preset with multiple categories by function, including but not limited to:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Web Servers**: Nginx, OpenResty, Apache
|
||||
- **Databases**: MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Percona
|
||||
- **Containers**: Docker, Podman
|
||||
- **Middleware**: Redis, Memcached
|
||||
- **Storage**: MinIO, S3fs
|
||||
- **Tools**: phpMyAdmin, Pure-FTPd, Supervisor, Rsync, Frp
|
||||
|
||||
## Next Steps
|
||||
|
||||
- [Native Applications](./app/native) - Learn how to install and manage native applications
|
||||
- [Runtime Environments](./app/environment) - Learn how to install programming language runtime environments
|
||||
- [Container Templates](./app/template) - Learn how to use container templates to quickly deploy applications
|
||||
98
zh_TW/advanced/app/environment.md
Normal file
98
zh_TW/advanced/app/environment.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
# Runtime Environment
|
||||
|
||||
Runtime environments are used to install runtimes for various programming languages, providing execution environments for websites and projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Languages
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel supports runtime environments for the following programming languages:
|
||||
|
||||
| Language | Available Versions | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Go | 1.20 - 1.25 | Suitable for building high-performance backend services |
|
||||
| Java | JDK 8, 11, 17, 21, 25 | Uses Amazon Corretto distribution |
|
||||
| Node.js | 20, 22, 24 | Suitable for frontend builds and Node applications |
|
||||
| PHP | 7.4 - 8.5 | Suitable for Web development |
|
||||
| Python | 3.10 - 3.14 | Suitable for scripts and Web applications |
|
||||
|
||||
## Runtime Environment List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the **Applications** page, click the **Runtime Environment** tab to view available runtime environments:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click the language category at the top to filter versions for a specific language:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Install Runtime Environment
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the **Applications** page
|
||||
2. Click the **Runtime Environment** tab
|
||||
3. Select the desired language category (or view all)
|
||||
4. Click the **Install** button for the corresponding version
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Version Selection Recommendations
|
||||
|
||||
- Production environments are recommended to use LTS (Long Term Support) versions
|
||||
- Versions marked "End of Life" are not recommended for new projects
|
||||
- Multiple versions can be installed simultaneously and specified for use in projects
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Manage Runtime Environment
|
||||
|
||||
Installed runtime environments will display a **Manage** button. Click to enter the management page:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Running Status
|
||||
|
||||
Displays the current status of the runtime environment, providing operations such as start, stop, restart, and reload.
|
||||
|
||||
### Module Management (PHP)
|
||||
|
||||
PHP runtime environment provides module management functionality, allowing installation or uninstallation of various PHP modules:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Common modules include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **OPcache**: PHP bytecode cache, improves performance
|
||||
- **Redis**: Connect to Redis database
|
||||
- **ImageMagick**: Image processing
|
||||
- **Swoole/Swow**: High-performance asynchronous framework
|
||||
- **ionCube**: PHP code encryption and decryption
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Files
|
||||
|
||||
You can edit PHP's main configuration file (php.ini) and FPM configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set as CLI Default Version
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Set as CLI Default Version** button to set the current version as the default PHP version used by the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multiple Version Coexistence
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel supports multiple versions of the same language coexisting. For example, you can install both PHP 7.4 and PHP 8.3 simultaneously, and different websites can use different PHP versions.
|
||||
|
||||
Installation path rules:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Go**: `/opt/ace/server/go/version`
|
||||
- **Java**: `/opt/ace/server/java/version`
|
||||
- **Node.js**: `/opt/ace/server/nodejs/version`
|
||||
- **PHP**: `/opt/ace/server/php/version`
|
||||
- **Python**: `/opt/ace/server/python/version`
|
||||
|
||||
## Using in Projects
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a project, you can select the runtime environment version to use in the project settings. See [Project Management](../project) documentation for details.
|
||||
|
||||
## Update Runtime Environment
|
||||
|
||||
When a new version is available, the latest version number will be displayed in the list. You can:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Uninstall the old version and install the new version
|
||||
2. Keep the old version and install the new version simultaneously (recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
Updating runtime environment versions may cause compatibility issues with projects that depend on that version. Please verify in a test environment before updating the production environment.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
83
zh_TW/advanced/app/native.md
Normal file
83
zh_TW/advanced/app/native.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
# Native Applications
|
||||
|
||||
Native applications are software installed directly on the system, offering better performance and lower resource usage compared to containerized deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
## Application List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the **Applications** page, which displays the native application list by default. You can filter different types of applications through the category tabs at the top.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Application Name**: Software name
|
||||
- **Description**: Brief description of the software
|
||||
- **Installed Version**: Currently installed version number (empty if not installed)
|
||||
- **Show on Homepage**: Whether to display in the quick applications on the panel homepage
|
||||
- **Actions**: Install, manage, or uninstall
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Application
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Install** button on the right side of the application, and an installation dialog will pop up:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Select Channel
|
||||
|
||||
Some applications provide multiple version channels. Click the dropdown to select the desired version series:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Select Version
|
||||
|
||||
After selecting a channel, the system will automatically fill in the latest version number for that channel:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Install** button to start installation. During installation, you can view detailed logs on the **Tasks** page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Manage Application
|
||||
|
||||
Installed applications will display a **Manage** button. Click to enter the application management page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Running Status
|
||||
|
||||
The management page first displays the application's running status:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The following operations are provided:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Start**: Start a stopped service
|
||||
- **Stop**: Stop a running service
|
||||
- **Restart**: Restart the service (will interrupt connections)
|
||||
- **Reload**: Reload configuration (without interrupting connections, recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
### Modify Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Modify Configuration** tab to directly edit the application's configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
Please ensure you understand the meaning of each parameter before modifying configuration files. Incorrect configuration may prevent the service from starting.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### View Logs
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Run Log** or **Error Log** tab to view application logs, which is helpful for troubleshooting.
|
||||
|
||||
## Uninstall Application
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Uninstall** button to uninstall the application. Before uninstalling, please ensure:
|
||||
|
||||
1. No websites or projects depend on this application
|
||||
2. Important configuration files and data have been backed up
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger Warning
|
||||
Uninstalling database applications (such as MySQL, PostgreSQL) will delete all database data. Please make sure to backup in advance!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Homepage Shortcut
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling the **Show on Homepage** switch, the application will appear in the quick applications area on the panel homepage for quick access to the management page.
|
||||
99
zh_TW/advanced/app/template.md
Normal file
99
zh_TW/advanced/app/template.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# Container Templates
|
||||
|
||||
Container templates provide Docker-based one-click deployment solutions for quickly deploying various common applications without manual configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using container templates, you need to install Docker first:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to **Applications** > **Native Applications**
|
||||
2. Find Docker, click **Install**
|
||||
3. Wait for installation to complete
|
||||
|
||||
## Template List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the **Applications** page, click the **Container Templates** tab to view available templates:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Deploy Application
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Deploy** button on the template card to start the deployment wizard.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Select Deployment Mode
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Create New Compose**: Create a new Docker Compose from the template
|
||||
- **Update Existing Compose**: Use the template to update an existing compose configuration
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Configure Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
Fill in configuration information according to application requirements:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Common configuration items:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Compose Name**: Used to identify this deployment
|
||||
- **Auto Start**: Whether to automatically start containers after creation
|
||||
- **Auto Firewall**: Whether to automatically allow ports
|
||||
- **Database Configuration**: Username, password, address, etc.
|
||||
- **Port Configuration**: Port the service listens on
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Preview and Edit
|
||||
|
||||
Preview the generated Docker Compose configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here you can:
|
||||
|
||||
- View and edit the **Compose File** (docker-compose.yml)
|
||||
- View and edit **Environment Variables**
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Confirm Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
After confirming all configurations are correct, click **Create** to complete deployment:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After deployment, the application will appear in the **Containers** > **Compose** page for management.
|
||||
|
||||
## Template vs Manual Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Using Template | Manual Deployment |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Configuration Difficulty | Simple, just fill in basic information | Need to write docker-compose.yml |
|
||||
| Flexibility | Uses preset configuration | Fully customizable |
|
||||
| Use Cases | Quick deployment of common applications | Special requirements, custom configuration |
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Template Descriptions
|
||||
|
||||
### WordPress
|
||||
|
||||
Open-source blog and content management system, suitable for building personal blogs or corporate websites.
|
||||
|
||||
### pgAdmin 4
|
||||
|
||||
Graphical management tool for PostgreSQL databases.
|
||||
|
||||
### phpMyAdmin
|
||||
|
||||
Graphical management tool for MySQL/MariaDB databases.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vaultwarden
|
||||
|
||||
Lightweight password management server, compatible with Bitwarden clients.
|
||||
|
||||
### Qinglong
|
||||
|
||||
Scheduled task management platform, supporting Python, JavaScript, Shell, and other scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenList
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-storage aggregation file listing program, supporting Alibaba Cloud Drive, OneDrive, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Update Cache
|
||||
|
||||
If the template list is incomplete or you need to get the latest templates, click the **Update Cache** button at the top of the page to refresh the template list.
|
||||
231
zh_TW/advanced/backup.md
Normal file
231
zh_TW/advanced/backup.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
|
||||
# Backup
|
||||
|
||||
The backup module is used to backup and restore website files and databases, supporting local backup and remote storage.
|
||||
|
||||
## Backup Page
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Backup Types
|
||||
|
||||
The backup module supports the following types of backups:
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | -------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Website | Backup website files |
|
||||
| MySQL | Backup Percona/MySQL/MariaDB databases |
|
||||
| PostgreSQL | Backup PostgreSQL databases |
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Backup
|
||||
|
||||
1. Select the backup type tab (Website/MySQL/PostgreSQL)
|
||||
2. Click **Create Backup**
|
||||
3. Select the website or database to backup
|
||||
4. Select storage location
|
||||
5. Click Confirm
|
||||
|
||||
Backup file formats:
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: `.zip` compressed package
|
||||
- Database: `.sql.zip` compressed SQL file
|
||||
|
||||
## Backup List
|
||||
|
||||
The backup list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Filename**: Backup file name
|
||||
- **Size**: Backup file size
|
||||
- **Update Date**: Backup time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Download, restore, delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Restore Backup
|
||||
|
||||
1. Find the backup to restore in the backup list
|
||||
2. Click the **Restore** button
|
||||
3. Confirm the restore operation
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger Warning
|
||||
The restore operation will overwrite existing data. Please ensure you have backed up current data!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Upload Backup
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Upload Backup** button to upload local backup files for data restoration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Storage Management
|
||||
|
||||
Switch to the **Storage** tab to manage backup storage locations.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Local Storage
|
||||
|
||||
The default storage location, backup files are saved locally on the server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Remote Storage
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Add Storage** to add remote storage, supporting:
|
||||
|
||||
- **S3 Compatible Storage**: AWS S3, Alibaba Cloud OSS, Tencent Cloud COS, etc.
|
||||
- **FTP/SFTP**: FTP or SFTP servers
|
||||
- **WebDAV**: WebDAV servers
|
||||
|
||||
Advantages of remote storage:
|
||||
|
||||
- Off-site backup to prevent data loss
|
||||
- Does not occupy server disk space
|
||||
- Convenient for sharing backups across multiple servers
|
||||
|
||||
### S3 Compatible Storage Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
S3 compatible storage is the most commonly used remote storage method. Most cloud storage providers offer S3 compatible interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Configuration Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Name | Name of the storage configuration for identification |
|
||||
| Type | Select S3 |
|
||||
| Access Key | Access Key ID |
|
||||
| Secret Key | Access Key Secret |
|
||||
| Style | Virtual Hosted or Path Style |
|
||||
| Region | Region code, e.g., `us-east-1`, `cn-hangzhou` |
|
||||
| Endpoint | S3 service endpoint URL |
|
||||
| Protocol | HTTPS (recommended) or HTTP |
|
||||
| Bucket | Bucket name |
|
||||
| Path | Sub-path for backup file storage (optional) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Access Style Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
S3 has two URL access styles:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Virtual Hosted Style**: `https://bucket.endpoint/key`
|
||||
- Bucket name as subdomain
|
||||
- AWS S3 uses this style by default
|
||||
|
||||
- **Path Style**: `https://endpoint/bucket/key`
|
||||
- Bucket name as part of the path
|
||||
- Self-hosted MinIO typically uses this style
|
||||
|
||||
#### Compatibility List
|
||||
|
||||
| Provider | Documentation | Compatible Access Style | Compatibility |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | --------------------------------- | ------------- |
|
||||
| Alibaba Cloud OSS | [Docs](https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/410748.html) | Virtual Hosted Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Tencent Cloud COS | [Docs](https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/436/41284) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Qiniu Cloud | [Docs](https://developer.qiniu.com/kodo/4088/s3-access-domainname) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Baidu Cloud BOS | [Docs](https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/BOS/s/Fjwvyq9xo) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| JD Cloud | [Docs](https://docs.jdcloud.com/cn/object-storage-service/api/regions-and-endpoints) | Virtual Hosted Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Kingsoft Cloud | [Docs](https://docs.ksyun.com/documents/6761) | Virtual Hosted Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| QingCloud QingStor | [Docs](https://docsv3.qingcloud.com/storage/object-storage/s3/intro/) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| NetEase Shufan | [Docs](https://sf.163.com/help/documents/89796157866430464) | Virtual Hosted Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Cloudflare R2 | [Docs](https://developers.cloudflare.com/r2/data-access/s3-api/) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Oracle Cloud | [Docs](https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Object/Tasks/s3compatibleapi.htm) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Upyun | [Docs](https://help.upyun.com/knowledge-base/aws-s3%E5%85%BC%E5%AE%B9/) | Virtual Hosted Style / Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Self-hosted MinIO | - | Path Style | ✅ |
|
||||
| Huawei Cloud OBS | - | Virtual Hosted Style | ❓ |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Note
|
||||
Huawei Cloud official documentation does not specify S3 API compatibility, but it works in actual testing.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
#### Configuration Examples
|
||||
|
||||
**Alibaba Cloud OSS**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Name: aliyun-oss
|
||||
Type: S3
|
||||
Access Key: Your AccessKey ID
|
||||
Secret Key: Your AccessKey Secret
|
||||
Style: Virtual Hosted
|
||||
Region: cn-hangzhou
|
||||
Endpoint: oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
|
||||
Protocol: HTTPS
|
||||
Bucket: your-bucket-name
|
||||
Path: backup (optional)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Tencent Cloud COS**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Name: tencent-cos
|
||||
Type: S3
|
||||
Access Key: Your SecretId
|
||||
Secret Key: Your SecretKey
|
||||
Style: Virtual Hosted
|
||||
Region: ap-guangzhou
|
||||
Endpoint: cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com
|
||||
Protocol: HTTPS
|
||||
Bucket: your-bucket-name
|
||||
Path: backup (optional)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Cloudflare R2**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Name: cloudflare-r2
|
||||
Type: S3
|
||||
Access Key: Your Access Key ID
|
||||
Secret Key: Your Secret Access Key
|
||||
Style: Path Style
|
||||
Region: auto
|
||||
Endpoint: <account-id>.r2.cloudflarestorage.com
|
||||
Protocol: HTTPS
|
||||
Bucket: your-bucket-name
|
||||
Path: backup (optional)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Self-hosted MinIO**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Name: minio
|
||||
Type: S3
|
||||
Access Key: minioadmin
|
||||
Secret Key: minioadmin
|
||||
Style: Path Style
|
||||
Region: us-east-1
|
||||
Endpoint: minio.example.com:9000
|
||||
Protocol: HTTP or HTTPS
|
||||
Bucket: backup
|
||||
Path: (optional)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
|
||||
- Please ensure the bucket has been created and has correct access permissions
|
||||
- It is recommended to create dedicated access keys for backups with limited permissions
|
||||
- Some providers' Endpoints need to include region information
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Scheduled Backup
|
||||
|
||||
Combined with the [Scheduled Tasks](./task/schedule) feature, you can set up automatic scheduled backups:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to **Tasks** > **Scheduled Tasks**
|
||||
2. Create a new task
|
||||
3. Select backup type
|
||||
4. Set execution schedule
|
||||
5. Select storage location
|
||||
|
||||
## Backup Strategy Recommendations
|
||||
|
||||
### Backup Frequency
|
||||
|
||||
| Data Type | Recommended Frequency |
|
||||
| ------------------- | ------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Database | Daily |
|
||||
| Website Files | Weekly |
|
||||
| Configuration Files | Immediately after modification |
|
||||
|
||||
### Retention Policy
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep daily backups for the last 7 days
|
||||
- Keep weekly backups for the last 4 weeks
|
||||
- Keep monthly backups for the last 3 months
|
||||
|
||||
### Storage Location
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep at least one local backup
|
||||
- Important data should also be backed up to remote storage
|
||||
- Regularly verify the integrity of backup files
|
||||
81
zh_TW/advanced/cert.md
Normal file
81
zh_TW/advanced/cert.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
# Certificate
|
||||
|
||||
The certificate module is used to manage SSL/TLS certificates, supporting automatic free certificate application through the ACME protocol, as well as uploading your own certificates.
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The certificate module is divided into three parts:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------------- | ---------------------------- |
|
||||
| [Certificate](./cert/cert) | Manage SSL certificates |
|
||||
| [Account](./cert/account) | Manage ACME accounts |
|
||||
| [DNS](./cert/dns) | Manage DNS API configuration |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Certificate Types
|
||||
|
||||
### Free Certificates
|
||||
|
||||
Automatically apply for free certificates from CAs like Let's Encrypt through the ACME protocol:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Let's Encrypt**: The most popular free certificate authority
|
||||
- **LiteSSL**: Free certificate service provided by TrustAsia
|
||||
- **Google**: Google's free certificate service
|
||||
- **GoogleCN**: Google certificate service mirror provided by AcePanel
|
||||
- **ZeroSSL**: Another free certificate option
|
||||
- **Buypass**: Norwegian free certificate service
|
||||
|
||||
Free certificates are typically valid for 90 days, and AcePanel supports automatic renewal.
|
||||
|
||||
### Paid Certificates
|
||||
|
||||
Certificates purchased from commercial CAs, typically valid for 1 year or longer:
|
||||
|
||||
- Longer validity period
|
||||
- Higher trust level
|
||||
- Provides insurance and technical support
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to purchase certificates, you can contact us through the "Certificate" link at the top of this page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Verification Methods
|
||||
|
||||
When applying for a certificate, you need to verify domain ownership. The following methods are supported:
|
||||
|
||||
### HTTP Verification
|
||||
|
||||
Place a verification file in the website root directory, and the CA verifies through HTTP access.
|
||||
|
||||
Requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- Domain is resolved to the server
|
||||
- Port 80 is accessible
|
||||
|
||||
### DNS Verification
|
||||
|
||||
Add a TXT record in the domain DNS for verification.
|
||||
|
||||
Requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- Have DNS management permissions for the domain
|
||||
- Configure DNS API (for automatic verification)
|
||||
|
||||
Advantages of DNS verification:
|
||||
|
||||
- Supports applying for wildcard certificates (\*.example.com)
|
||||
- Does not require port 80 to be accessible
|
||||
- Suitable for intranet servers
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create an ACME account (first time use)
|
||||
2. If DNS verification is needed, configure DNS API
|
||||
3. Create a certificate, select verification method
|
||||
4. Apply the certificate to the website
|
||||
|
||||
## Next Steps
|
||||
|
||||
- [Certificate Management](./cert/cert) - Learn how to apply for and manage certificates
|
||||
- [Account Management](./cert/account) - Learn how to manage ACME accounts
|
||||
- [DNS Configuration](./cert/dns) - Learn how to configure DNS API
|
||||
84
zh_TW/advanced/cert/account.md
Normal file
84
zh_TW/advanced/cert/account.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
# Account Management
|
||||
|
||||
The account management page is used to manage ACME accounts. ACME accounts are used to apply for certificates from certificate authorities.
|
||||
|
||||
## Account List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Certificate** > **Account** tab to view the account list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Email**: Account email
|
||||
- **CA**: Certificate Authority
|
||||
- **Key Type**: Account key type
|
||||
- **Actions**: Modify, delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Account
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create Account** button
|
||||
2. Fill in the configuration:
|
||||
- **Email**: Used to receive certificate-related notifications
|
||||
- **CA**: Select certificate authority
|
||||
- **Key Type**: Select key algorithm
|
||||
- **KID**: Optional, some CAs require KID
|
||||
- **HMAC**: Optional, some CAs require HMAC key
|
||||
3. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
### Certificate Authority (CA)
|
||||
|
||||
| CA | Description |
|
||||
| ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Let's Encrypt | Most popular free CA, certificate valid for 90 days |
|
||||
| LiteSSL | Free certificate service provided by TrustAsia |
|
||||
| Google | Google's free certificate service |
|
||||
| GoogleCN | Google certificate service mirror provided by AcePanel |
|
||||
| ZeroSSL | Free CA, certificate valid for 90 days |
|
||||
| Buypass | Norwegian free CA, certificate valid for 180 days |
|
||||
|
||||
### Key Type
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| P256 (ECC) | Recommended, shorter key, better performance |
|
||||
| P384 (ECC) | Higher security ECC key |
|
||||
| RSA 2048 | Traditional RSA key, best compatibility |
|
||||
| RSA 4096 | Higher security RSA key |
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Recommendation
|
||||
Generally recommended to use P256 (ECC) key, balancing security and performance.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Modify Account
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Modify** button on the right side of the account to modify the account email.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
After modifying the email, certificate-related notifications will be sent to the new email.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Account
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Delete** button on the right side of the account to delete the account.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
After deleting an account, certificates applied with that account cannot be renewed. Please migrate certificates to another account or delete related certificates first.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Account Usage
|
||||
|
||||
ACME accounts are used for:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Proving your identity to the CA
|
||||
2. Receiving certificate expiration reminders
|
||||
3. Managing applied certificates
|
||||
4. Revoking certificates
|
||||
|
||||
## Multiple Accounts
|
||||
|
||||
You can create multiple accounts:
|
||||
|
||||
- Different CAs require different accounts
|
||||
- Can use different accounts for different projects
|
||||
- Convenient for managing and distinguishing certificates
|
||||
103
zh_TW/advanced/cert/cert.md
Normal file
103
zh_TW/advanced/cert/cert.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
# Certificate Management
|
||||
|
||||
The certificate management page is used to apply for, upload, and manage SSL/TLS certificates.
|
||||
|
||||
## Certificate List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the **Certificate** page, which displays the certificate list by default.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Domain**: Domains included in the certificate
|
||||
- **Type**: Certificate type (ACME/Upload)
|
||||
- **Associated Account**: ACME account used
|
||||
- **Issuer**: Certificate authority
|
||||
- **Expiration Time**: Certificate expiration time
|
||||
- **Next Renewal Time**: Automatic renewal time
|
||||
- **Auto Renewal**: Whether auto renewal is enabled
|
||||
- **Actions**: Renew, download, delete, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Certificate
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Create Certificate** button to apply for a new certificate.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Items
|
||||
|
||||
- **Domain**: Domains to apply certificate for, supports multiple domains
|
||||
- **Key Type**: RSA or ECC
|
||||
- **Website**: Website associated with this certificate
|
||||
- **Account**: ACME account associated with this certificate
|
||||
- **DNS**: DNS API associated with this certificate
|
||||
|
||||
### Domain Format
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
example.com # Single domain
|
||||
www.example.com # Subdomain
|
||||
*.example.com # Wildcard domain (requires DNS verification)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Note
|
||||
Wildcard certificates (\*.example.com) can only be applied through DNS verification.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Upload Certificate
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Upload Certificate** button to upload an existing certificate.
|
||||
|
||||
Required:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Certificate File**: PEM format certificate (.crt or .pem), please include complete certificate chain
|
||||
- **Private Key File**: PEM format private key (.key)
|
||||
|
||||
## Apply Certificate
|
||||
|
||||
After applying or uploading a certificate, you need to enable HTTPS in the website settings and select the certificate.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enter the website edit page
|
||||
2. Switch to the **HTTPS** tab
|
||||
3. Enable HTTPS
|
||||
4. Select certificate
|
||||
5. Save configuration
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto Renewal
|
||||
|
||||
ACME certificates support auto renewal:
|
||||
|
||||
- After certificate issuance, the recommended renewal time is obtained through ARI
|
||||
- The system will automatically attempt renewal before the renewal time
|
||||
- After successful renewal, website configuration is automatically updated
|
||||
- Notification is sent if renewal fails
|
||||
|
||||
## Certificate Operations
|
||||
|
||||
### Manual Renewal
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Renew** button to manually trigger certificate renewal.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Certificate
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Download** button to download certificate files, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete certificate chain (.crt)
|
||||
- Private key file (.key)
|
||||
|
||||
### Delete Certificate
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Delete** button to delete the certificate.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### Application Failed
|
||||
|
||||
- Check if the domain is correctly resolved to the server
|
||||
- Check if port 80 is accessible (HTTP verification)
|
||||
- Check if DNS API configuration is correct (DNS verification)
|
||||
|
||||
### Renewal Failed
|
||||
|
||||
- Check if domain resolution has changed
|
||||
- Check if DNS API has expired
|
||||
- Check panel logs for detailed errors
|
||||
99
zh_TW/advanced/cert/dns.md
Normal file
99
zh_TW/advanced/cert/dns.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# DNS Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The DNS configuration page is used to manage DNS APIs for applying certificates through DNS verification.
|
||||
|
||||
## DNS List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Certificate** > **DNS** tab to view the DNS configuration list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Remark Name**: Configuration name
|
||||
- **Type**: DNS provider type
|
||||
- **Actions**: Modify, delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Create DNS Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create DNS** button
|
||||
2. Select DNS provider
|
||||
3. Fill in API credentials
|
||||
4. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported DNS Providers
|
||||
|
||||
### Domestic Providers
|
||||
|
||||
| Provider | Required Credentials |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Alibaba Cloud DNS | AccessKey ID, AccessKey Secret |
|
||||
| Tencent Cloud DNSPod | SecretId, SecretKey |
|
||||
| Huawei Cloud DNS | AccessKeyId, SecretAccessKey |
|
||||
| West.cn DNS | Username, API Password |
|
||||
|
||||
### International Providers
|
||||
|
||||
| Provider | Required Credentials |
|
||||
| ---------- | ---------------------- |
|
||||
| Cloudflare | API Token |
|
||||
| Gcore DNS | API Key |
|
||||
| Porkbun | API Key, Secret Key |
|
||||
| NameSilo | API Token |
|
||||
| ClouDNS | Auth ID, Auth Password |
|
||||
|
||||
## Obtaining API Credentials
|
||||
|
||||
### Alibaba Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to Alibaba Cloud console
|
||||
2. Go to **AccessKey Management**
|
||||
3. Create AccessKey
|
||||
4. Record AccessKey ID and AccessKey Secret
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Security Notice
|
||||
It is recommended to create a sub-account and only grant DNS management permissions. Avoid using the main account AccessKey.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Tencent Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to Tencent Cloud console
|
||||
2. Go to **Access Management** > **API Key Management**
|
||||
3. Create key
|
||||
4. Record SecretId and SecretKey
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloudflare
|
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to Cloudflare console
|
||||
2. Go to **My Profile** > **API Tokens**
|
||||
3. Create Token, select **Edit zone DNS** template
|
||||
4. Record the generated Token
|
||||
|
||||
## DNS Verification Principle
|
||||
|
||||
1. When applying for a certificate, the CA requires adding a specific TXT record in the domain DNS
|
||||
2. AcePanel automatically adds the verification record through DNS API
|
||||
3. CA verifies the TXT record exists
|
||||
4. Certificate is issued after verification passes
|
||||
5. AcePanel automatically deletes the verification record
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
DNS verification is suitable for:
|
||||
|
||||
- Applying for wildcard certificates (\*.example.com)
|
||||
- Server port 80 is not accessible
|
||||
- Intranet servers
|
||||
- Origin servers behind CDN
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### Verification Failed
|
||||
|
||||
- Check if API credentials are correct
|
||||
- Check if API permissions are sufficient
|
||||
- Check if the domain is managed by that DNS provider
|
||||
|
||||
### DNS Propagation Delay
|
||||
|
||||
DNS records need some time to propagate after being added, usually ranging from a few minutes to a few hours. If verification fails, you can retry later.
|
||||
56
zh_TW/advanced/container.md
Normal file
56
zh_TW/advanced/container.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
# Container
|
||||
|
||||
The container module provides complete Docker container management functionality, including management of containers, compose, images, networks, and volumes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the container feature, you need to install Docker or Podman first:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to **Applications** > **Native Applications**
|
||||
2. Find Docker or Podman, click **Install**
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The container module is divided into five parts:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [Container](./container/container) | Manage running container instances |
|
||||
| [Compose](./container/compose) | Manage multi-container applications using Docker Compose |
|
||||
| [Image](./container/image) | Manage local images |
|
||||
| [Network](./container/network) | Manage Docker networks |
|
||||
| [Volume](./container/volume) | Manage data volumes |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
|
||||
### Create Container
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the **Container** page
|
||||
2. Click **Create Container**
|
||||
3. Enter the image name (e.g., `nginx:latest`)
|
||||
4. Configure port mapping, volume mounts, etc.
|
||||
5. Click **Create**
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Container Templates
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to quickly deploy common applications, it is recommended to use [Container Templates](./app/template), which allows one-click deployment without manual configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Container vs Native Application
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Container | Native Application |
|
||||
| ------------------ | ---------------------- | ----------------------------- |
|
||||
| Isolation | Fully isolated | Shared system environment |
|
||||
| Performance | Slight overhead | Native performance |
|
||||
| Deployment | Standardized, portable | Depends on system environment |
|
||||
| Resource Usage | Higher | Lower |
|
||||
| Version Management | Easy to switch | Requires manual management |
|
||||
|
||||
## Next Steps
|
||||
|
||||
- [Container Management](./container/container) - Learn how to manage containers
|
||||
- [Compose Management](./container/compose) - Learn how to use Docker Compose
|
||||
- [Image Management](./container/image) - Learn how to manage images
|
||||
- [Network Management](./container/network) - Learn how to manage networks
|
||||
- [Volume Management](./container/volume) - Learn how to manage data volumes
|
||||
108
zh_TW/advanced/container/compose.md
Normal file
108
zh_TW/advanced/container/compose.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
# Compose
|
||||
|
||||
The compose feature is based on Docker Compose, used to define and run multi-container applications. Describe the application's services, networks, and volumes through a YAML file, then start the entire application with one click.
|
||||
|
||||
## Compose List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Container** > **Compose** tab to view the compose list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Name**: Compose project name
|
||||
- **Directory**: Directory where docker-compose.yml file is located
|
||||
- **Status**: Running status
|
||||
- **Created Time**: Creation time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Start, stop, edit, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Compose
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create Compose** button
|
||||
2. Enter compose name
|
||||
3. Write or paste docker-compose.yml content
|
||||
4. Configure environment variables (optional)
|
||||
5. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### docker-compose.yml Example
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: '3'
|
||||
services:
|
||||
web:
|
||||
image: nginx:latest
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "80:80"
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- app
|
||||
app:
|
||||
image: php:8.4-fpm
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./html:/var/www/html
|
||||
db:
|
||||
image: mysql:8.4
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: your_password
|
||||
MYSQL_DATABASE: myapp
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
db_data:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Compose Operations
|
||||
|
||||
### Start Compose
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Start** button and a confirmation dialog will pop up:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Force Pull Images**: When checked, will pull the latest images before starting
|
||||
|
||||
After clicking confirm, the startup progress will be displayed:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Starting compose will create and start all defined service containers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Stop Compose
|
||||
|
||||
Stopping compose will stop all related containers, but will not delete containers and data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Delete Compose
|
||||
|
||||
Deleting compose will stop and delete all related containers.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
Deleting compose will not delete data volumes. To delete data volumes, please manually delete them on the **Volume** page.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Edit Compose
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Edit** button in the compose list to modify the docker-compose.yml file content and environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After modification, you need to restart the compose for changes to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
Compose is suitable for the following scenarios:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Multi-container Applications**: Such as Web application + database + cache
|
||||
- **Development Environment**: Quickly set up a consistent development environment
|
||||
- **Microservices Architecture**: Manage multiple interdependent services
|
||||
|
||||
## Difference from Container Templates
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Compose | Container Templates |
|
||||
| -------------------- | --------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Configuration Method | Write YAML manually | Graphical interface |
|
||||
| Flexibility | Fully customizable | Use preset configuration + customization |
|
||||
| Use Cases | Custom complex applications | Quick deployment of common applications |
|
||||
| Learning Cost | Need to understand Compose syntax | No learning required |
|
||||
93
zh_TW/advanced/container/container.md
Normal file
93
zh_TW/advanced/container/container.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
# Container Management
|
||||
|
||||
Containers are the core concept of Docker, being running instances of images. Through the container management page, you can create, start, stop, and manage containers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Container List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the **Container** page, which displays the container list by default.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Container Name**: Name of the container
|
||||
- **Status**: Running status switch
|
||||
- **Image**: Image used by the container
|
||||
- **Ports**: Port mapping (host port -> container port)
|
||||
- **Running Status**: Detailed running status information
|
||||
- **Actions**: Terminal, logs, rename, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Container
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Create Container** button to open the creation dialog.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Settings
|
||||
|
||||
- **Container Name**: Optional, auto-generated if left empty
|
||||
- **Image**: Docker image name, e.g., `nginx:latest`, `mysql:8.0`
|
||||
- **Network**: Select the network for the container to use
|
||||
- **Restart Policy**: Restart behavior after container exits
|
||||
- None: Do not auto restart
|
||||
- always: Always restart
|
||||
- on-failure: Restart on failure
|
||||
- unless-stopped: Restart unless manually stopped
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Options
|
||||
|
||||
- **TTY (-t)**: Allocate a pseudo-TTY
|
||||
- **STDIN (-i)**: Keep STDIN open
|
||||
- **Auto Remove**: Automatically delete container when stopped
|
||||
- **Privileged Mode**: Grant container full system privileges (use with caution)
|
||||
|
||||
### Port Mapping
|
||||
|
||||
Map container internal ports to host ports, format: `host_port:container_port`
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For example: `8080:80` means mapping container port 80 to host port 8080.
|
||||
|
||||
### Volume Mounts
|
||||
|
||||
Mount host directories or data volumes to the container, format: `host_path:container_path`
|
||||
|
||||
For example: `/opt/ace/data:/data` means mounting the host's `/opt/ace/data` directory to the container's `/data` directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resource Limits
|
||||
|
||||
Limit the CPU and memory resources the container can use.
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
Set container environment variables, format: `KEY=VALUE`
|
||||
|
||||
## Container Operations
|
||||
|
||||
### Batch Operations
|
||||
|
||||
After selecting multiple containers, you can perform batch operations:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Start**: Start selected containers
|
||||
- **Stop**: Stop selected containers
|
||||
- **Restart**: Restart selected containers
|
||||
- **Force Stop**: Force stop selected containers
|
||||
- **Pause**: Pause selected containers
|
||||
- **Resume**: Resume paused containers
|
||||
- **Delete**: Delete selected containers
|
||||
|
||||
### Single Container Operations
|
||||
|
||||
- **Terminal**: Open the container's terminal to execute commands inside the container
|
||||
- **Logs**: View container runtime logs
|
||||
- **Rename**: Modify container name
|
||||
- **More**: View details, export, and other operations
|
||||
|
||||
## Clean Containers
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Clean Containers** to delete all stopped containers and free up system resources.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
The cleanup operation cannot be undone. Please ensure stopped containers are no longer needed.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
77
zh_TW/advanced/container/image.md
Normal file
77
zh_TW/advanced/container/image.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# Image
|
||||
|
||||
Images are templates for containers, containing all files and configurations needed to run applications. Through the image management page, you can pull, view, and delete local images.
|
||||
|
||||
## Image List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Container** > **Image** tab to view the local image list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **ID**: Image ID
|
||||
- **Container Count**: Number of containers using this image
|
||||
- **Image**: Image name and tag
|
||||
- **Size**: Disk space occupied by the image
|
||||
- **Created Time**: Image creation time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Delete, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pull Image
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Pull Image** button
|
||||
2. Enter the image name, e.g., `nginx:latest`, `mysql:8.4`
|
||||
3. Click confirm to start pulling
|
||||
|
||||
Image name format: `[registry_address/]image_name[:tag]`
|
||||
|
||||
- `nginx` - Pull the latest tag of the official nginx image
|
||||
- `nginx:1.28` - Pull a specific version
|
||||
- `mysql:8.4` - Pull MySQL version 8.4
|
||||
- `registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xxx/yyy:latest` - Pull from Alibaba Cloud image registry
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Note
|
||||
Pulling Docker Hub images from servers in China may be slow. It is recommended to configure an image accelerator or use domestic image sources.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Image
|
||||
|
||||
Select an image and click the **Delete** button to delete the image.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
If the image is being used by containers, you need to delete the related containers before deleting the image.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Clean Images
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Clean Images** to delete all unused images and free up disk space.
|
||||
|
||||
The cleanup operation will delete:
|
||||
|
||||
- Dangling images
|
||||
- Images not used by any container
|
||||
|
||||
## Image Sources
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Hub
|
||||
|
||||
Docker's official image registry, containing a large number of official and community images.
|
||||
|
||||
Common official images:
|
||||
|
||||
- `nginx` - Web server
|
||||
- `mysql` / `mariadb` - Database
|
||||
- `redis` - Cache
|
||||
- `postgres` - PostgreSQL database
|
||||
- `node` - Node.js runtime environment
|
||||
- `python` - Python runtime environment
|
||||
|
||||
### Domestic Image Sources
|
||||
|
||||
- Alibaba Cloud: `registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com`
|
||||
- Tencent Cloud: `ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com`
|
||||
- Huawei Cloud: `swr.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com`
|
||||
|
||||
### Private Registry
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a private image registry, you can directly use the full image address to pull.
|
||||
76
zh_TW/advanced/container/network.md
Normal file
76
zh_TW/advanced/container/network.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
# Network
|
||||
|
||||
Docker networks are used for communication between containers. Through the network management page, you can create, view, and delete networks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Network List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Container** > **Network** tab to view the network list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Name**: Network name
|
||||
- **Driver**: Network driver type
|
||||
- **Scope**: Network scope
|
||||
- **Subnet**: Network subnet address
|
||||
- **Gateway**: Network gateway address
|
||||
- **Created Time**: Creation time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Default Networks
|
||||
|
||||
Docker automatically creates the following networks after installation:
|
||||
|
||||
| Network Name | Driver | Description |
|
||||
| ------------ | ------ | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| bridge | bridge | Default network, containers access external network through NAT |
|
||||
| host | host | Container directly uses host network, no network isolation |
|
||||
| none | null | No network, container is completely isolated |
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel also creates the `acepanel-network` network for containers deployed by panel compose templates. Please do not delete it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Network
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create Network** button
|
||||
2. Enter network name
|
||||
3. Select network driver
|
||||
4. Configure subnet and gateway (optional)
|
||||
5. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
### Network Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
- **bridge**: Bridge network, the most commonly used network type. Containers connect through a virtual bridge and can communicate with each other.
|
||||
- **host**: Host network, container directly uses the host's network stack, best performance but no isolation.
|
||||
- **overlay**: Overlay network, used for cross-host container communication (Swarm mode).
|
||||
- **macvlan**: MAC VLAN network, assigns independent MAC addresses to containers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Network Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Specify Network When Creating Container
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a container, select the network to use in the **Network** option.
|
||||
|
||||
### Communication Between Containers
|
||||
|
||||
Containers in the same network can access each other by container name.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in the `acepanel-network` network:
|
||||
|
||||
- Container A is named `web`
|
||||
- Container B is named `db`
|
||||
- Container A can access Container B's database through `db:3306`
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Network
|
||||
|
||||
Select a network and click the **Delete** button to delete the network.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
|
||||
- Default networks (bridge, host, none) and `acepanel-network` cannot be deleted
|
||||
- If there are containers in the network, you need to delete or disconnect the containers before deleting the network
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Clean Networks
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Clean Networks** to delete all unused custom networks.
|
||||
77
zh_TW/advanced/container/volume.md
Normal file
77
zh_TW/advanced/container/volume.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# Volume
|
||||
|
||||
Volumes are Docker-managed data storage used to persist container data. Compared to directly mounting host directories, volumes are managed by Docker, making them more secure and portable.
|
||||
|
||||
## Volume List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Container** > **Volume** tab to view the volume list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Name**: Volume name
|
||||
- **Driver**: Storage driver
|
||||
- **Scope**: Volume scope
|
||||
- **Mount Point**: Actual storage path of the volume on the host
|
||||
- **Created Time**: Creation time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Volume
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create Volume** button
|
||||
2. Enter volume name
|
||||
3. Select driver (default local)
|
||||
4. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Volumes
|
||||
|
||||
### Mount Volume When Creating Container
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a container, add volume mounts in the **Volume** option:
|
||||
|
||||
- **volume_name:container_path** - Use named volume
|
||||
- **host_path:container_path** - Directly mount host directory
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
- `mysql_data:/var/lib/mysql` - Mount mysql_data volume to container's /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
- `/opt/ace/data:/data` - Mount host's /opt/ace/data directory to container's /data
|
||||
|
||||
### Volume vs Bind Mount
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Volume | Bind Mount |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Management | Docker managed | User managed |
|
||||
| Storage Location | Docker data directory | Any host path |
|
||||
| Backup | Requires Docker commands | Directly backup directory |
|
||||
| Portability | High | Depends on host path |
|
||||
| Use Cases | Data that needs persistence like databases | Configuration files, code directories |
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Volume
|
||||
|
||||
Select a volume and click the **Delete** button to delete the volume.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger Warning
|
||||
Deleting a volume will permanently delete all data in the volume. This operation cannot be undone!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
If the volume is being used by containers, you need to delete the related containers before deleting the volume.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Clean Volumes
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Clean Volumes** to delete all unused volumes and free up disk space.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Note
|
||||
Please confirm that unused volumes do not contain important data before cleaning.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Backup
|
||||
|
||||
Volume data is stored in the Docker data directory (usually `/var/lib/docker/volumes/`). You can backup through the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Use `docker run` to create a temporary container that mounts the volume and exports data
|
||||
2. Directly backup the Docker data directory (requires stopping Docker service)
|
||||
3. (In development) Use AcePanel's [Backup Feature](../backup) for backup
|
||||
77
zh_TW/advanced/database.md
Normal file
77
zh_TW/advanced/database.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# Database
|
||||
|
||||
The database module is used to manage MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, and other databases. It supports creating databases, managing users, and configuring database servers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Before using the database feature, you need to install database software first:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to **Applications** > **Native Applications**
|
||||
2. Install Percona, MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The database module is divided into three parts:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------------- | ------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [Database](./database/database) | Create and manage databases |
|
||||
| [User](./database/user) | Manage database users and permissions |
|
||||
| [Server](./database/server) | Manage database server connections |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Databases
|
||||
|
||||
| Database | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Percona | High-performance fork of MySQL, suitable for high-load scenarios |
|
||||
| MySQL | The world's most popular open-source relational database |
|
||||
| MariaDB | Open-source fork of MySQL, fully compatible with MySQL |
|
||||
| PostgreSQL | Powerful open-source object-relational database |
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
|
||||
### Create Database
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the **Database** page
|
||||
2. Click **Create Database**
|
||||
3. Select database type and server
|
||||
4. Enter database name
|
||||
5. Choose whether to create a user and set permissions
|
||||
6. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
### Create User
|
||||
|
||||
1. Switch to the **User** tab
|
||||
2. Click **Create User**
|
||||
3. Enter username and password
|
||||
4. Set access permissions
|
||||
5. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect to Database
|
||||
|
||||
### Local Connection
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Host: 127.0.0.1 or localhost
|
||||
Port: Percona/MySQL/MariaDB 3306, PostgreSQL 5432
|
||||
Socket: Percona/MySQL/MariaDB /tmp/mysql.sock, PostgreSQL /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Remote Connection
|
||||
|
||||
To connect to the database remotely:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open the database port in the firewall
|
||||
2. Create a user that allows remote access (set host to `%`)
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Security Notice
|
||||
It is not recommended to expose database ports to the public network. For remote management, it is recommended to use SSH tunnels or VPN.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Next Steps
|
||||
|
||||
- [Database Management](./database/database) - Learn how to create and manage databases
|
||||
- [User Management](./database/user) - Learn how to manage database users
|
||||
- [Server Management](./database/server) - Learn how to manage database servers
|
||||
58
zh_TW/advanced/database/database.md
Normal file
58
zh_TW/advanced/database/database.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
# Database Management
|
||||
|
||||
The database management page is used to create, view, and delete databases. AcePanel now uses UTF-8 encoding by default when creating databases.
|
||||
|
||||
## Database List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the **Database** page, which displays the database list by default.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Type**: Database type (MySQL/PostgreSQL)
|
||||
- **Database Name**: Database name
|
||||
- **Server**: The database server it belongs to
|
||||
- **Encoding**: Character encoding
|
||||
- **Comment**: Remarks (PostgreSQL supported)
|
||||
- **Actions**: Delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Database
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create Database** button
|
||||
2. Fill in the configuration:
|
||||
- **Server**: Select database server
|
||||
- **Database Name**: Can only use letters, numbers, and underscores
|
||||
3. Choose whether to create a user and set permissions (optional)
|
||||
4. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete Database
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Delete** button on the right side of the database to delete it.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger Warning
|
||||
Deleting a database will permanently delete all data in that database. This operation cannot be undone! Please make sure to backup important data in advance.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Database Naming Conventions
|
||||
|
||||
- Can only use letters, numbers, and underscores
|
||||
- Cannot start with a number
|
||||
- Avoid using database reserved words
|
||||
- Recommend using meaningful names, such as `wordpress`, `myapp_production`
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### Failed to Create Database
|
||||
|
||||
- Check if the database name follows naming conventions
|
||||
- Check if a database with the same name already exists
|
||||
- Check if the database service is running normally
|
||||
|
||||
### Database Encoding Issues
|
||||
|
||||
If garbled characters appear, check:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Whether the database encoding is correct
|
||||
2. Whether the correct encoding is specified when connecting
|
||||
3. The encoding settings of the application
|
||||
86
zh_TW/advanced/database/server.md
Normal file
86
zh_TW/advanced/database/server.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
# Server Management
|
||||
|
||||
The server management page is used to manage database server connections, supporting both local and remote database servers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Server List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Database** > **Server** tab to view the server list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Type**: Database type (MySQL/PostgreSQL)
|
||||
- **Name**: Server name
|
||||
- **Username**: Administrator username
|
||||
- **Password**: Administrator password
|
||||
- **Host**: Server address and port
|
||||
- **Comment**: Remarks
|
||||
- **Status**: Connection status
|
||||
- **Update Date**: Last update time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Terminal, sync, modify, delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Local Server
|
||||
|
||||
After installing database software, AcePanel will automatically add local servers. These servers cannot be deleted by users:
|
||||
|
||||
- **local_mysql**: Local Percona/MySQL/MariaDB server
|
||||
- **local_postgresql**: Local PostgreSQL server
|
||||
|
||||
## Add Remote Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Add Server** button
|
||||
2. Fill in the configuration:
|
||||
- **Type**: Select database type
|
||||
- **Name**: Server name (for identification)
|
||||
- **Host**: Server address
|
||||
- **Port**: Database port
|
||||
- **Username**: Administrator username
|
||||
- **Password**: Administrator password
|
||||
3. Click Add
|
||||
|
||||
### Remote Server Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
- Connect to cloud databases (such as Alibaba Cloud RDS, Tencent Cloud CDB)
|
||||
- Connect to database services in containers
|
||||
- Connect to databases on other servers
|
||||
- Database read-write separation architecture
|
||||
|
||||
## Server Operations
|
||||
|
||||
### Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Terminal** button to open the database command line terminal, where you can directly execute SQL statements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Sync
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Sync** button to synchronize database and user information. When databases or users are created directly in the database, you can use this function to sync to the panel.
|
||||
|
||||
### Modify
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Modify** button to modify server connection information, such as password, host address, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Delete
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Delete** button to delete the server configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
Deleting the server configuration will not delete the actual database service, it only removes the server management from the panel.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Connection Test
|
||||
|
||||
After adding or modifying a server, the system will automatically test the connection. If the connection fails, please check:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Whether the server address and port are correct
|
||||
2. Whether the username and password are correct
|
||||
3. Whether the firewall allows the connection
|
||||
4. Whether the database service is running normally
|
||||
5. Whether the database user is allowed to connect from the current host
|
||||
|
||||
## Default Ports
|
||||
|
||||
| Database | Default Port |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ------------ |
|
||||
| Percona/MySQL/MariaDB | 3306 |
|
||||
| PostgreSQL | 5432 |
|
||||
83
zh_TW/advanced/database/user.md
Normal file
83
zh_TW/advanced/database/user.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
# User Management
|
||||
|
||||
The user management page is used to create and manage database users and set user permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
## User List
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Database** > **User** tab to view the user list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Type**: Database type
|
||||
- **Username**: Database username
|
||||
- **Password**: User password (click to copy)
|
||||
- **Host**: Allowed connection hosts
|
||||
- **Server**: The database server it belongs to
|
||||
- **Permissions**: Databases the user has permissions for
|
||||
- **Comment**: Remarks
|
||||
- **Status**: User status
|
||||
- **Update Date**: Last update time
|
||||
- **Actions**: Modify, delete
|
||||
|
||||
## Create User
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the **Create User** button
|
||||
2. Fill in the configuration:
|
||||
- **Server**: Select database server
|
||||
- **Username**: Database username
|
||||
- **Password**: User password (strong password recommended)
|
||||
- **Host**: Allowed connection host address
|
||||
- **Permissions**: Select databases the user can access
|
||||
3. Click Create
|
||||
|
||||
### Host Settings
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `localhost` | Only allow local connections |
|
||||
| `127.0.0.1` | Only allow local IP connections |
|
||||
| `%` | Allow connections from any host |
|
||||
| `192.168.1.%` | Allow connections from specified subnet |
|
||||
| `192.168.1.100` | Only allow connections from specified IP |
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Security Notice
|
||||
Production environments are not recommended to use `%` to allow connections from any host. Should be restricted to specific IP addresses or subnets.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Modify User
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Modify** button on the right side of the user to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Modify password
|
||||
- Modify allowed connection hosts
|
||||
- Modify database permissions
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete User
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Delete** button on the right side of the user to delete the user.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
After deleting a user, applications using that user to connect to the database will not work properly.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Permission Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
### Percona/MySQL/MariaDB Permissions
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a user, you can select databases to grant permissions:
|
||||
|
||||
- Select specific databases: User can only access selected databases
|
||||
- No selection: User has no database permissions
|
||||
|
||||
### PostgreSQL Permissions
|
||||
|
||||
PostgreSQL permission management is more fine-grained. You can set different permissions for databases, schemas, tables, etc. The panel only supports granting database access permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Password Security
|
||||
|
||||
- Use strong passwords containing uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters
|
||||
- Password length recommended 16 characters or more
|
||||
- Use different database users for different applications
|
||||
- Change passwords regularly
|
||||
206
zh_TW/advanced/file.md
Normal file
206
zh_TW/advanced/file.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
|
||||
# File
|
||||
|
||||
The file module provides a powerful graphical file manager. The design philosophy is to restore the Windows Explorer operation experience as much as possible, supporting right-click menus, drag-and-drop upload, keyboard shortcuts, and other features.
|
||||
|
||||
## File Manager
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Core Features
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows-like Operation Experience
|
||||
|
||||
- **Right-click Menu**: Right-click on files or directories to pop up an action menu
|
||||
- **Drag-and-drop Upload**: Directly drag local files to the browser window to upload
|
||||
- **Multi-select Operations**: Support Ctrl+click for multi-select, Shift+click for range selection
|
||||
- **Keyboard Shortcuts**: Common operations have corresponding keyboard shortcuts
|
||||
|
||||
### Keyboard Shortcuts
|
||||
|
||||
| Shortcut | Function |
|
||||
| -------- | ---------- |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+C` | Copy |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+X` | Cut |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+V` | Paste |
|
||||
| `Delete` | Delete |
|
||||
| `F2` | Rename |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+A` | Select All |
|
||||
|
||||
## Navigation
|
||||
|
||||
### Path Navigation
|
||||
|
||||
The top displays breadcrumb navigation of the current path. Click to quickly jump to any parent directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quick Buttons
|
||||
|
||||
- **Back**: Return to the previous visited directory
|
||||
- **Forward**: Go to the next directory
|
||||
- **Parent Directory**: Return to parent directory
|
||||
- **Refresh**: Refresh current directory
|
||||
- **Home Directory**: Return to default directory
|
||||
|
||||
## File List
|
||||
|
||||
The file list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
| Column | Description |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Name | File or directory name |
|
||||
| Size | File size, directories show "Calculate" which can be clicked to calculate |
|
||||
| Permissions | File permissions (e.g., 0755) |
|
||||
| Owner/Group | File owner and group |
|
||||
| Modified Time | Last modified time |
|
||||
| Actions | Open, compress, rename, delete, more |
|
||||
|
||||
### Select Files
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After selecting files, batch operation buttons appear at the top:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Copy**: Copy selected files
|
||||
- **Move**: Move selected files
|
||||
- **Compress**: Compress selected files
|
||||
- **Permissions**: Modify permissions
|
||||
- **Delete**: Delete selected files
|
||||
|
||||
### More Actions
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **More** button on the file row to display more action options:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Copy**: Copy file to another directory
|
||||
- **Move**: Move file to another directory
|
||||
- **Permissions**: Modify file permissions and owner
|
||||
- **Compress**: Compress file
|
||||
- **Copy Path**: Copy the full path of the file
|
||||
- **Properties**: View detailed file properties
|
||||
|
||||
## Toolbar
|
||||
|
||||
### New
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **New** button to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Create new file
|
||||
- Create new directory
|
||||
|
||||
### Upload
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Upload** button to upload local files to the server.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported upload methods:
|
||||
|
||||
- Click to select files for upload
|
||||
- **Drag-and-drop Upload**: Directly drag files to the page to upload
|
||||
|
||||
### Remote Download
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Remote Download** button, enter a URL address to download remote files to the current directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Use cases:
|
||||
|
||||
- Download software installation packages
|
||||
- Download remote backup files
|
||||
- Get files from other servers
|
||||
|
||||
### Search
|
||||
|
||||
Enter keywords in the search box to search for files:
|
||||
|
||||
- Default searches current directory
|
||||
- Check **Include Subdirectories** to search recursively
|
||||
|
||||
### Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Terminal** button to open a terminal in the current directory for convenient command line operations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Sort
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Sort** button to sort the file list by different fields.
|
||||
|
||||
## File Editor
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel has a built-in powerful code editor based on Monaco Editor (the same editor core as VS Code).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Editor Features
|
||||
|
||||
- **Syntax Highlighting**: Supports syntax highlighting for various programming languages
|
||||
- **Code Folding**: Supports code block folding
|
||||
- **Line Numbers**: Displays line numbers for easy positioning
|
||||
- **Minimap**: Displays code thumbnail on the right side
|
||||
- **Word Wrap**: Can toggle word wrap mode
|
||||
- **Multi-file Editing**: Supports opening multiple files simultaneously with tab switching
|
||||
|
||||
### Editor Shortcuts
|
||||
|
||||
| Shortcut | Function |
|
||||
| -------------- | ----------------- |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+S` | Save current file |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+Shift+S` | Save all files |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+F` | Search |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+H` | Replace |
|
||||
| `Ctrl+G` | Go to line |
|
||||
|
||||
### Editor Toolbar
|
||||
|
||||
- **Save**: Save current file
|
||||
- **Save All**: Save all modified files
|
||||
- **Refresh**: Reload file content
|
||||
- **Search**: Open search panel
|
||||
- **Replace**: Open replace panel
|
||||
- **Go to**: Jump to specified line
|
||||
- **Font Size**: Adjust editor font size
|
||||
- **Toggle Word Wrap**: Enable/disable word wrap
|
||||
- **Toggle Minimap**: Show/hide right-side minimap
|
||||
- **Settings**: Editor settings
|
||||
|
||||
### Fullscreen Mode
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Maximize** button for fullscreen editing to get more editing space:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Sidebar File Tree
|
||||
|
||||
The left side of the editor displays the file tree of the current directory, allowing you to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Quickly switch to edit other files
|
||||
- Create new files
|
||||
- Search files
|
||||
|
||||
### Status Bar
|
||||
|
||||
The editor bottom status bar displays:
|
||||
|
||||
- Full file path
|
||||
- Line ending type (LF/CRLF)
|
||||
- Cursor position (line, column)
|
||||
- Indentation settings (spaces/Tab)
|
||||
- File language type
|
||||
|
||||
## Permission Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
Linux file permissions are represented by three groups of numbers:
|
||||
|
||||
| Permission | Number | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------ | ----------- |
|
||||
| r | 4 | Read |
|
||||
| w | 2 | Write |
|
||||
| x | 1 | Execute |
|
||||
|
||||
For example `0755`:
|
||||
|
||||
- Owner: 7 (4+2+1) = read+write+execute
|
||||
- Group: 5 (4+1) = read+execute
|
||||
- Others: 5 (4+1) = read+execute
|
||||
|
||||
Common permissions:
|
||||
|
||||
- `0644`: Regular files
|
||||
- `0755`: Executable files and directories
|
||||
- `0600`: Private files (such as keys)
|
||||
105
zh_TW/advanced/monitor.md
Normal file
105
zh_TW/advanced/monitor.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
# Monitor
|
||||
|
||||
The monitor module is used to record and view server performance data, including CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
## Monitor Page
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Monitor Settings
|
||||
|
||||
### Enable Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
After turning on the **Enable Monitoring** switch, the system will periodically collect performance data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Retention Days
|
||||
|
||||
Set the retention time for monitoring data, default is 30 days. Data exceeding the retention time will be automatically cleaned up.
|
||||
|
||||
### Clear Monitor Records
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Clear Monitor Records** button to manually clear all historical monitoring data.
|
||||
|
||||
## Monitoring Metrics
|
||||
|
||||
### Load Average
|
||||
|
||||
System load reflects the busyness of the CPU:
|
||||
|
||||
- **1-minute load**: Average load over the last 1 minute
|
||||
- **5-minute load**: Average load over the last 5 minutes
|
||||
- **15-minute load**: Average load over the last 15 minutes
|
||||
|
||||
Load value reference:
|
||||
|
||||
- Load < CPU cores: System running smoothly
|
||||
- Load = CPU cores: System running at full capacity
|
||||
- Load > CPU cores: System overloaded, may experience lag
|
||||
|
||||
### CPU Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Displays CPU usage percentage, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- User mode usage
|
||||
- System mode usage
|
||||
- Idle rate
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Displays memory usage:
|
||||
|
||||
- Used memory
|
||||
- Available memory
|
||||
- Cache/Buffer
|
||||
|
||||
### Disk I/O
|
||||
|
||||
Displays disk read/write speed:
|
||||
|
||||
- Read speed (KB/s or MB/s)
|
||||
- Write speed (KB/s or MB/s)
|
||||
|
||||
You can select the disk device to monitor.
|
||||
|
||||
### Network Traffic
|
||||
|
||||
Displays network interface traffic:
|
||||
|
||||
- Send speed
|
||||
- Receive speed
|
||||
|
||||
You can select the network interface to monitor.
|
||||
|
||||
## Time Range
|
||||
|
||||
Each monitoring chart supports selecting a time range:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Yesterday**: View yesterday's data
|
||||
- **Today**: View today's data
|
||||
- **Last 7 days**: View data from the last week
|
||||
- **Custom**: Select any time range
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
### Performance Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
Analyze server performance bottlenecks through monitoring data:
|
||||
|
||||
- Sustained high CPU load: Consider optimizing programs or upgrading CPU
|
||||
- Insufficient memory: Consider adding memory or optimizing memory usage
|
||||
- High disk I/O: Consider using SSD or optimizing database queries
|
||||
- Insufficient network bandwidth: Consider upgrading bandwidth
|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
When problems occur, view historical monitoring data to locate the time and cause of the problem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Capacity Planning
|
||||
|
||||
Based on historical data trends, predict future resource needs and plan for expansion in advance.
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
|
||||
- Monitoring data will occupy some disk space
|
||||
- The longer the retention days, the more space it occupies
|
||||
- It is recommended to set appropriate retention days based on actual needs
|
||||
156
zh_TW/advanced/project.md
Normal file
156
zh_TW/advanced/project.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
||||
# Project
|
||||
|
||||
The project module is used to manage backend applications, supporting multiple languages including Go, Java, Node.js, PHP, Python, etc. Projects run as system services, supporting automatic restart, auto-start on boot, and other features.
|
||||
|
||||
## Project Types
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | Description | Use Cases |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [Go](./project/go) | Go language projects | Gin, Echo, Fiber frameworks |
|
||||
| [Java](./project/java) | Java projects | Spring Boot, Tomcat, etc. |
|
||||
| [Node.js](./project/nodejs) | Node.js projects | Express, Koa, NestJS, etc. |
|
||||
| [PHP](./project/php) | PHP projects | Laravel Octane, Swoole, etc. |
|
||||
| [Python](./project/python) | Python projects | Django, Flask, FastAPI, etc. |
|
||||
| [General](./project/general) | Other types of projects | Any executable program |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Project vs Website
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Project | Website |
|
||||
| ------------------ | -------------------------------- | ---------------------------- |
|
||||
| Run Mode | Independent process | Depends on Web server |
|
||||
| Process Management | Auto restart, auto-start on boot | Managed by Web server |
|
||||
| Use Cases | Backend services, APIs | Traditional Web applications |
|
||||
| External Access | Requires reverse proxy | Direct access |
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Project
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the **Project** page
|
||||
2. Click **Create Project**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Items
|
||||
|
||||
- **Project Name**: Project identifier, used as service name
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: Directory where project files are located
|
||||
- **Run User**: System user to run the project, default www
|
||||
- **Start Command**: Command to start the project
|
||||
- **Reverse Proxy**: Whether to automatically create a reverse proxy website
|
||||
|
||||
## Project Management
|
||||
|
||||
The project list displays the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Name**: Project name
|
||||
- **Description**: Project description
|
||||
- **Type**: Project type (Go/Java/Node.js, etc.)
|
||||
- **Status**: Running status
|
||||
- **Auto Start**: Whether to auto-start on boot
|
||||
- **Directory**: Project directory
|
||||
- **Actions**: Start, stop, restart, logs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Project Operations
|
||||
|
||||
- **Start**: Start the project
|
||||
- **Stop**: Stop the project
|
||||
- **Restart**: Restart the project
|
||||
- **Logs**: View project runtime logs
|
||||
- **Edit**: Modify project configuration
|
||||
- **Delete**: Delete the project
|
||||
|
||||
## Edit Project
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Edit** button in the project list to modify project configuration. The edit dialog contains multiple tabs:
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Configure basic project information:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Project Name**: Project identifier, used as service name
|
||||
- **Description**: Project description information
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: Directory where project files are located
|
||||
- **Working Directory**: Working directory when the program runs, defaults to project directory
|
||||
- **Run User**: System user to run the project
|
||||
|
||||
### Run Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Configure project runtime parameters:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Start Command**: Command to start the project
|
||||
- **Pre-start Command**: Command to run before starting (optional)
|
||||
- **Post-start Command**: Command to run after starting (optional)
|
||||
- **Stop Command**: Custom stop command (optional)
|
||||
- **Reload Command**: Custom reload command (optional)
|
||||
- **Restart Policy**: Restart on failure, always restart, never restart
|
||||
- **Restart Interval**: Wait time between restarts
|
||||
- **Max Restart Count**: Maximum number of consecutive restarts
|
||||
- **Start Timeout**: Timeout for waiting for service to start
|
||||
- **Stop Timeout**: Timeout for waiting for service to stop
|
||||
- **Standard Output**: How to handle standard output
|
||||
- **Standard Error**: How to handle standard error
|
||||
- **Environment Variables**: Set environment variables for project runtime
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Configure service dependencies to control startup order:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Requires**: Strong dependencies, if these services are unavailable, the project will fail
|
||||
- **Wants**: Weak dependencies, if these services fail, the project will still start
|
||||
- **After**: Start this project after the specified services
|
||||
- **Before**: Start this project before the specified services
|
||||
|
||||
Common services: `network.target`, `mysqld.service`, `postgresql.service`, `redis.service`
|
||||
|
||||
### Resource Limits
|
||||
|
||||
Set resource limits to prevent services from consuming too many system resources:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Memory Limit**: Limit the maximum memory used by the project, 0 means unlimited
|
||||
- **CPU Quota**: Limit CPU usage, 100% = 1 CPU core
|
||||
|
||||
### Security Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Security options to enhance service isolation:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **No New Privileges**: Prevent the process from gaining new privileges
|
||||
- **Protect /tmp**: Create a private /tmp directory for the service
|
||||
- **Protect /home**: Restrict access to the /home directory
|
||||
- **Protect System**: Set read-only protection level for system directories
|
||||
- `true`: /usr, /boot are read-only
|
||||
- `full`: + /etc is read-only
|
||||
- `strict`: Entire filesystem is read-only
|
||||
- **Read-Write Paths**: Paths the service can read and write
|
||||
- **Read-Only Paths**: Paths the service can only read
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
Security settings may affect certain features. Please test thoroughly before enabling.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Process Management
|
||||
|
||||
Projects use systemd for process management, with the following features:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Auto Restart**: Automatically restart after abnormal process exit
|
||||
- **Auto Start on Boot**: Automatically start the project when the system boots
|
||||
- **Log Management**: Automatically record standard output and error output
|
||||
|
||||
## Next Steps
|
||||
|
||||
- [Go Project](./project/go) - Deploy Go applications
|
||||
- [Java Project](./project/java) - Deploy Java applications
|
||||
- [Node.js Project](./project/nodejs) - Deploy Node.js applications
|
||||
- [PHP Project](./project/php) - Deploy PHP applications
|
||||
- [Python Project](./project/python) - Deploy Python applications
|
||||
- [General Project](./project/general) - Deploy other types of applications
|
||||
132
zh_TW/advanced/project/general.md
Normal file
132
zh_TW/advanced/project/general.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
# General Project
|
||||
|
||||
General projects are used to deploy any type of executable program, not limited to specific programming languages.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
- Rust applications
|
||||
- C/C++ applications
|
||||
- Shell scripts
|
||||
- Other compiled language applications
|
||||
- Custom startup scripts
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating a General Project
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the **Projects** page
|
||||
2. Click **Create Project**
|
||||
3. Fill in the configuration:
|
||||
- **Project Name**: Project identifier
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: Directory where the executable is located
|
||||
- **Startup Command**: Command to start the program
|
||||
4. Enable **Reverse Proxy** as needed
|
||||
|
||||
## Startup Command Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust Application
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Run compiled binary
|
||||
./myapp
|
||||
|
||||
# Run with arguments
|
||||
./myapp --config config.toml --port 8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Shell Script
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Run script
|
||||
/bin/bash start.sh
|
||||
|
||||
# Or run directly (requires shebang and execute permission)
|
||||
./start.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Startup Script
|
||||
|
||||
Create `start.sh`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
export ENV=production
|
||||
./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Startup command: `/bin/bash start.sh`
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
You can set environment variables in the startup command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Single environment variable
|
||||
ENV=production ./myapp
|
||||
|
||||
# Multiple environment variables
|
||||
ENV=production PORT=8080 ./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or edit the project directly and add environment variables in **Runtime Settings**.
|
||||
|
||||
## Working Directory
|
||||
|
||||
The project runs in the specified project directory, and relative paths are resolved based on that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to change directories, you can use `cd` in the startup command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp/bin && ./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Permission Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure the executable has execute permission:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
chmod +x myapp
|
||||
chmod +x start.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Running User
|
||||
|
||||
By default, projects run as the `www` user. If the program requires special permissions, you can select a different user.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning Note
|
||||
Running as root user may pose security risks, please choose carefully.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Log Output
|
||||
|
||||
The program's standard output (stdout) and standard error (stderr) are recorded in logs, which can be viewed on the project management page.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that programs output logs to standard output rather than writing to files for unified management.
|
||||
|
||||
## Signal Handling
|
||||
|
||||
When a project stops, a SIGTERM signal is sent. The program should handle this signal properly to achieve graceful shutdown:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// Rust example
|
||||
use signal_hook::{consts::SIGTERM, iterator::Signals};
|
||||
|
||||
fn main() {
|
||||
let mut signals = Signals::new(&[SIGTERM]).unwrap();
|
||||
// Handle SIGTERM signal
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// C example
|
||||
#include <signal.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void handle_sigterm(int sig) {
|
||||
// Clean up resources
|
||||
exit(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
signal(SIGTERM, handle_sigterm);
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
120
zh_TW/advanced/project/go.md
Normal file
120
zh_TW/advanced/project/go.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
# Go Project
|
||||
|
||||
Go projects are used to deploy backend applications developed with Go language, such as Gin, Echo, Fiber frameworks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Go runtime environment: **Applications** > **Runtime Environment** > **Go**
|
||||
2. Compiled Go executable file or source code
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Methods
|
||||
|
||||
### Method 1: Deploy Compiled Binary File
|
||||
|
||||
1. Compile Go project locally:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Cross-compile for Linux amd64
|
||||
GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Upload binary file to server
|
||||
3. Create project, fill in start command: `./myapp`
|
||||
|
||||
### Method 2: Compile on Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. Upload source code to server
|
||||
2. Compile in terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
go build -o myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create project, fill in start command: `./myapp`
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Go Project
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the **Project** page
|
||||
2. Click **Create Project**
|
||||
3. Fill in configuration:
|
||||
- **Project Name**: `myapp`
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: `/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **Start Command**: `./myapp` or `go1.24 run main.go`
|
||||
4. Enable **Reverse Proxy** for external access
|
||||
|
||||
## Start Command Examples
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Run compiled binary file
|
||||
./myapp
|
||||
|
||||
# Run with specified Go version
|
||||
go1.24 run main.go
|
||||
|
||||
# Run with parameters
|
||||
./myapp -port 8080 -config ./config.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
# Set environment variables
|
||||
GIN_MODE=release ./myapp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
### Gin
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
r := gin.Default()
|
||||
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
|
||||
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": "Hello"})
|
||||
})
|
||||
r.Run(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start command: `GIN_MODE=release ./myapp`
|
||||
|
||||
### Echo
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
e := echo.New()
|
||||
e.GET("/", func(c echo.Context) error {
|
||||
return c.String(200, "Hello")
|
||||
})
|
||||
e.Start(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Fiber
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
app := fiber.New()
|
||||
app.Get("/", func(c *fiber.Ctx) error {
|
||||
return c.SendString("Hello")
|
||||
})
|
||||
app.Listen(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ensure binary file has execute permission: `chmod +x myapp`
|
||||
2. Production environments are recommended to use compiled binary files, not `go run`
|
||||
3. It is recommended to use environment variables or configuration files to manage configuration, avoid hardcoding
|
||||
111
zh_TW/advanced/project/java.md
Normal file
111
zh_TW/advanced/project/java.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
# Java Project
|
||||
|
||||
Java projects are used to deploy Spring Boot, Tomcat, and other Java applications.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Java runtime environment: **Applications** > **Runtime Environment** > **Java** (Corretto JDK)
|
||||
2. Packaged JAR file or WAR file
|
||||
|
||||
## Deploy Spring Boot Application
|
||||
|
||||
### Package Project
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Maven
|
||||
mvn clean package -DskipTests
|
||||
|
||||
# Gradle
|
||||
./gradlew build -x test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Upload and Deploy
|
||||
|
||||
1. Upload JAR file to server (e.g., `/opt/ace/project/myapp/app.jar`)
|
||||
2. Create project:
|
||||
- **Project Name**: `myapp`
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: `/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **Start Command**: `java21 -jar app.jar`
|
||||
3. Enable **Reverse Proxy**
|
||||
|
||||
## Start Command Examples
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Basic startup
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify configuration file
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod
|
||||
|
||||
# Set JVM parameters
|
||||
java21 -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -jar app.jar
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify port
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar --server.port=8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## JVM Parameter Recommendations
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Recommended production environment configuration
|
||||
java21 \
|
||||
-Xms512m \
|
||||
-Xmx1024m \
|
||||
-XX:+UseG1GC \
|
||||
-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200 \
|
||||
-jar app.jar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Common parameter descriptions:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | ------------------------ |
|
||||
| `-Xms` | Initial heap memory size |
|
||||
| `-Xmx` | Maximum heap memory size |
|
||||
| `-XX:+UseG1GC` | Use G1 garbage collector |
|
||||
| `-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis` | Maximum GC pause time |
|
||||
|
||||
## Multiple JDK Versions
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel supports installing multiple JDK versions, paths like `/opt/ace/server/java/{version}/bin/java`, with `java{version}` commands linked by default for convenience.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration File
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot configuration file `application.yml` example:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
server:
|
||||
port: 8080
|
||||
|
||||
spring:
|
||||
datasource:
|
||||
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
|
||||
username: root
|
||||
password: your_password
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### Out of Memory
|
||||
|
||||
Increase JVM heap memory:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
java21 -Xms1g -Xmx2g -jar app.jar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Port Conflict
|
||||
|
||||
Modify startup port:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
java21 -jar app.jar --server.port=8081
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Slow Startup
|
||||
|
||||
Check if there are external dependency connection timeouts, or add the following parameters to speed up startup:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-XX:TieredStopAtLevel=1 -noverify
|
||||
```
|
||||
135
zh_TW/advanced/project/nodejs.md
Normal file
135
zh_TW/advanced/project/nodejs.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
# Node.js Project
|
||||
|
||||
Node.js projects are used to deploy Express, Koa, NestJS, Next.js, and other Node.js applications.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Node.js runtime environment: **Applications** > **Runtime Environment** > **Node.js**
|
||||
2. Project source code
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Steps
|
||||
|
||||
1. Upload project code to server
|
||||
2. Install dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
npm24 install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create project:
|
||||
- **Project Name**: `myapp`
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: `/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **Start Command**: `node24 app.js`
|
||||
4. Enable **Reverse Proxy**
|
||||
|
||||
## Start Command Examples
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Run directly
|
||||
node24 app.js
|
||||
|
||||
# Use npm scripts
|
||||
npm24 start
|
||||
|
||||
# Use npm run
|
||||
npm24 run start:prod
|
||||
|
||||
# Set environment variables
|
||||
NODE_ENV=production node24 app.js
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify port
|
||||
PORT=3000 node24 app.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
### Express
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const express = require('express');
|
||||
const app = express();
|
||||
|
||||
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
|
||||
res.send('Hello World');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
app.listen(3000);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start command: `node24 app.js`
|
||||
|
||||
### NestJS
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Build
|
||||
npm24 run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start command: `node24 dist/main.js`
|
||||
|
||||
### Next.js
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Build
|
||||
npm24 run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start command: `npm24 start`
|
||||
|
||||
### Nuxt.js
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Build
|
||||
npm24 run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start command: `node24 .output/server/index.mjs`
|
||||
|
||||
## Process Management
|
||||
|
||||
AcePanel uses systemd to manage Node.js processes, automatically handling:
|
||||
|
||||
- Automatic restart on process crash
|
||||
- Automatic startup on boot
|
||||
- Log recording
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to use `.env` files to manage environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# .env
|
||||
NODE_ENV=production
|
||||
PORT=3000
|
||||
DATABASE_URL=mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load using the `dotenv` package:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
require('dotenv').config();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependency Installation Failed
|
||||
|
||||
Try clearing cache and reinstalling:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json
|
||||
npm24 install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Out of Memory
|
||||
|
||||
Increase Node.js memory limit:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096" node24 app.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Port Already in Use
|
||||
|
||||
Modify the port the application listens on, or check if another process is using it.
|
||||
97
zh_TW/advanced/project/php.md
Normal file
97
zh_TW/advanced/project/php.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
# PHP Project
|
||||
|
||||
PHP projects are used to deploy PHP applications that require long-running processes, such as Laravel Octane, Swoole, Workerman, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip Tip
|
||||
Traditional PHP-FPM applications (such as WordPress, Laravel) should be deployed using [PHP Website](../website/php), not as projects.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Cases
|
||||
|
||||
- Laravel Octane (Swoole/RoadRunner)
|
||||
- Swoole applications
|
||||
- Workerman applications
|
||||
- ReactPHP applications
|
||||
- Other PHP applications requiring long-running processes
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install PHP runtime: **Apps** > **Runtimes** > **PHP**
|
||||
2. Install Swoole or other modules as needed
|
||||
|
||||
## Deploying Laravel Octane
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating a Project
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create project:
|
||||
- **Project Name**: `myapp`
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: `/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **Startup Command**: `php84 artisan octane:start --host=0.0.0.0 --port=8000`
|
||||
2. Enable **Reverse Proxy**
|
||||
|
||||
## Startup Command Examples
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Laravel Octane (Swoole)
|
||||
php84 artisan octane:start --host=0.0.0.0 --port=8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Laravel Octane (RoadRunner)
|
||||
php84 artisan octane:start --server=roadrunner --host=0.0.0.0 --port=8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Swoole HTTP Server
|
||||
php84 server.php
|
||||
|
||||
# Workerman
|
||||
php84 start.php start
|
||||
|
||||
# Laravel Queue Worker
|
||||
php84 artisan queue:work --daemon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Swoole Application Example
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
$server = new Swoole\HTTP\Server("0.0.0.0", 9501);
|
||||
|
||||
$server->on("request", function ($request, $response) {
|
||||
$response->header("Content-Type", "text/plain");
|
||||
$response->end("Hello World");
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
$server->start();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Startup command: `php84 server.php`
|
||||
|
||||
## Workerman Application Example
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
|
||||
|
||||
use Workerman\Worker;
|
||||
|
||||
$worker = new Worker("http://0.0.0.0:8080");
|
||||
$worker->onMessage = function($connection, $request) {
|
||||
$connection->send("Hello World");
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Worker::runAll();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Startup command: `php84 start.php start`
|
||||
|
||||
## Queue Processing
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel Queue Worker can also run as a project:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
php84 artisan queue:work --daemon --tries=3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
|
||||
1. Long-running PHP applications need to be aware of memory leak issues
|
||||
2. Code updates require restarting the project to take effect
|
||||
3. It is recommended to configure process monitoring for automatic restart on exceptions
|
||||
149
zh_TW/advanced/project/python.md
Normal file
149
zh_TW/advanced/project/python.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
# Python Project
|
||||
|
||||
Python projects are used to deploy Django, Flask, FastAPI, and other Python web applications.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Python runtime: **Apps** > **Runtimes** > **Python**
|
||||
2. Project source code
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Steps
|
||||
|
||||
1. Upload project code to the server
|
||||
2. Create virtual environment and install dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/ace/project/myapp
|
||||
python3.13 -m venv venv
|
||||
source venv/bin/activate
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create project:
|
||||
- **Project Name**: `myapp`
|
||||
- **Project Directory**: `/opt/ace/project/myapp`
|
||||
- **Startup Command**: See examples below
|
||||
4. Enable **Reverse Proxy**
|
||||
|
||||
## Startup Command Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Django
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Development server (not recommended for production)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Using Gunicorn (recommended)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn myproject.wsgi:application -b 0.0.0.0:8000 -w 4
|
||||
|
||||
# Using uWSGI
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/uwsgi --http 0.0.0.0:8000 --module myproject.wsgi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Flask
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Development server (not recommended for production)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/python app.py
|
||||
|
||||
# Using Gunicorn (recommended)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn app:app -b 0.0.0.0:8000 -w 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Using Uvicorn
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Using Gunicorn + Uvicorn Workers (recommended)
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn main:app -b 0.0.0.0:8000 -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Framework Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
### Django Production Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
`settings.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
DEBUG = False
|
||||
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['your-domain.com']
|
||||
STATIC_ROOT = '/opt/ace/project/myapp/static/'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Collect static files:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/python manage.py collectstatic
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### FastAPI Example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Gunicorn Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Create `gunicorn.conf.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bind = "0.0.0.0:8000"
|
||||
workers = 4
|
||||
worker_class = "sync" # Or "uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker" for FastAPI
|
||||
timeout = 30
|
||||
keepalive = 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Startup command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
/opt/ace/project/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn -c gunicorn.conf.py myproject.wsgi:application
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Virtual Environment
|
||||
|
||||
It is strongly recommended to use virtual environments to isolate project dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Create virtual environment
|
||||
python3.13 -m venv venv
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate virtual environment
|
||||
source venv/bin/activate
|
||||
|
||||
# Install dependencies
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Deactivate virtual environment
|
||||
deactivate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Issues
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependency Installation Failed
|
||||
|
||||
Some packages require compilation, ensure necessary system dependencies are installed:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# AlmaLinux/Rocky Linux
|
||||
yum install gcc python3-devel
|
||||
|
||||
# Ubuntu/Debian
|
||||
apt install gcc python3-dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Static Files 404
|
||||
|
||||
Django production environment needs to configure Nginx to serve static files directly, or use WhiteNoise.
|
||||
|
||||
### Database Connection Issues
|
||||
|
||||
Check database configuration and network connection, ensure the database service is running properly.
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user